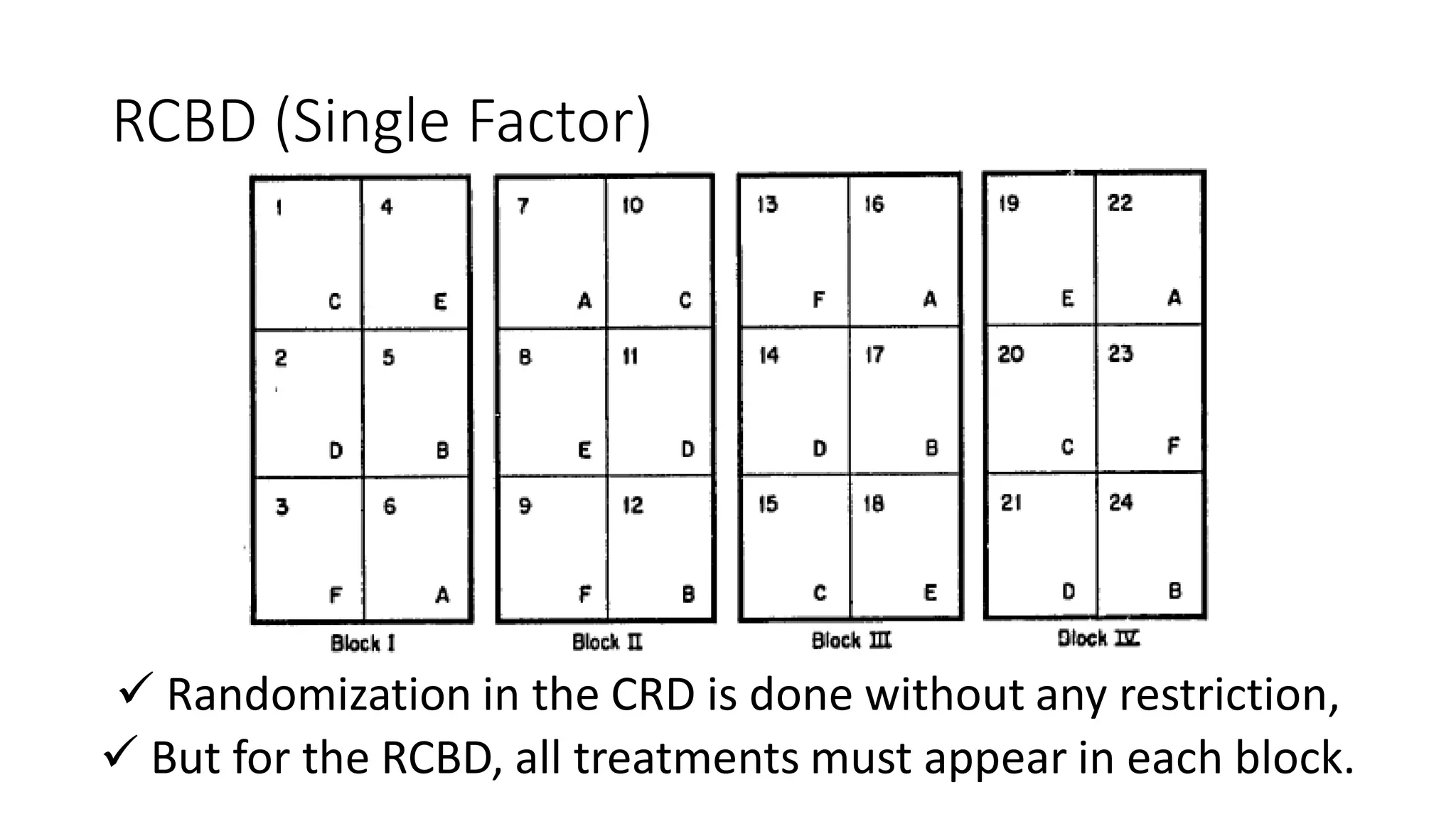
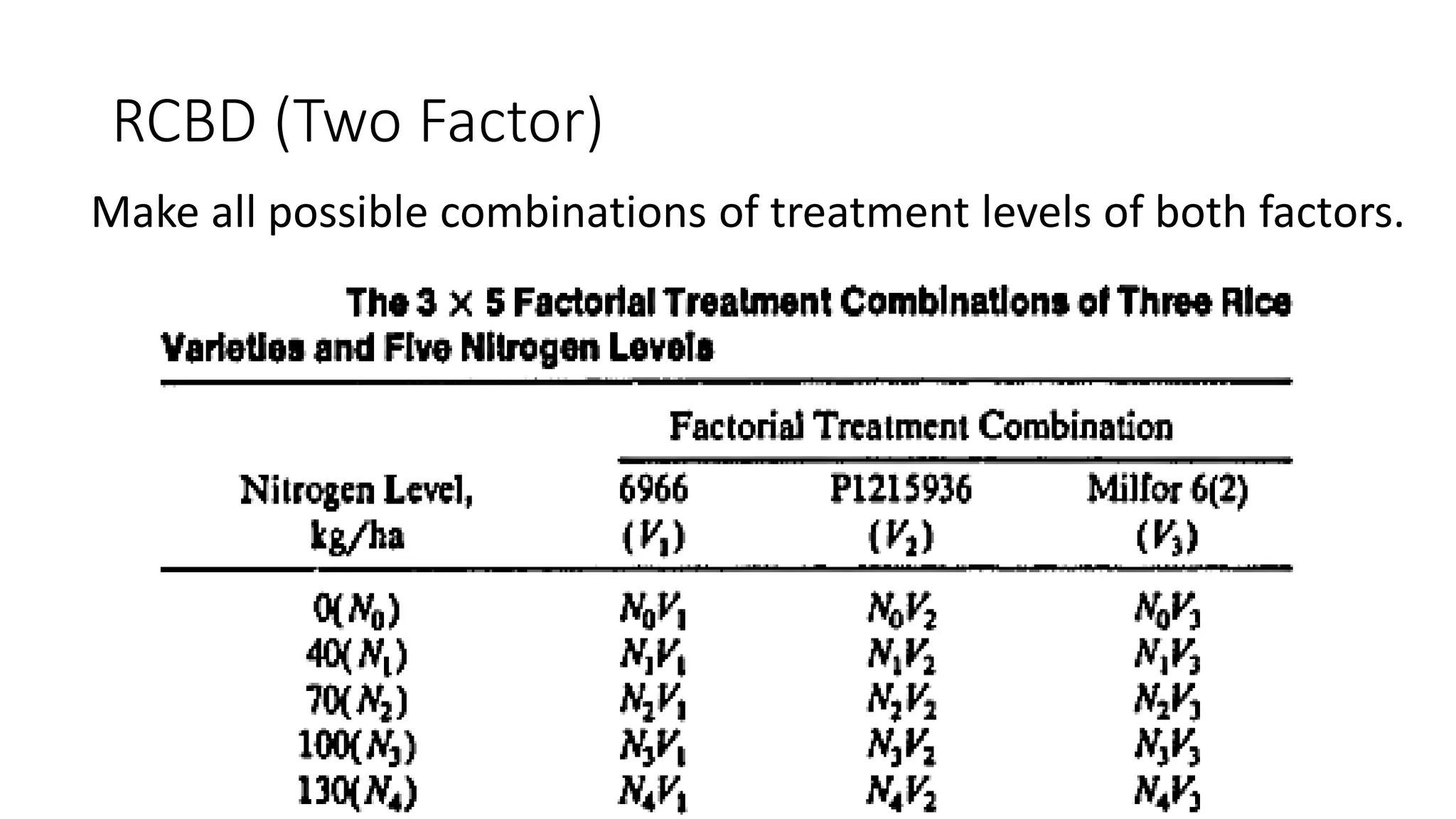
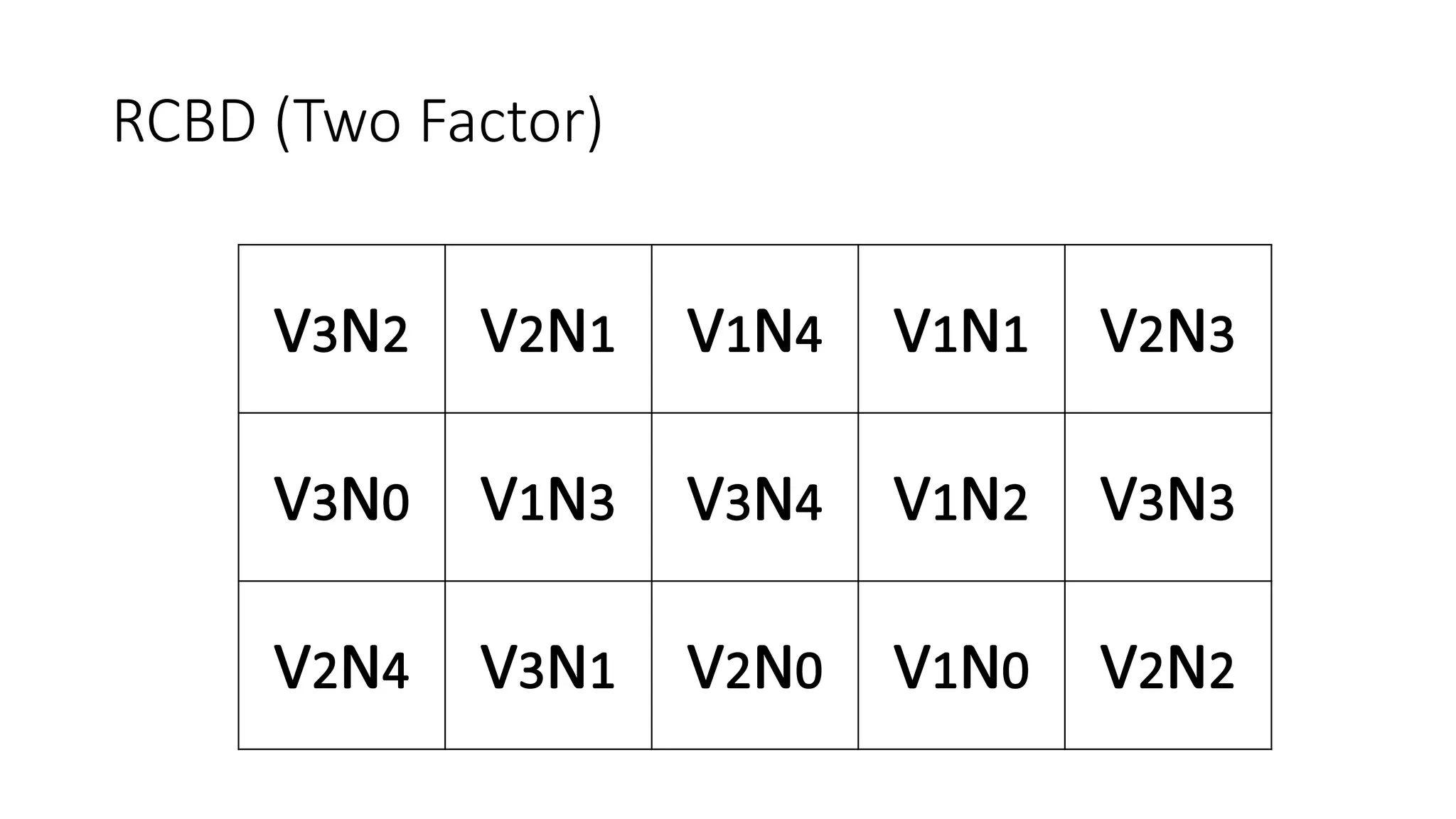
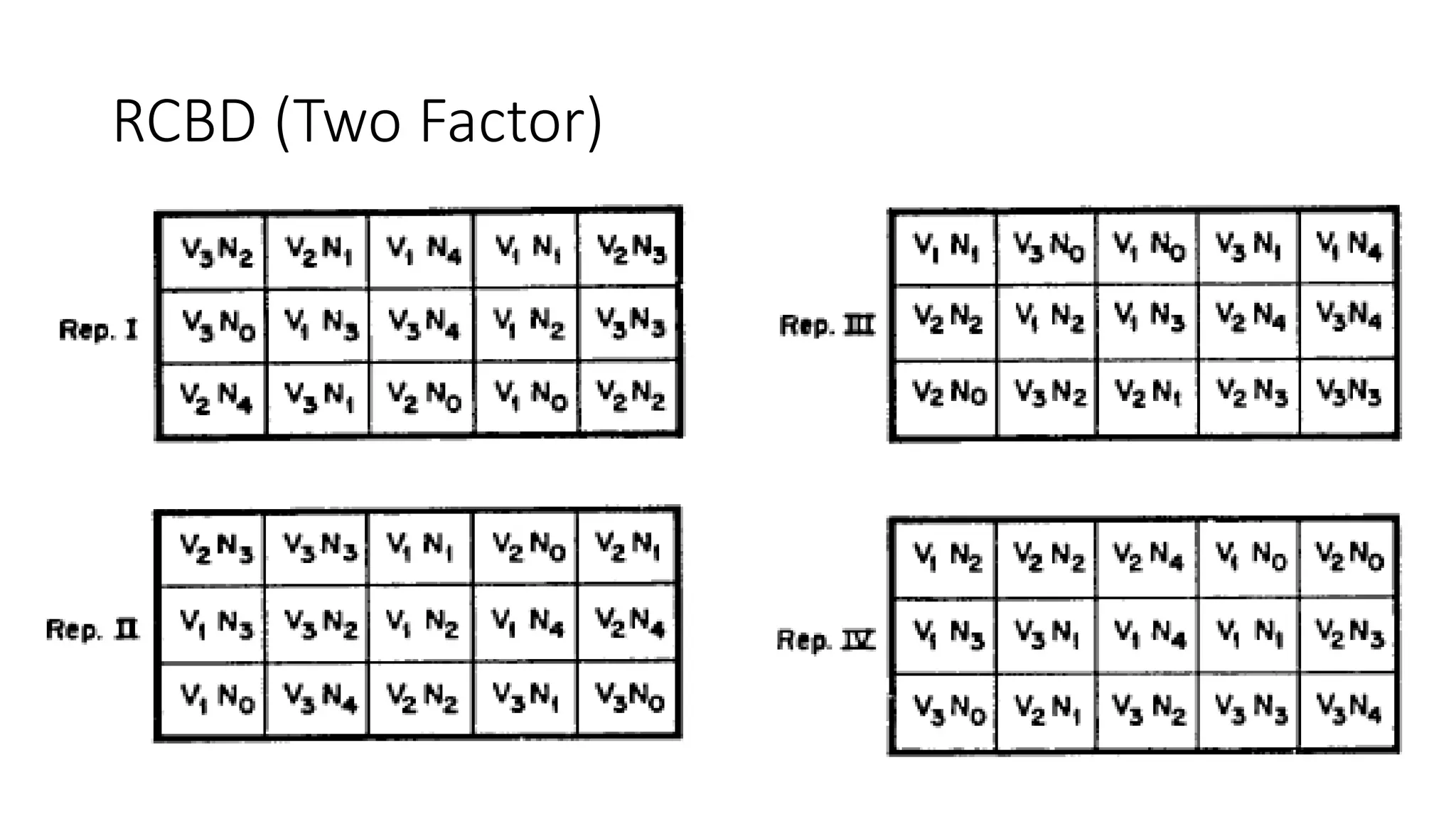
1. The document outlines different experimental designs including single factor and double factor designs. It discusses completely randomized design (CRD) and randomized complete block design (RCBD) for single factor experiments.
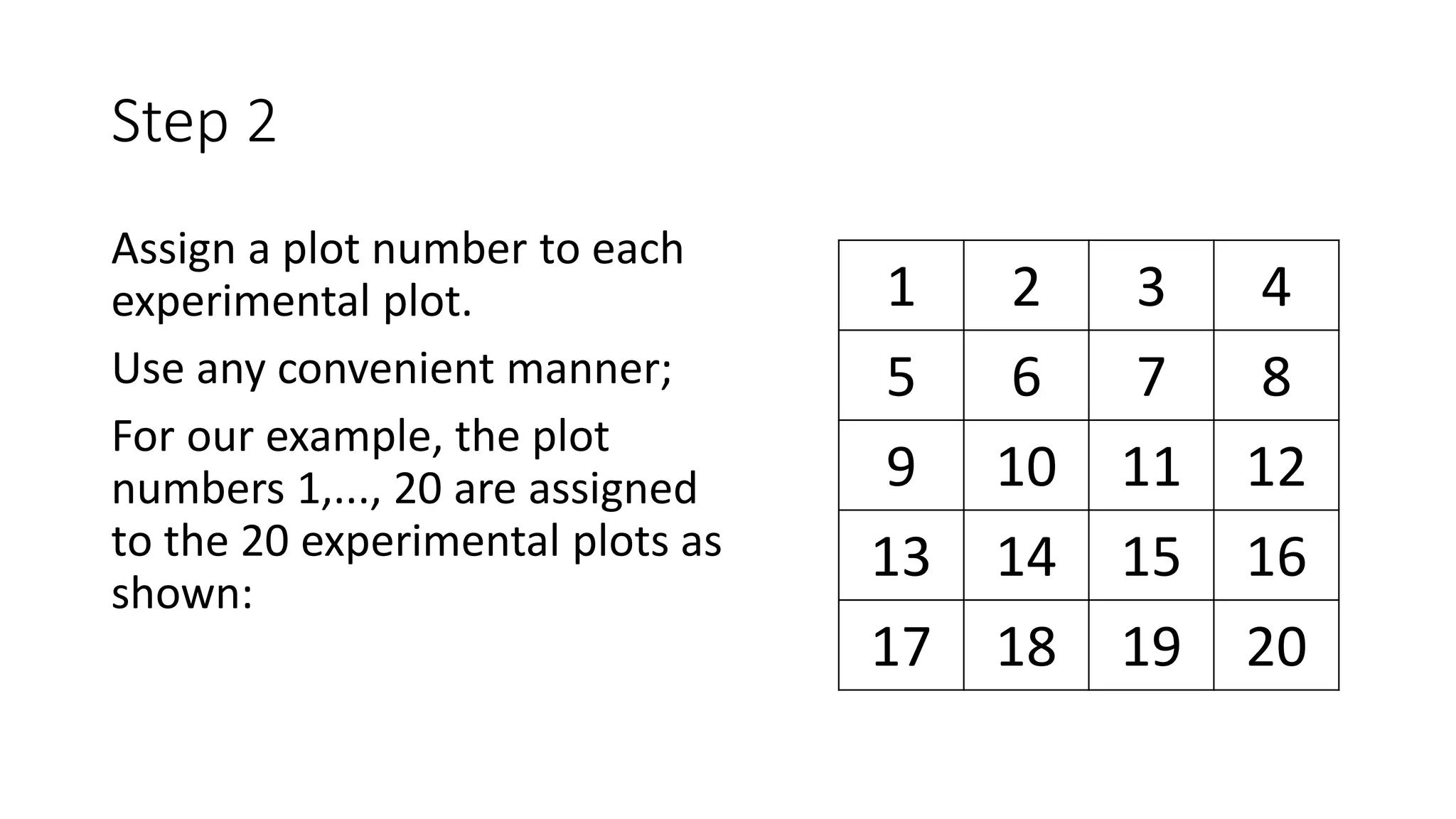
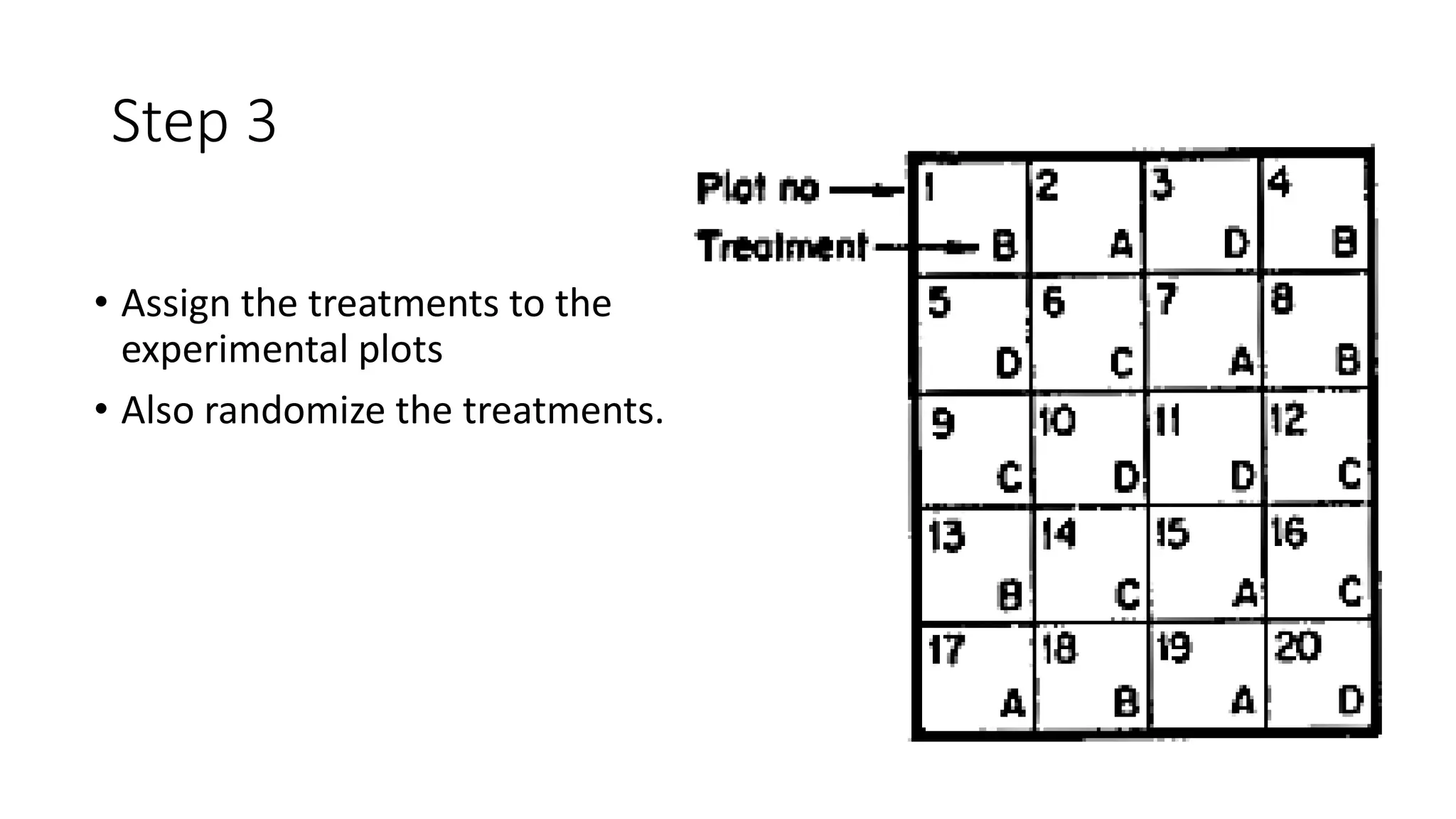
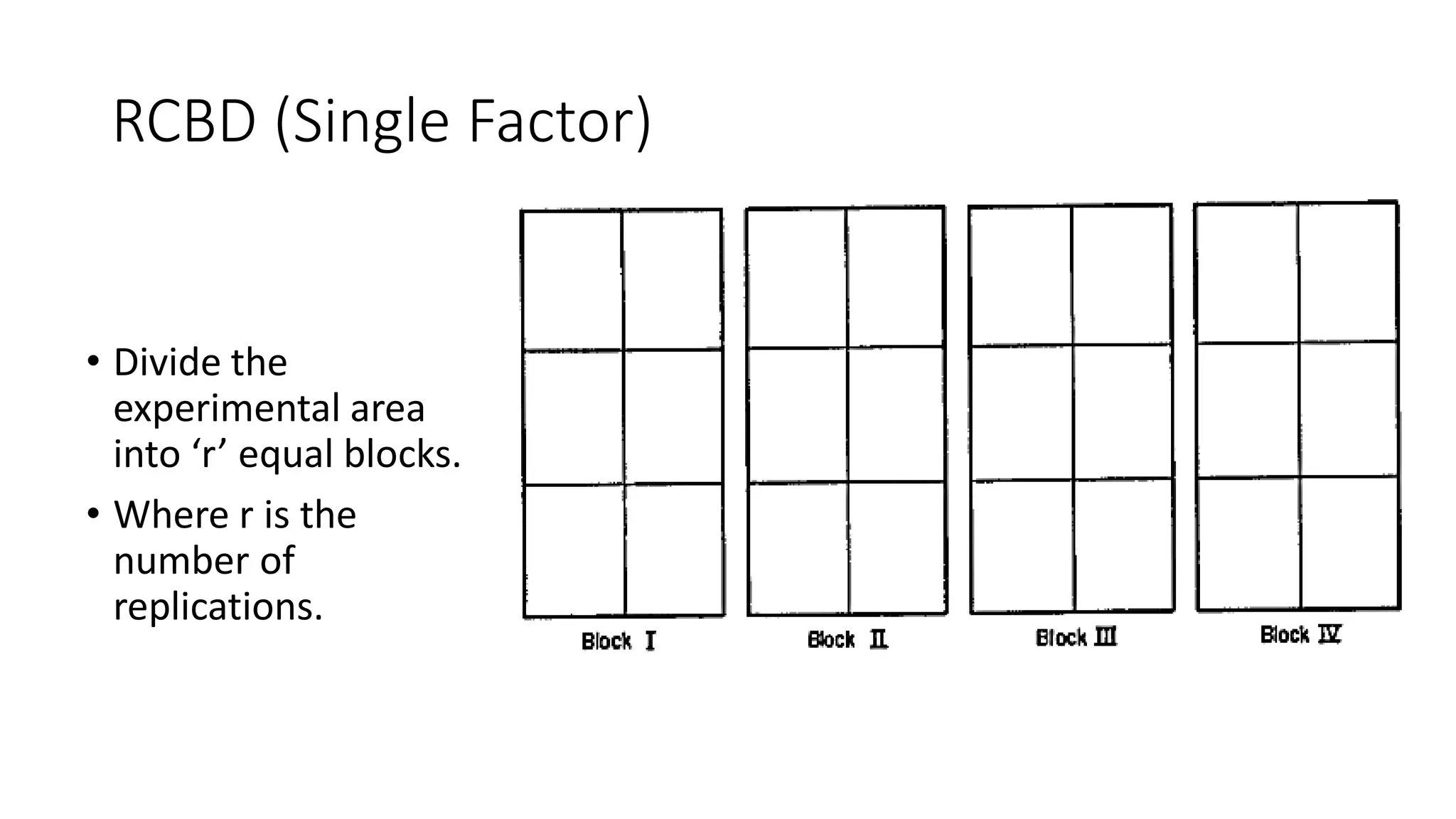
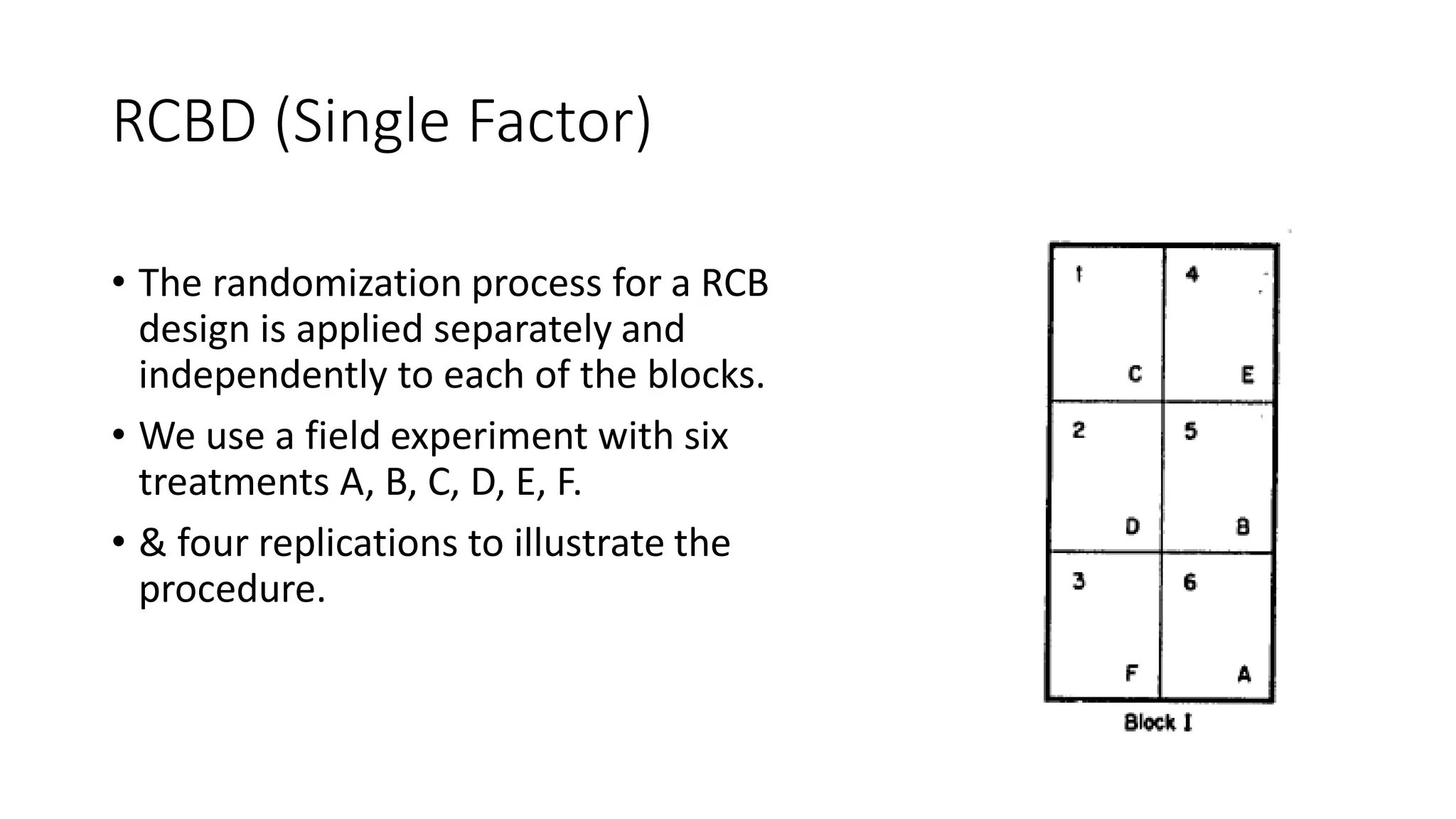
2. For CRD, treatments are assigned completely at random to experimental units. For RCBD, the experimental area is divided into blocks of equal size with all treatments represented in each block to account for soil variability.
3. A two factor design involves all possible combinations of selected levels for two or more factors as treatments. For a two factor RCBD, all possible combinations of treatment levels for the two factors are used.