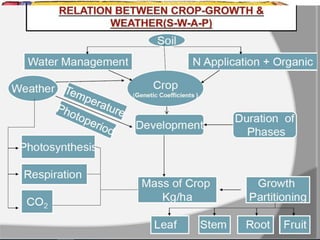
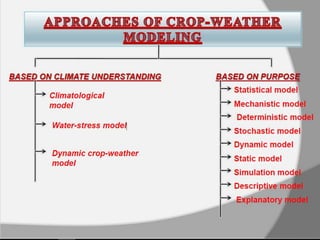
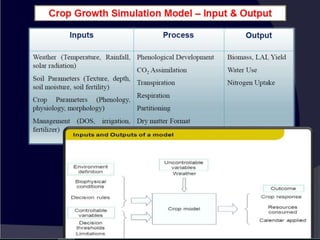
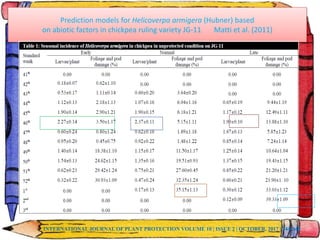
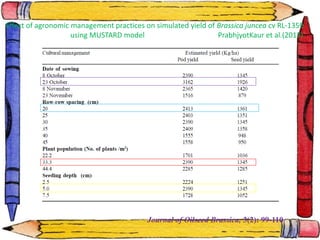
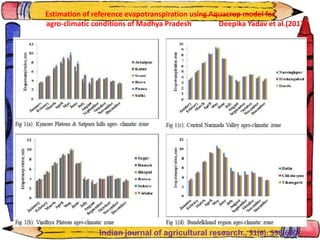
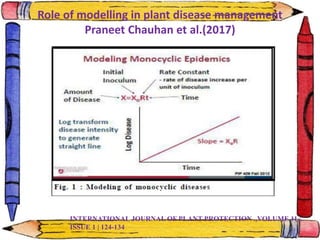
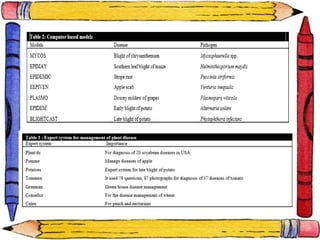
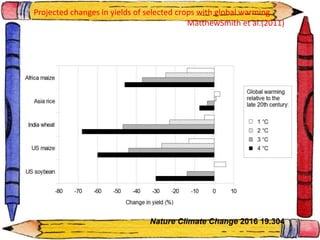
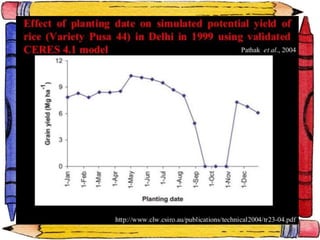
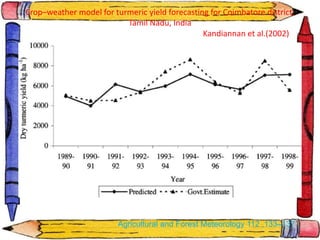
The document discusses crop-weather modeling. It defines crop-weather modeling as using mathematical models to simulate crop growth and yield based on temperature, day length, and other weather parameters. It notes that crop-weather models have various applications, including optimizing management, predicting impacts of climate change, and performing "what-if" experiments. The document also outlines different types of crop models and lists some advantages of crop-weather modeling, such as reducing field experiments and helping to maximize agricultural production.