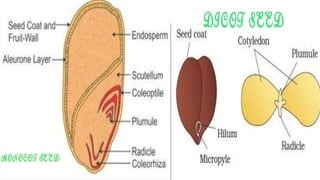
Seed dormancy refers to seeds not germinating during unsuitable conditions for seedling survival. There are three main types of dormancy - physical, physiological, and morphological. Dormancy prevents germination through impermeable seed coats, immature embryos, or germination inhibitors. Common methods to break dormancy include scarification, stratification, light exposure, and chemical treatments like gibberellic acid soaking. These treatments help prepare the seed and environment for successful germination.