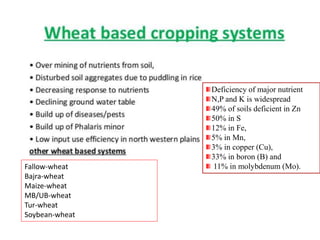
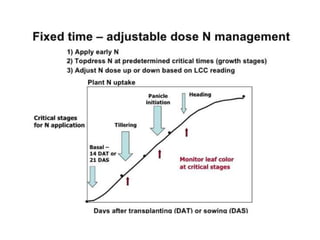
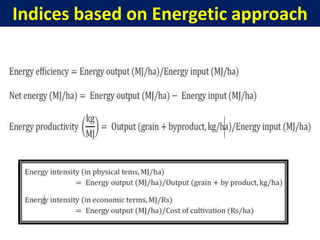
Cropping systems are an important component of farming systems that represent the cropping patterns and interactions between crops, resources, and technology on a farm. Key aspects of cropping systems include crop rotation, multiple cropping, intercropping, and mixed cropping. Various indices are used to evaluate cropping systems, including land equivalent ratio (LER), cultivated land utilization index (CLUI), relative crowding coefficient (RCC), multiple cropping index (MCI), crop intensity index (CII), and competition index. These indices assess factors like land use efficiency, crop yields, resource use, and economic viability of different cropping patterns.