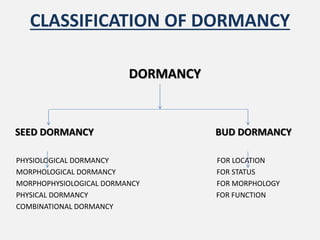
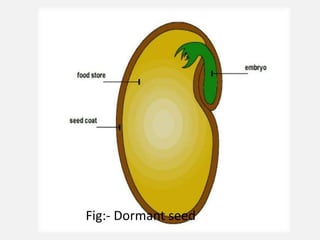
This document discusses seed dormancy, which refers to viable seeds failing to germinate under favorable conditions. There are several types of dormancy, including physiological caused by an immature embryo, morphological caused by an underdeveloped embryo, physical caused by impermeable seed coats, and combinational with both physiological and physical factors. Dormancy prevents germination under unfavorable conditions and can be overcome naturally, such as through microbial action on seed coats, or artificially using treatments like scarification, stratification, or hormone applications. The document provides classifications and mechanisms of dormancy as well as methods to break dormancy for seed germination.