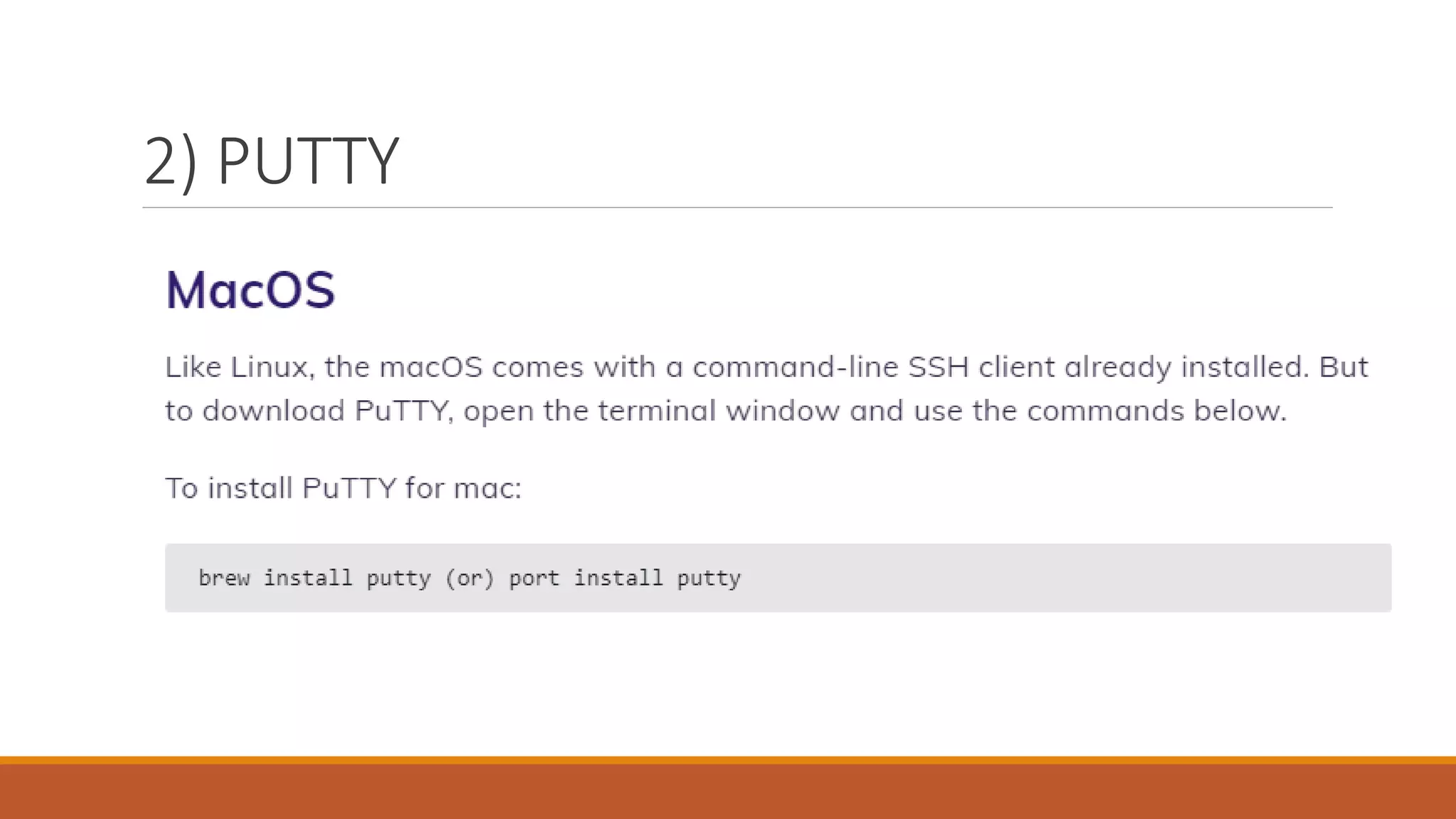
This document summarizes how network services are managed. It discusses several key tools that network administrators use to debug, understand, and configure networks, including Wireshark for packet analysis, PuTTY for remote connections, Traceroute for following packet routes, Nagios and Shinken for supervision and monitoring, Cacti and Munin for metrics and performance monitoring, Nmap for discovery and mapping of network services, and Ping for basic network connectivity testing. The goal of these tools is to provide network administrators with visibility into their networks and troubleshoot any issues.