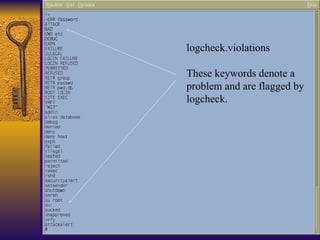
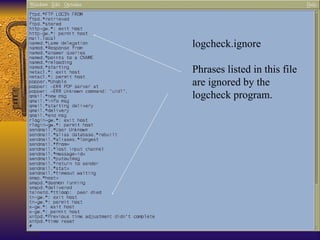
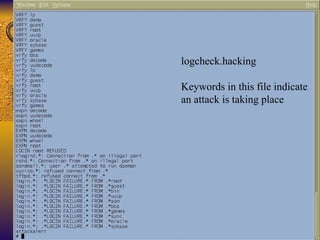
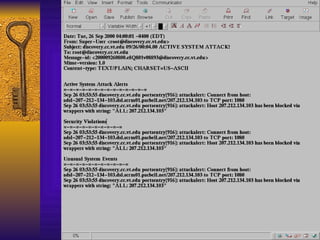
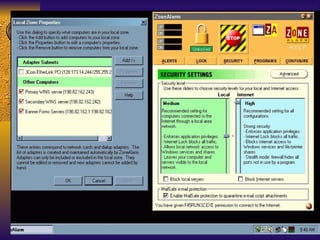
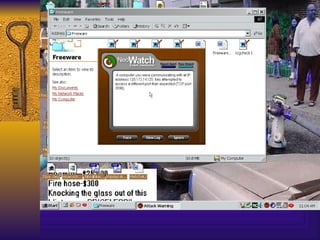
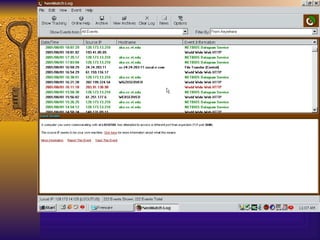
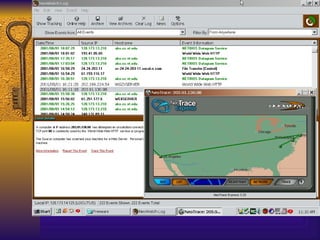
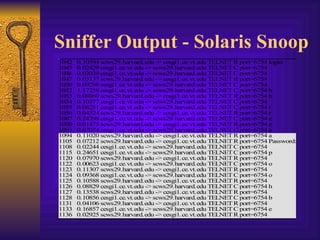
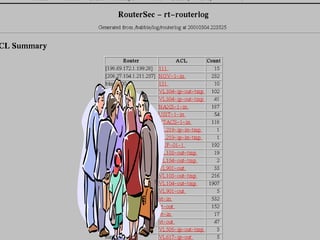
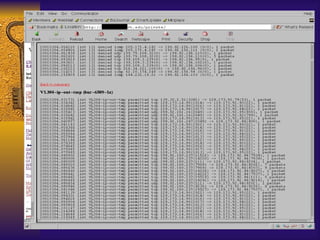
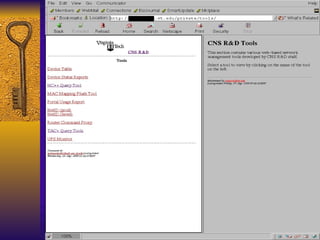
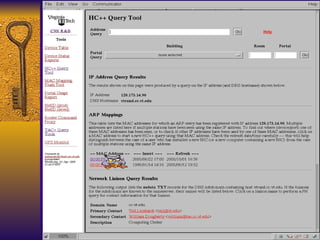
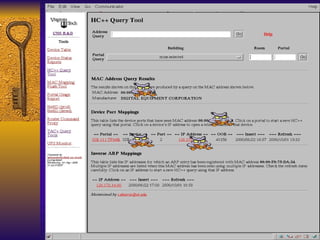
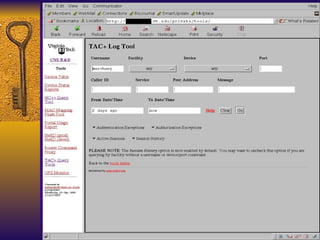
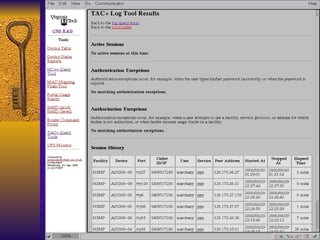
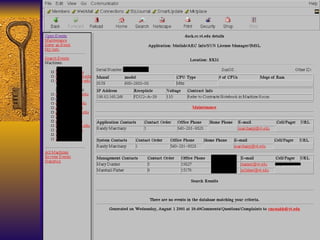
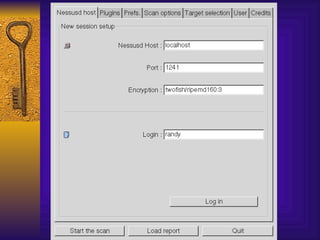
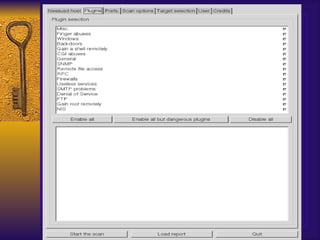
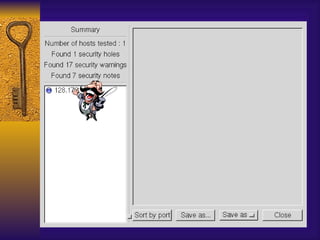
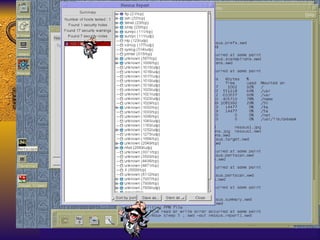
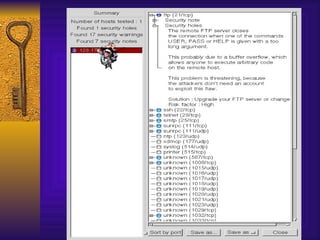
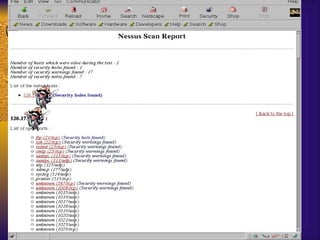
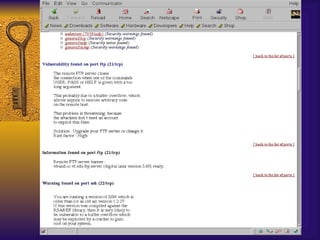
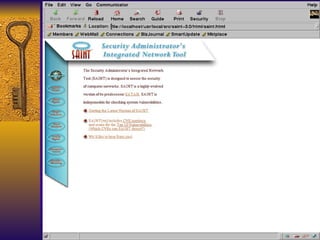
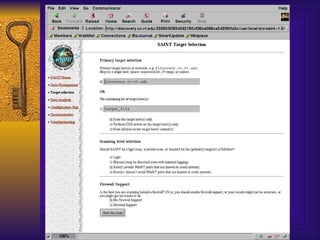
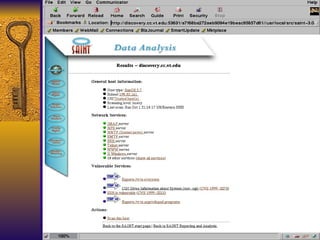
The document summarizes various free security tools that can be used to gain experience with system and network security. It describes tools for port scanning (Nessus, Saint, Nmap), firewalls (TCP Wrappers, Portsentry), intrusion detection (Snort, Logcheck), and system administration (Sudo, Lsof, Crack). The document recommends using freeware tools to familiarize yourself with security issues before evaluating commercial vendor tools.
![Freeware Security Tools You Need Randy Marchany VA Tech Computing Center Blacksburg, VA 24060 [email_address] 540-231-9523 NetSec2001](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freeware-security-tools-you-need-13904/75/Freeware-Security-Tools-You-Need-1-2048.jpg)








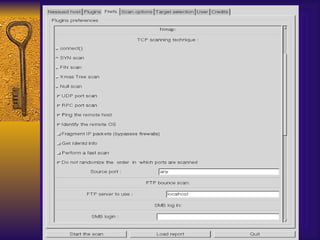
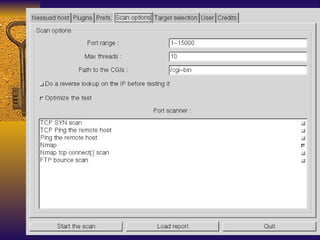
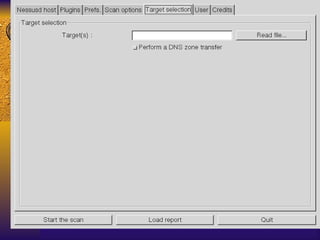



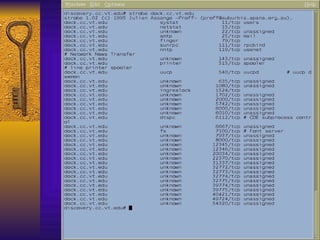
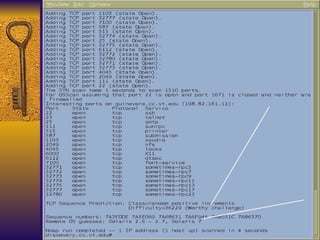





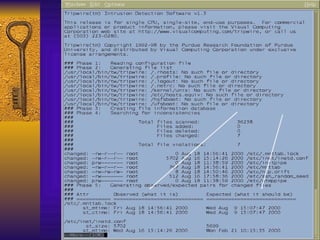






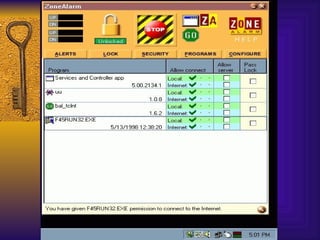
![TCP Wrappers Access Control is enabled by default. 2 files /etc/hosts.deny – restrict access if IP addr here /etc/hosts.allow – allow access if IP addr here Can restrict to [email_address] if services are enabled Reverse lookup is done. Paranoid selection terminates the connection immediately if there’s a mismatch. Set KILL_IP_OPTIONS in Makefile to refuse connections that use source routing. This prevents IP spoofing although your routers should do this.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freeware-security-tools-you-need-13904/85/Freeware-Security-Tools-You-Need-45-320.jpg)




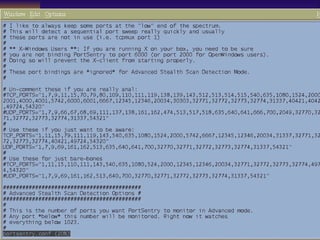



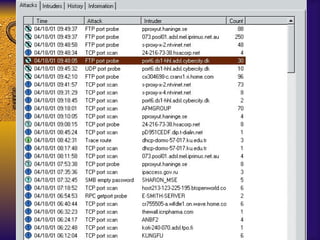
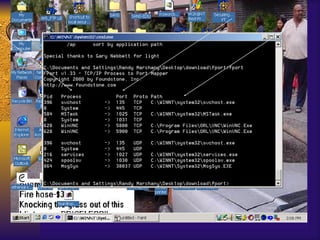
![IP Filter Log Format Jul 30 01:46:52 myhost.vt.edu ipmon[147]: [ID 702911local0.warning] 01:46:52.196772 hme0 @0:5 b 194.143.66.126,21 ->198.82.255.255, 21 PR tcp len 20 40 -S IN Jul 30 01:47:03 myhost.vt.edu ipmon[147]: [ID 702911local0.warning] 01:47:03.269595 hme0 @0:5 b 194.143.66.126,21 ->198.82.255.255, 21 PR tcp len 20 40 -S IN Jul 30 05:53:51 myhost.vt.edu ipmon[147]: [ID 702911local0.warning] 05:53:50.699235 hme0 @0:5 b 203.90.84.163,1781 ->198.82.255.255, 21 PR tcp len 20 60 -S IN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freeware-security-tools-you-need-13904/85/Freeware-Security-Tools-You-Need-55-320.jpg)