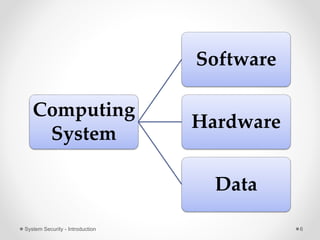
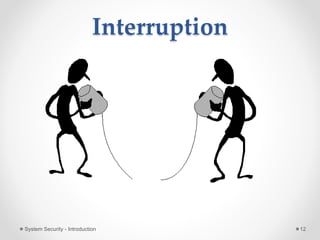
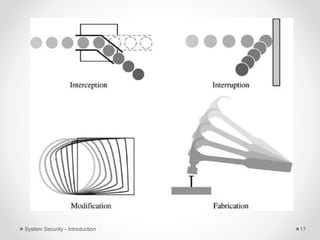
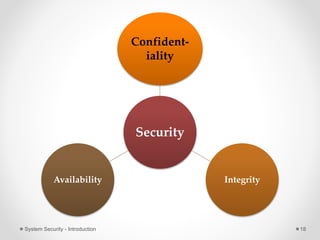
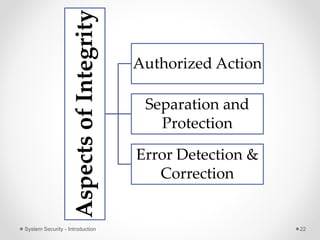
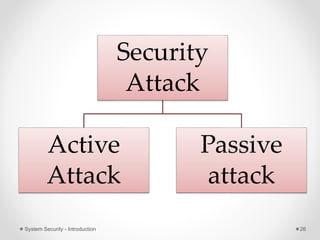
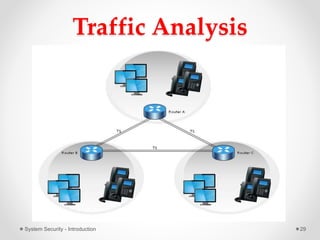
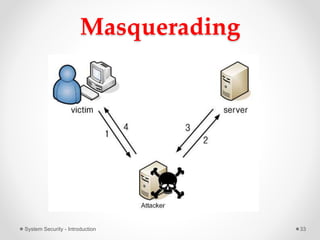
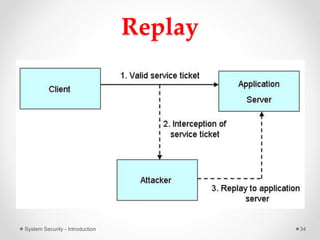
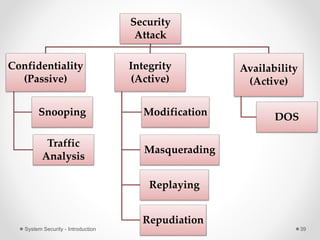
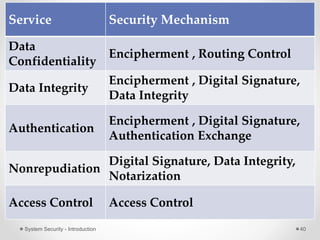
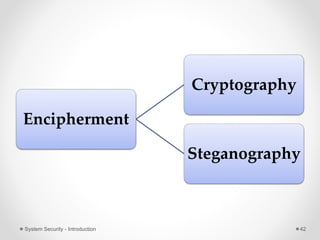
This document provides an introduction to system security. It outlines the prerequisites for the course, including computer networks, operating systems, algorithms, computer organization and data structures. The syllabus covers cryptography, access control, software security and network security. It defines key security concepts like vulnerabilities, threats, attacks, and controls. The document discusses different types of threats like interception, interruption, modification and fabrication. It also covers the goals of security - confidentiality, integrity and availability. Different security attacks both active and passive are defined. Finally, it introduces security mechanisms like encipherment, digital signatures and access control to protect confidentiality, integrity and availability.