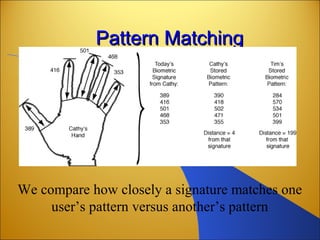
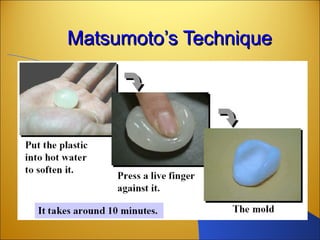
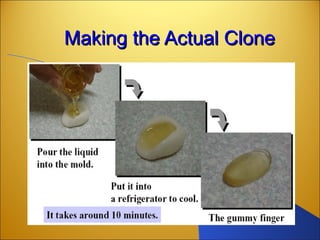
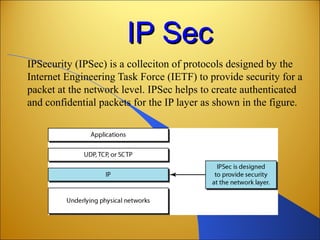
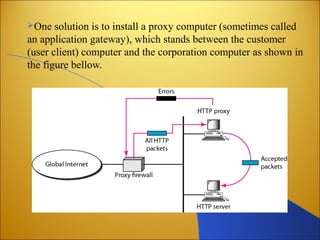
Botnets are networks of compromised computers that are used to conduct criminal online activities like spamming and phishing. They are controlled by botmasters through command and control servers. The document discusses how botnets utilize platforms like Windows and Unix machines, and spyware, adware, and malware to conduct spamming, phishing, denial of service attacks, and steal personal information. It also summarizes various network security measures that can help prevent the spread of botnets, including user education, firewalls, IPSec, SSL/TLS, RADIUS authentication, security tokens, and biometrics.













![SECURE TOKENSECURE TOKEN
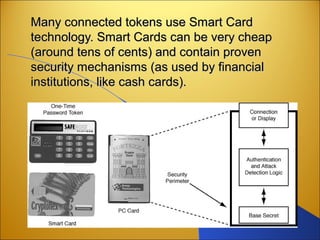
•A security token (or sometimes a hardware token, hard token,
authentication token, USB token, cryptographic token[1]
, or
key fob) may be a physical device that an authorized user of
computer services is given to ease authentication. The term
may also refer to software tokens.
• Security tokens are used to prove one's identity electronically
(as in the case of a customer trying to access their bank
account). The token is used in addition to or in place of a
password to prove that the customer is who they claim to be.
The token acts like an electronic key to access something.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/network-security5-160218204450/85/Network-security-16-320.jpg)