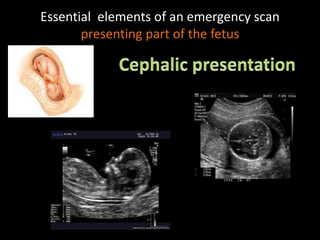
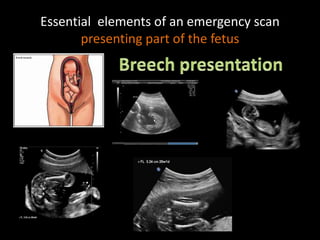
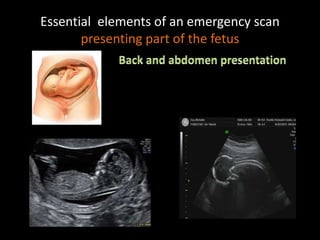
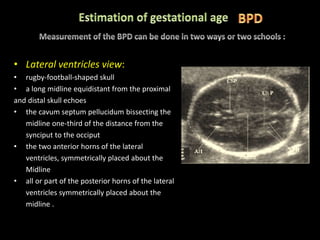
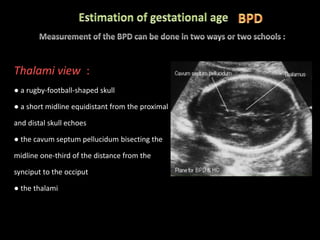
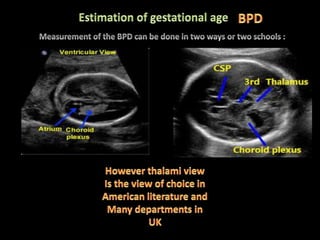
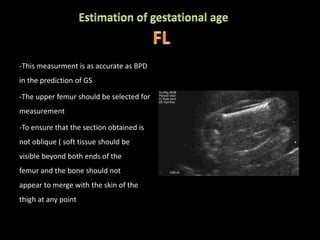
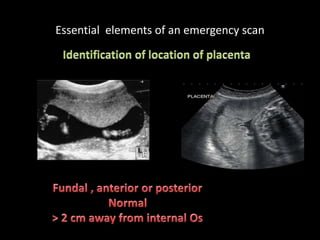
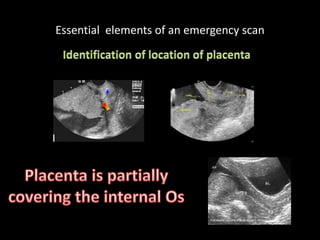
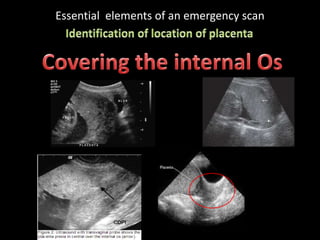
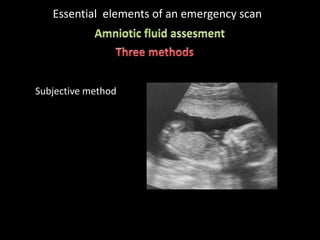
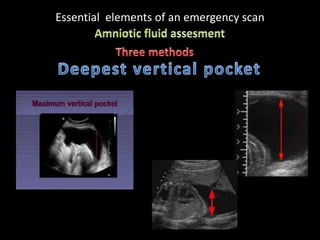
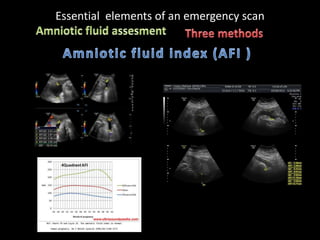
This document provides an overview of a lecture on second and third trimester emergencies during pregnancy. It discusses essential elements of an emergency ultrasound scan, including determining the fetal lie and position, measuring gestational age using BPD and femur length, locating the placenta, and assessing amniotic fluid levels. Potential emergencies that may occur during this time include preterm labor, placental issues, hemorrhage, and too much or too little amniotic fluid. The document outlines techniques for evaluating these elements in an emergency scan.