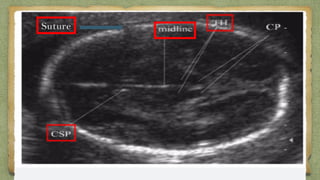
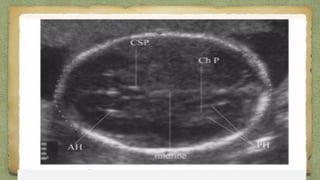
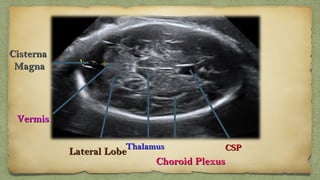
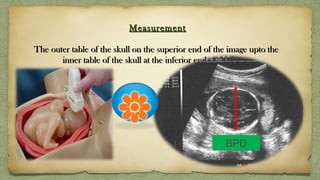
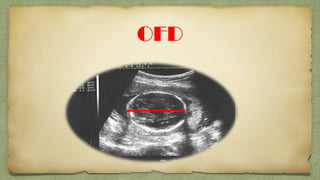
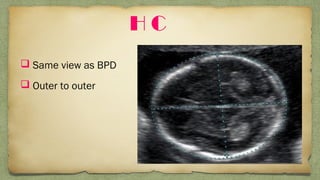
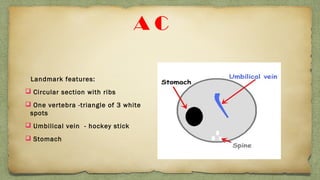
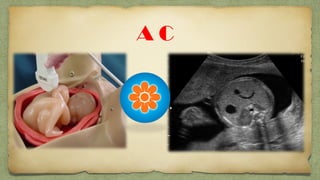
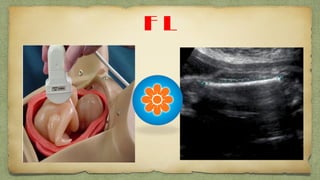
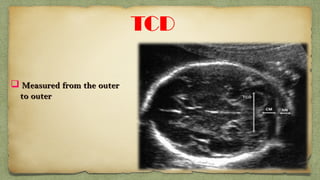
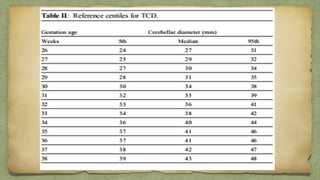
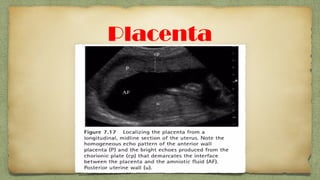
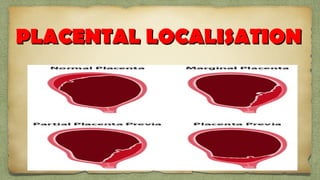
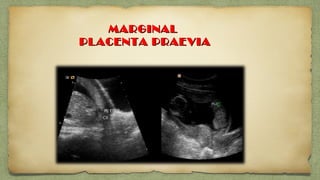
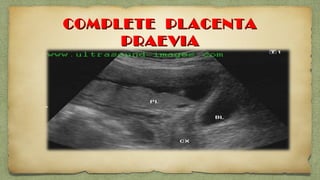
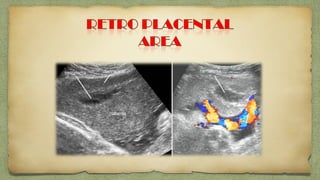
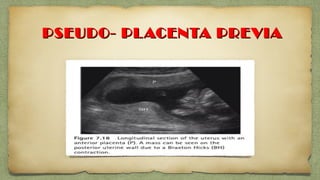
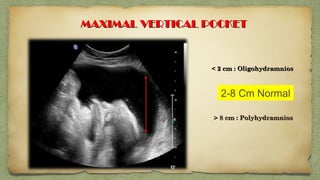
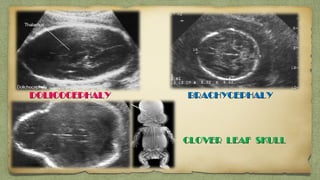
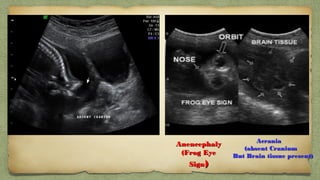
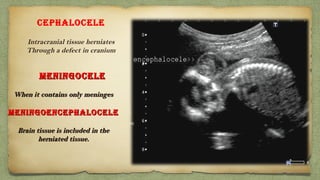
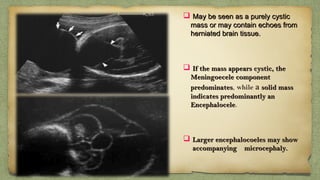
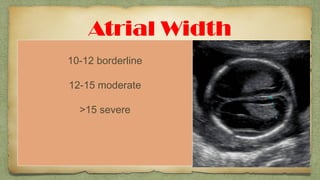
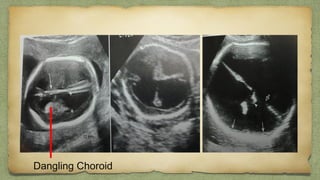
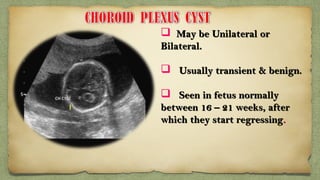
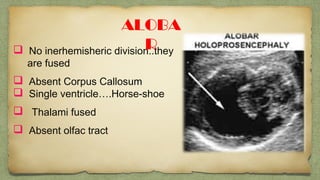
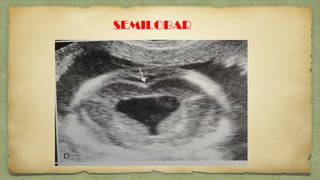
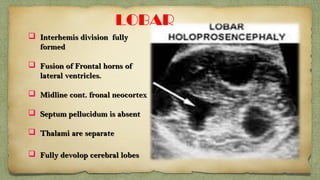
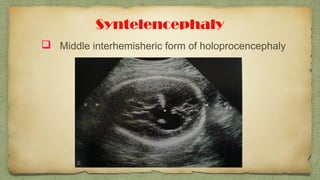
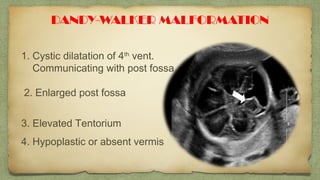
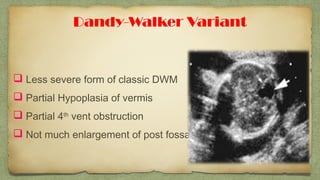
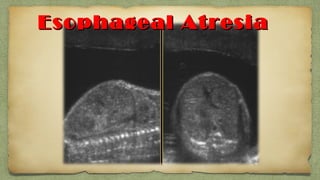
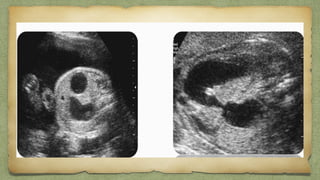
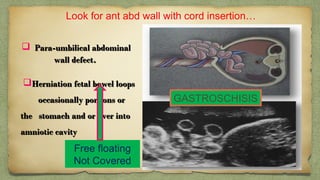
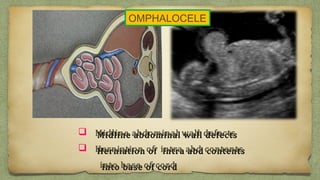
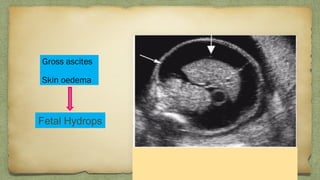
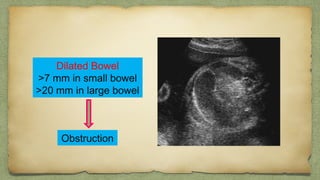
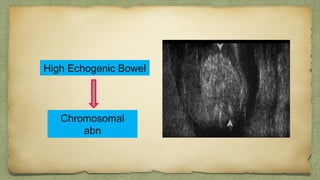
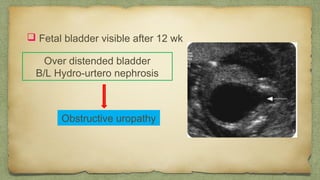
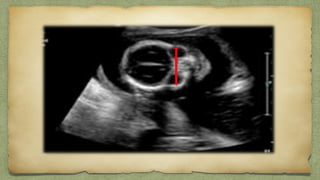
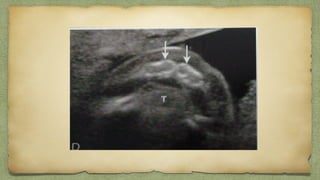
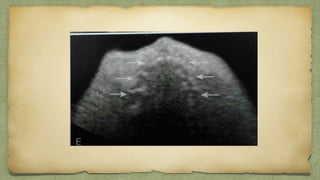
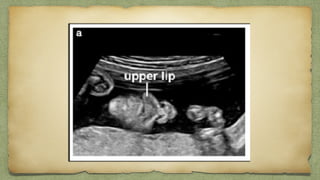
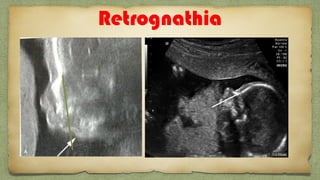
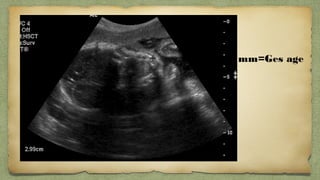
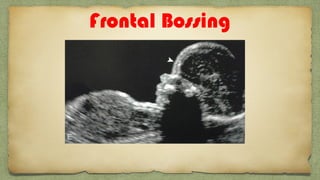
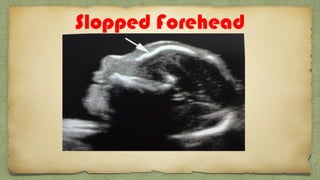
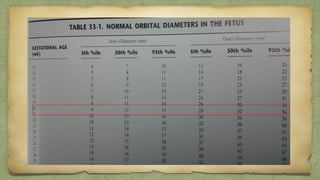
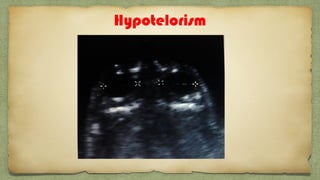
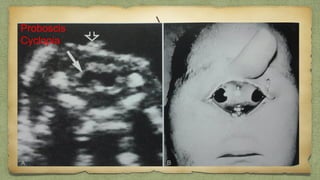
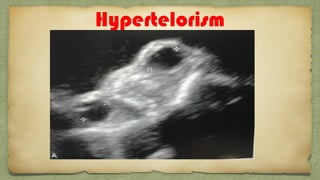
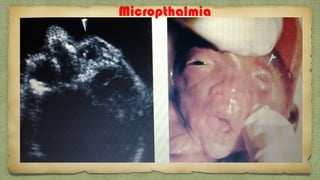
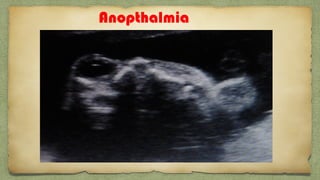
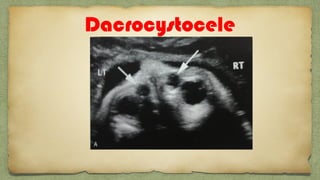
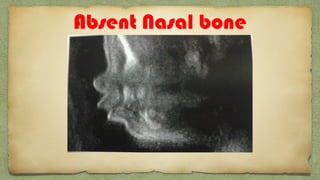
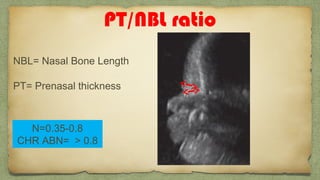
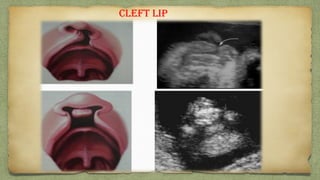
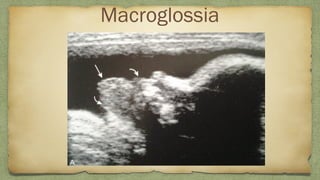
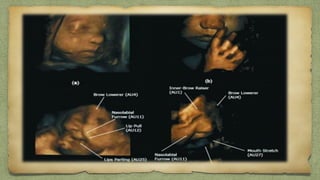
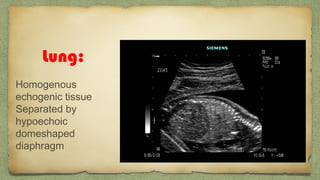
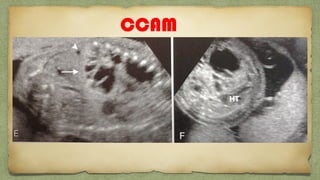
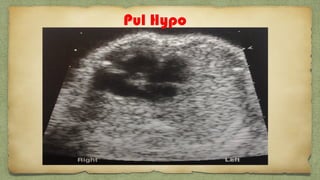
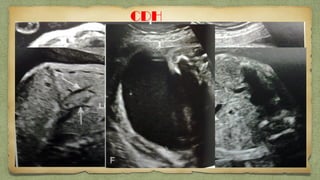
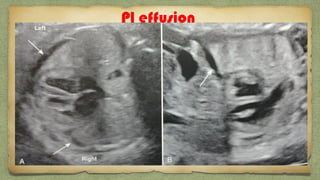
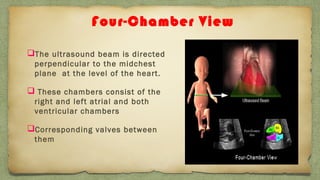
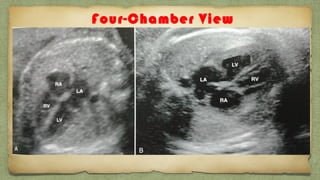
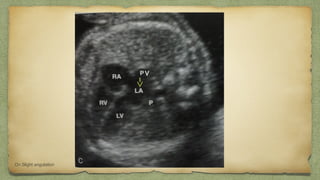
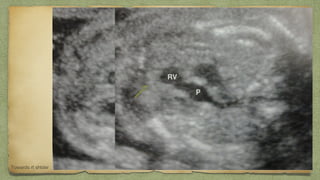
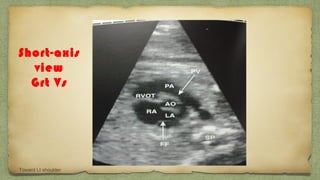
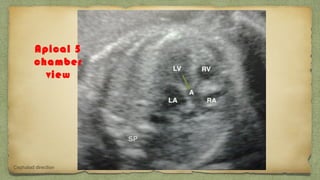
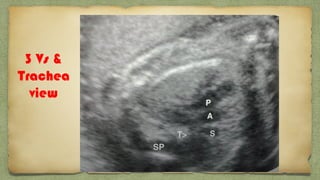
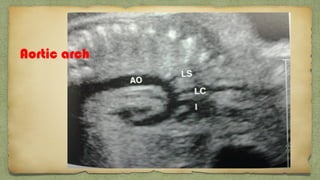
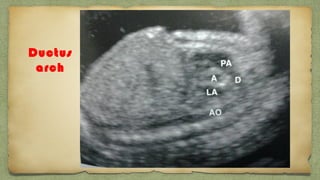
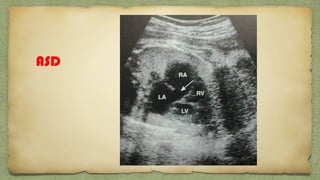
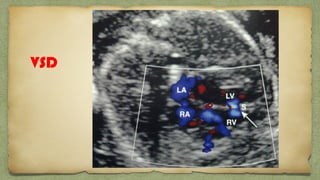
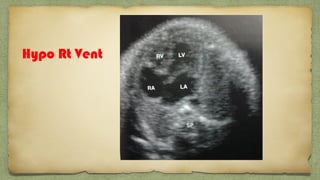
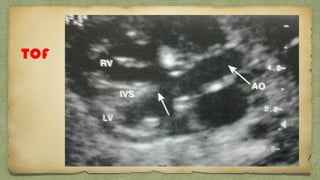
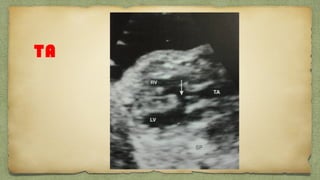
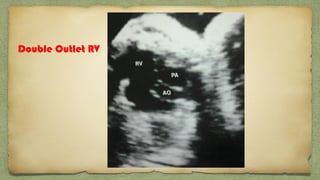
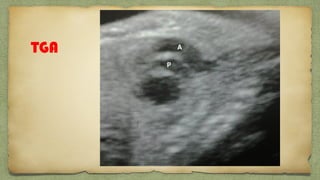
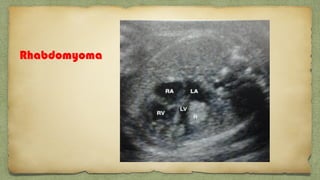
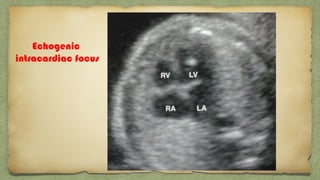
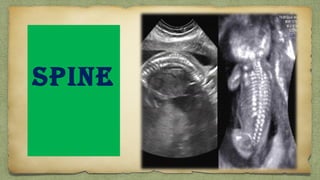
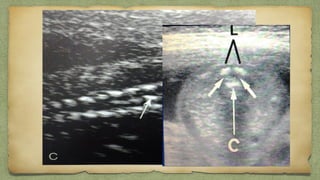
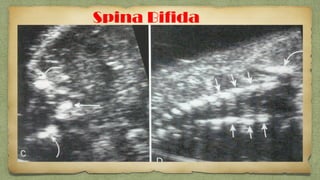
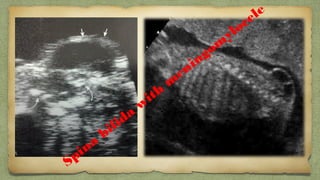
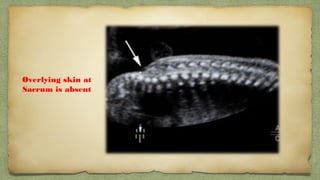
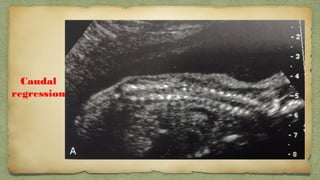
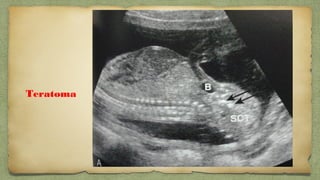
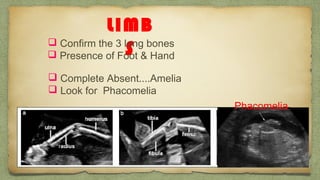
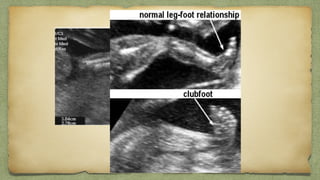
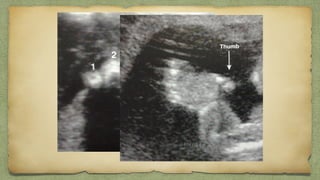
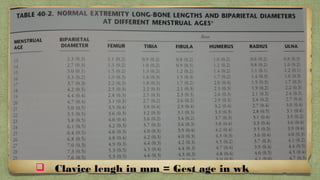
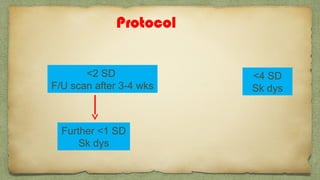
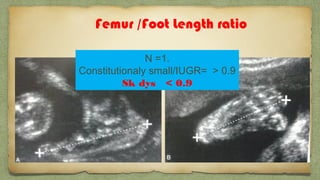
The document provides details about performing and interpreting a fetal anatomy scan between 18-20 weeks of gestation. It describes assessing various fetal anatomical structures including the brain, skull, abdomen, lungs, heart, spine, and limbs. Key measurements and normal ranges are outlined. Common congenital anomalies that may be detected on the scan are also described for various structures. The purpose of the anatomy scan is to evaluate fetal anatomy and screen for potential fetal anomalies.