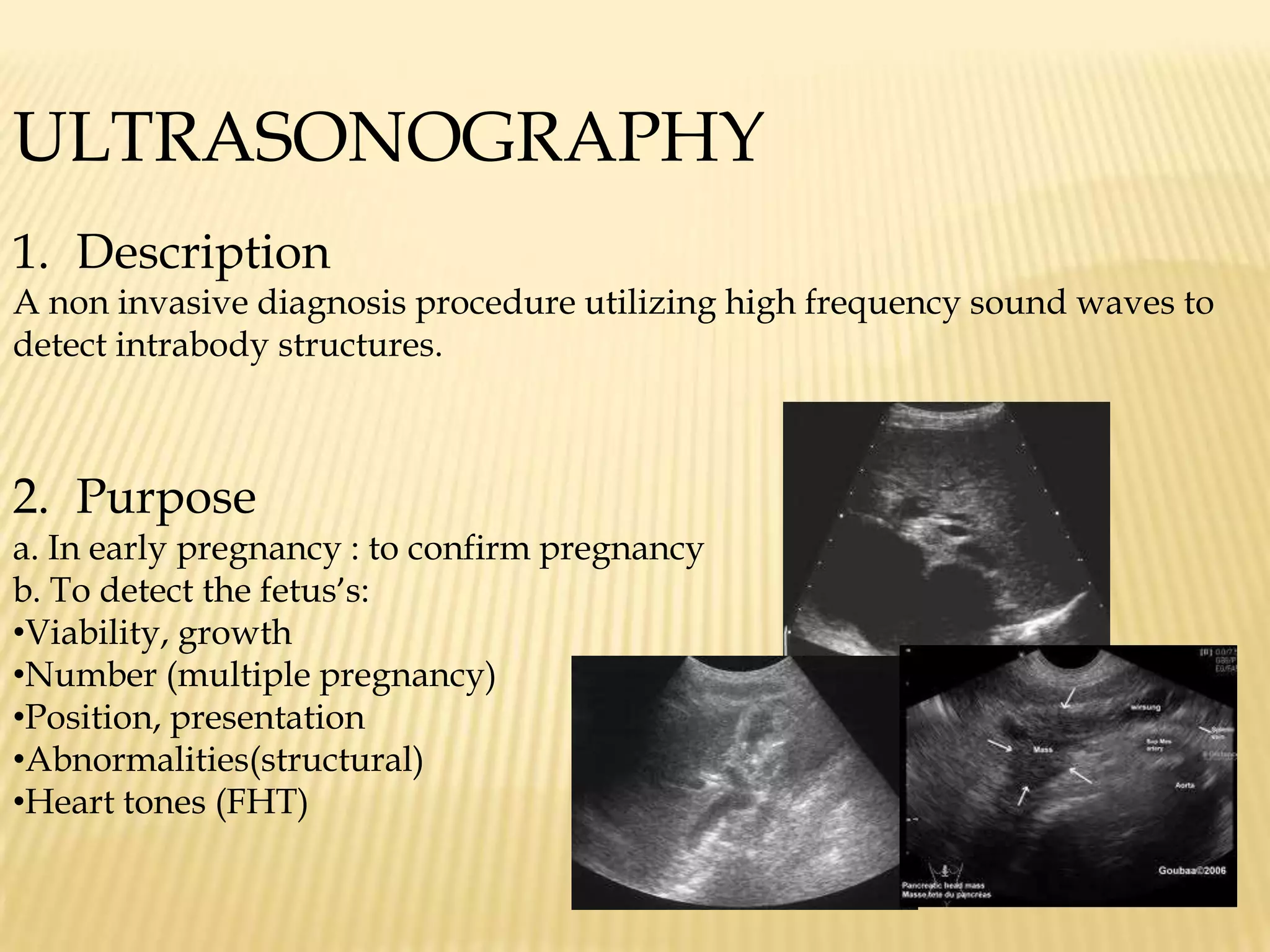
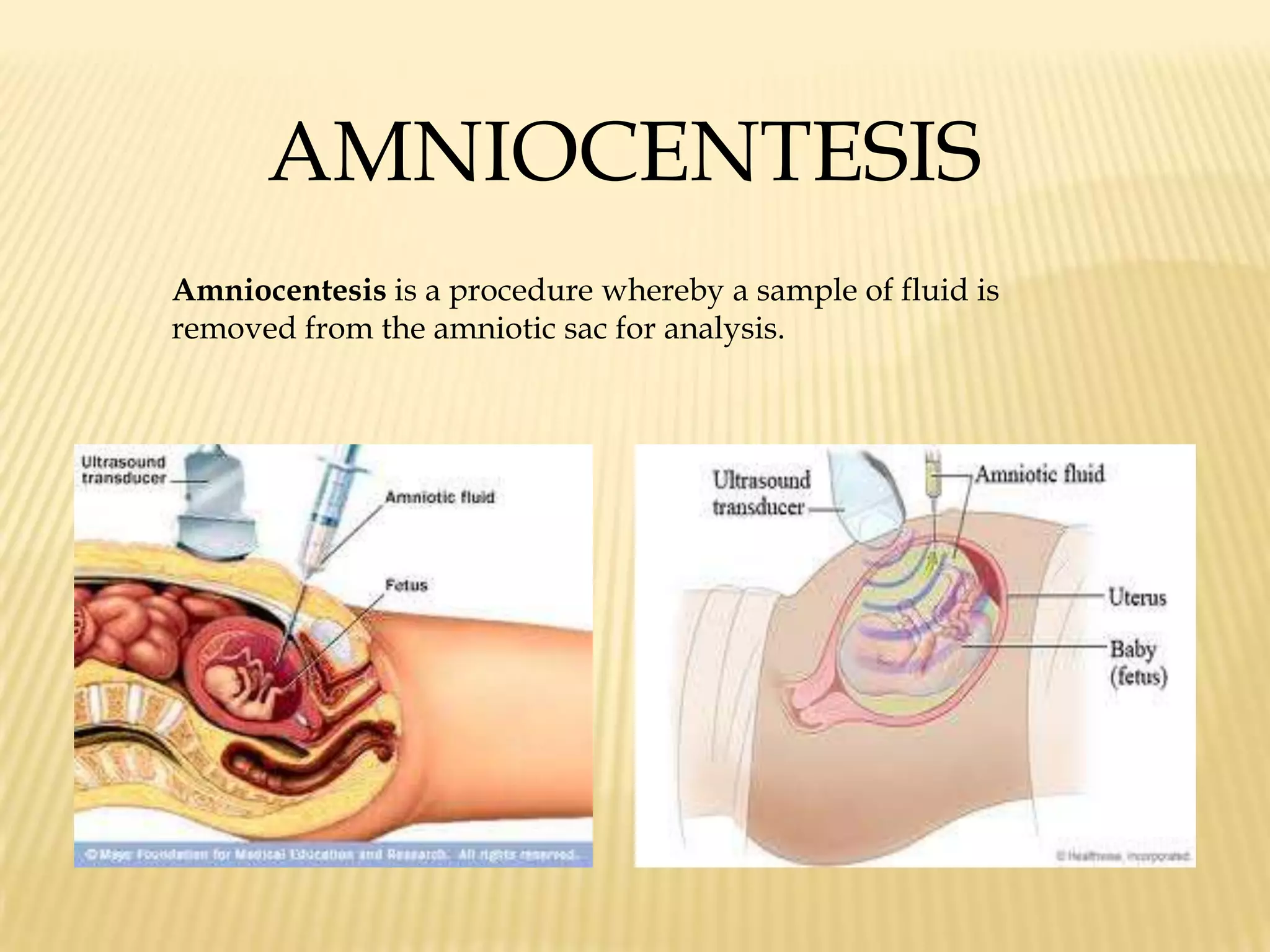
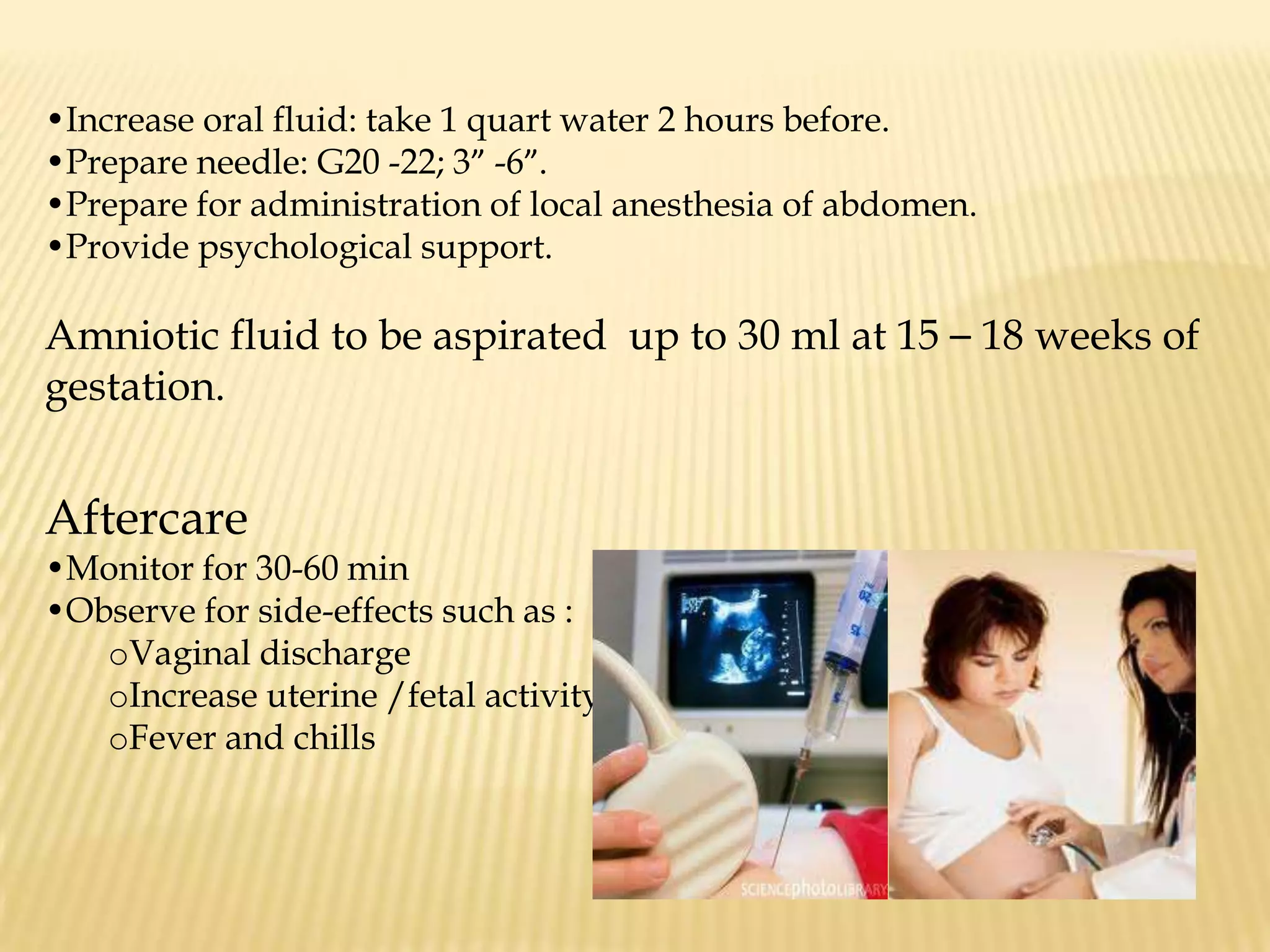
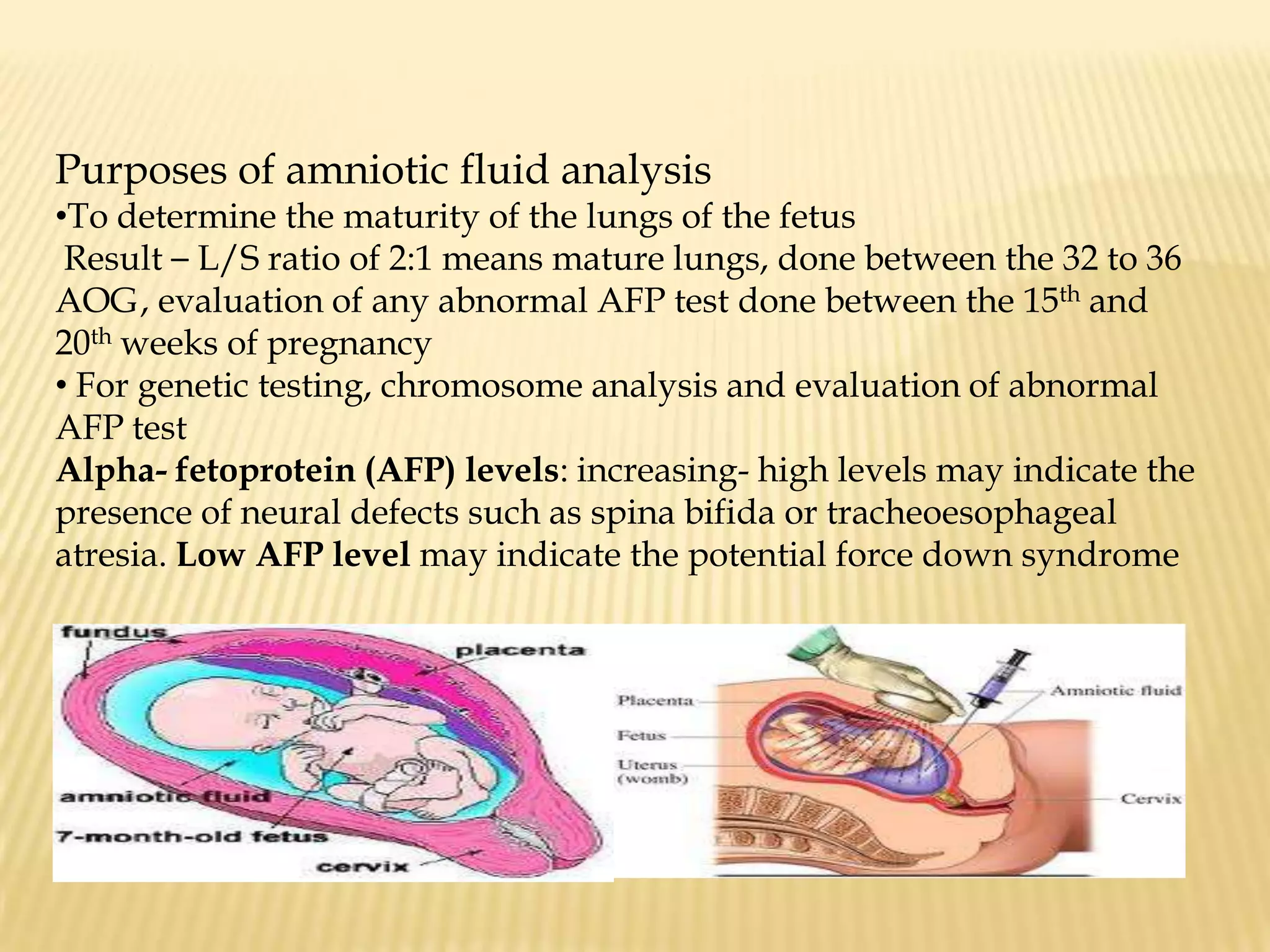
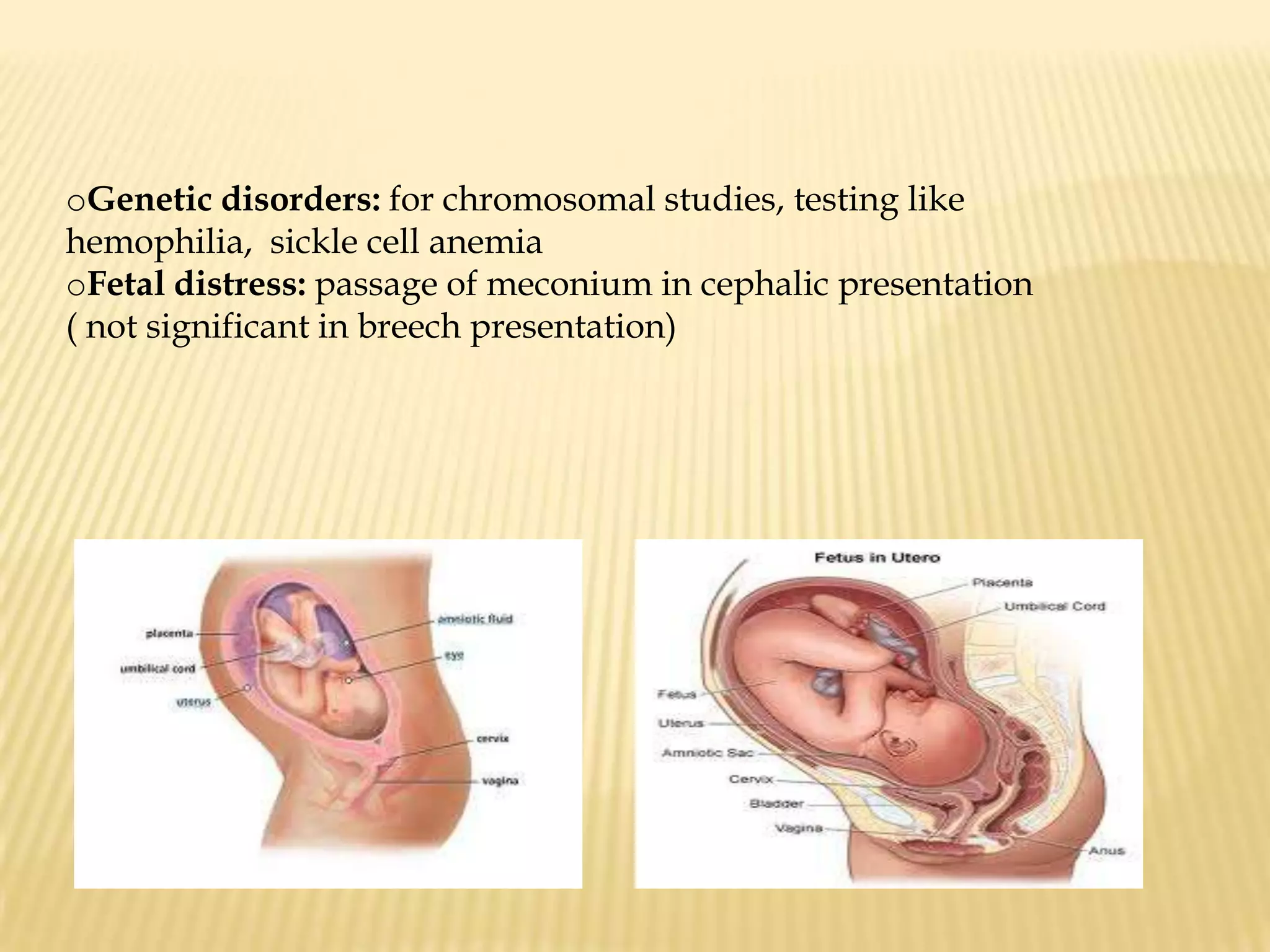
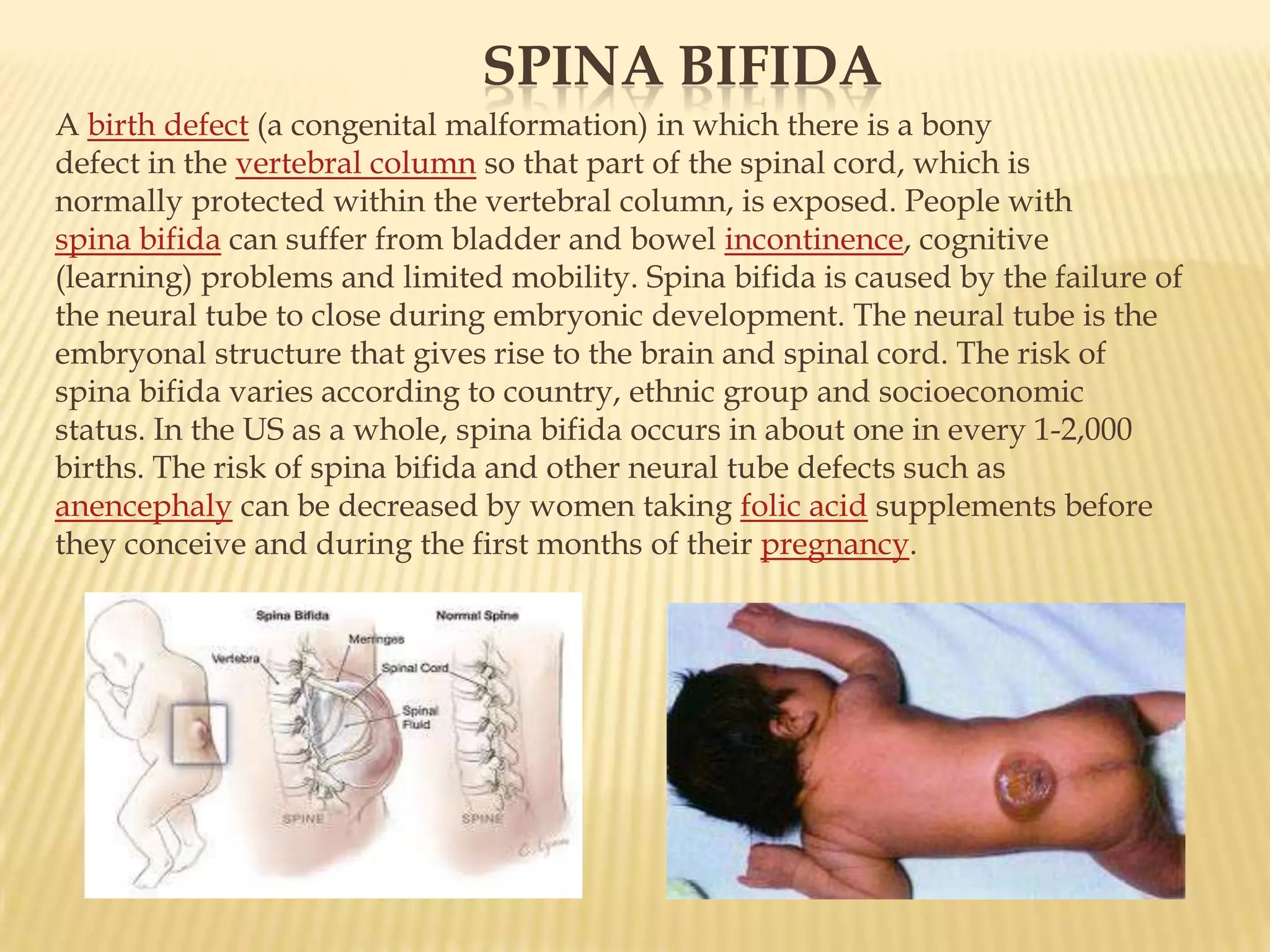
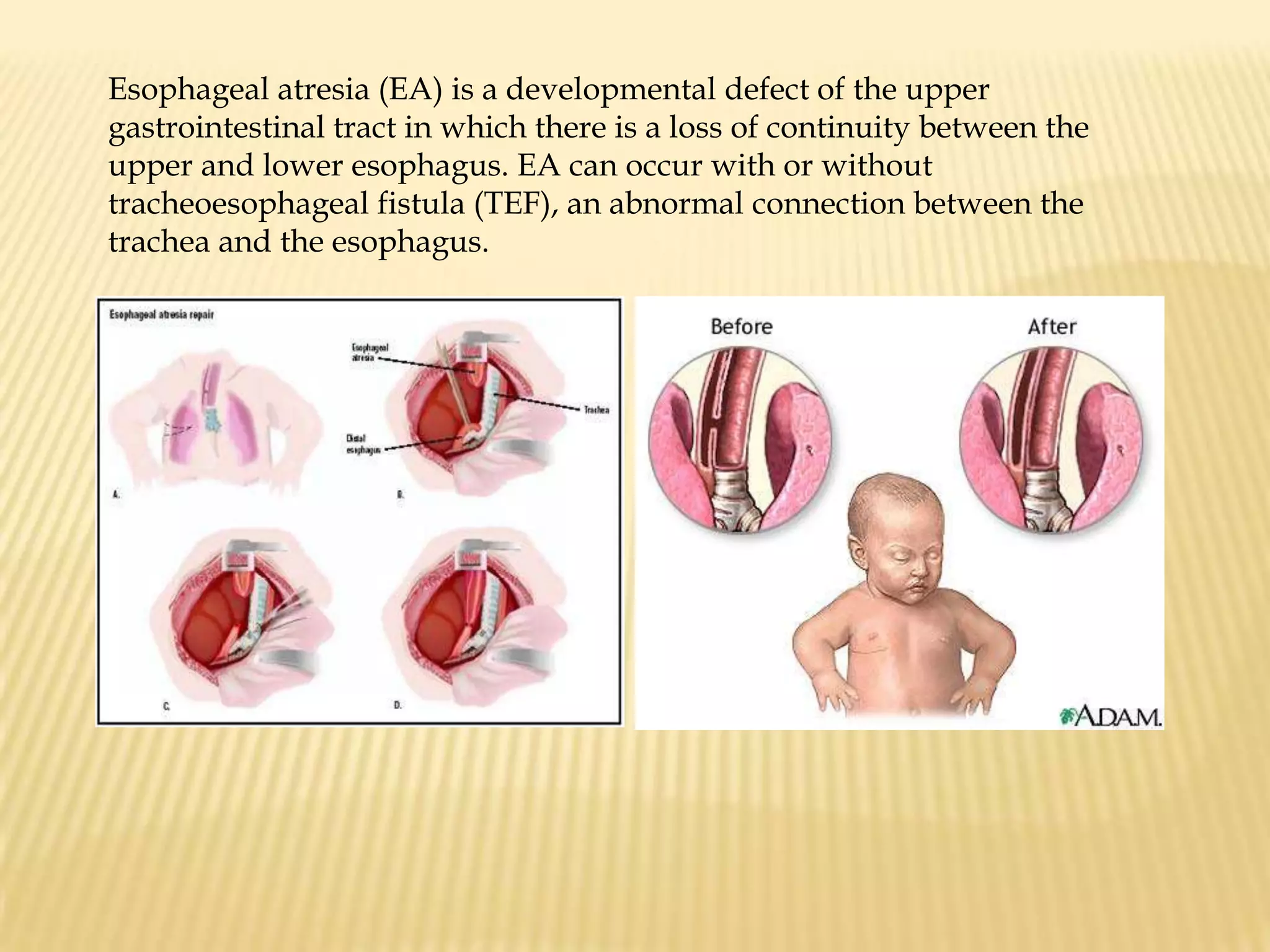
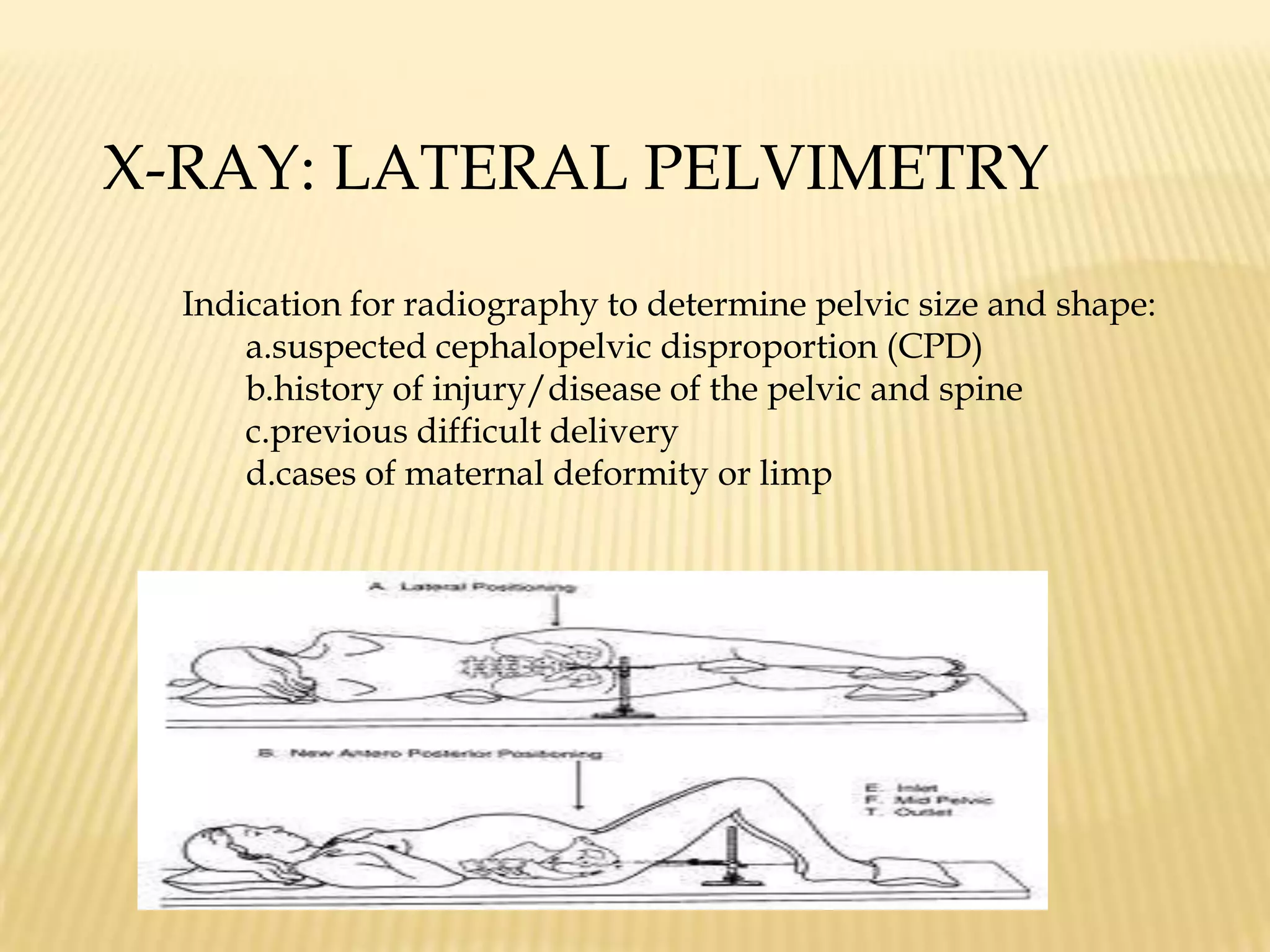
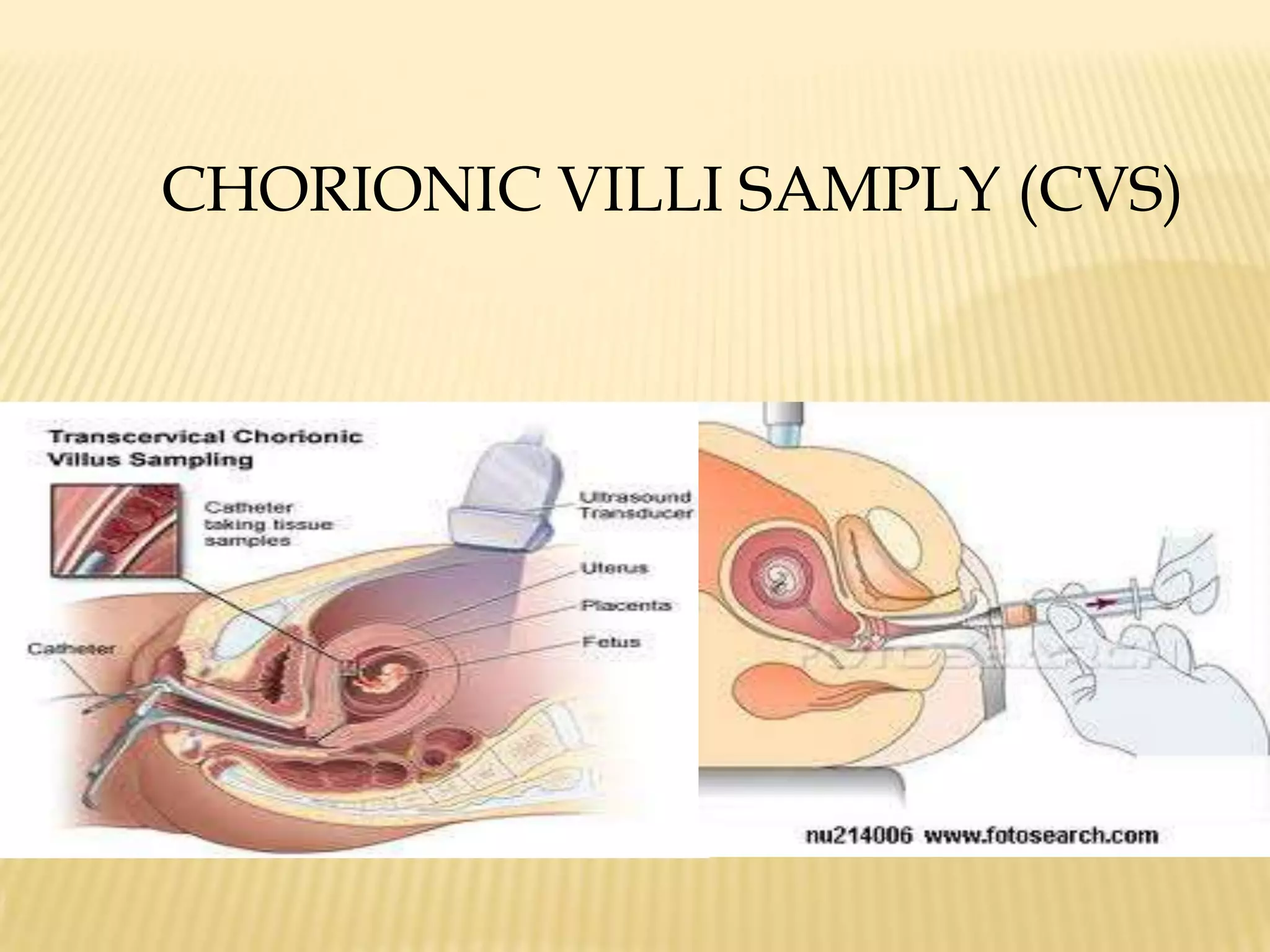
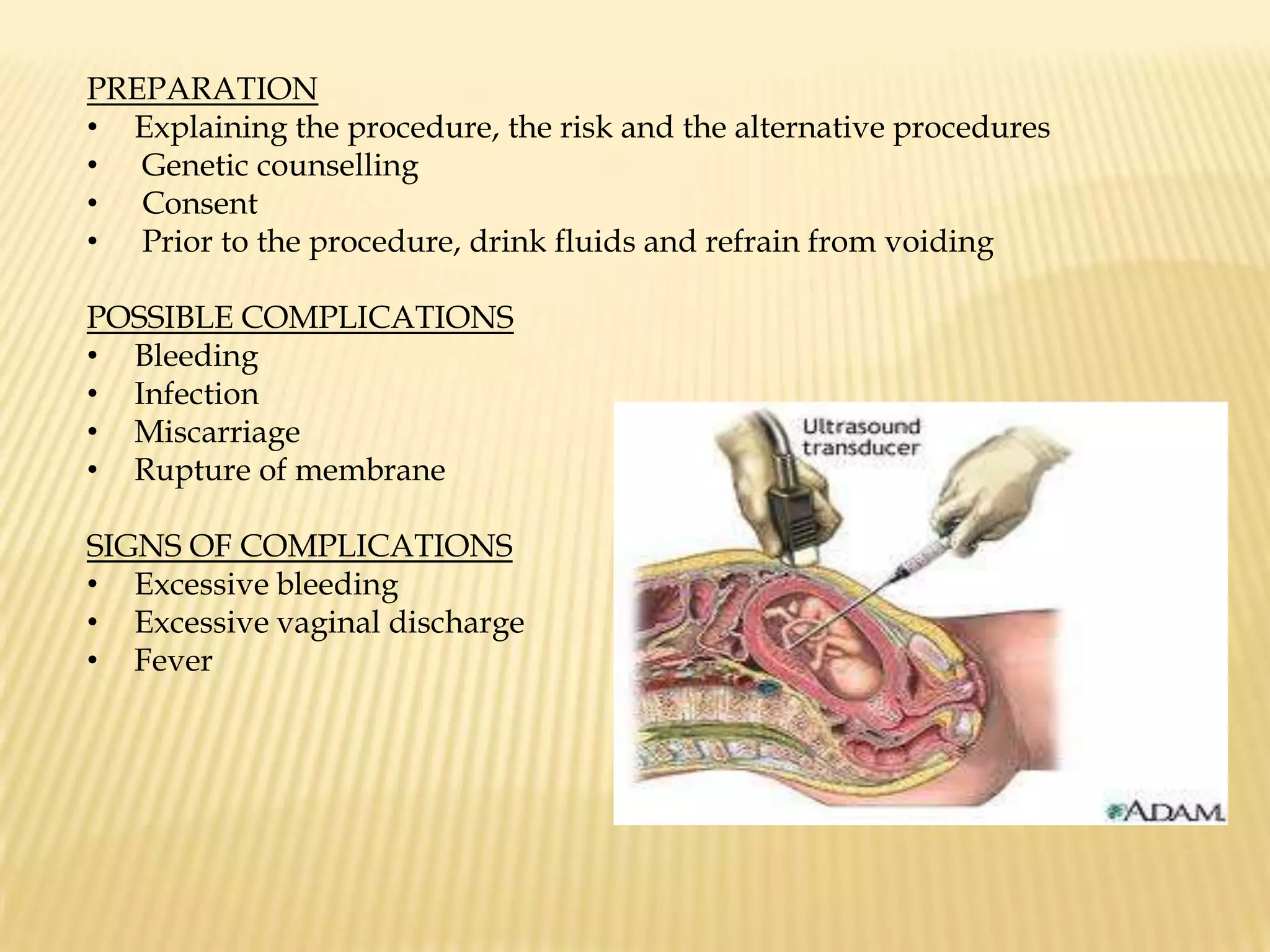
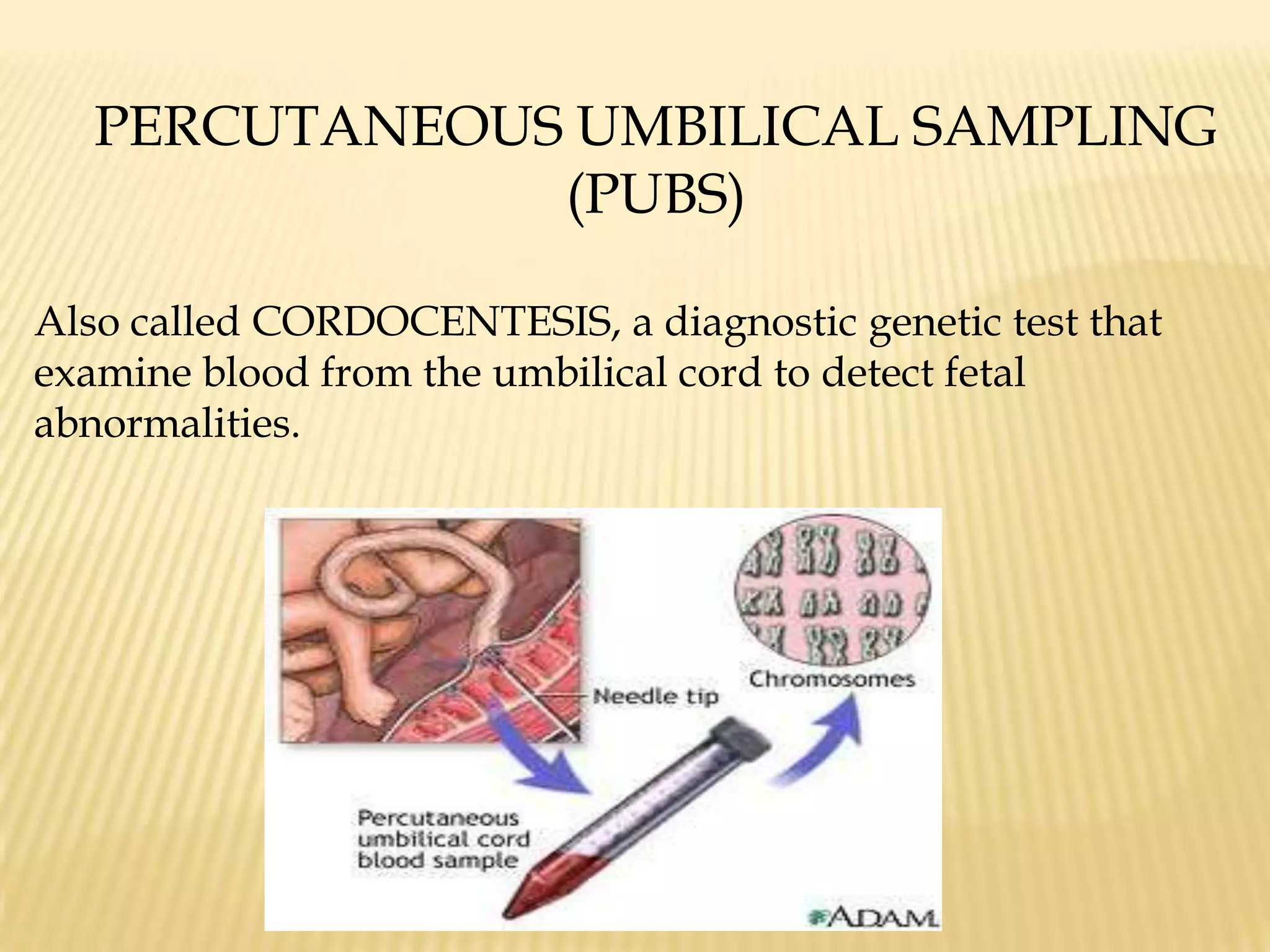
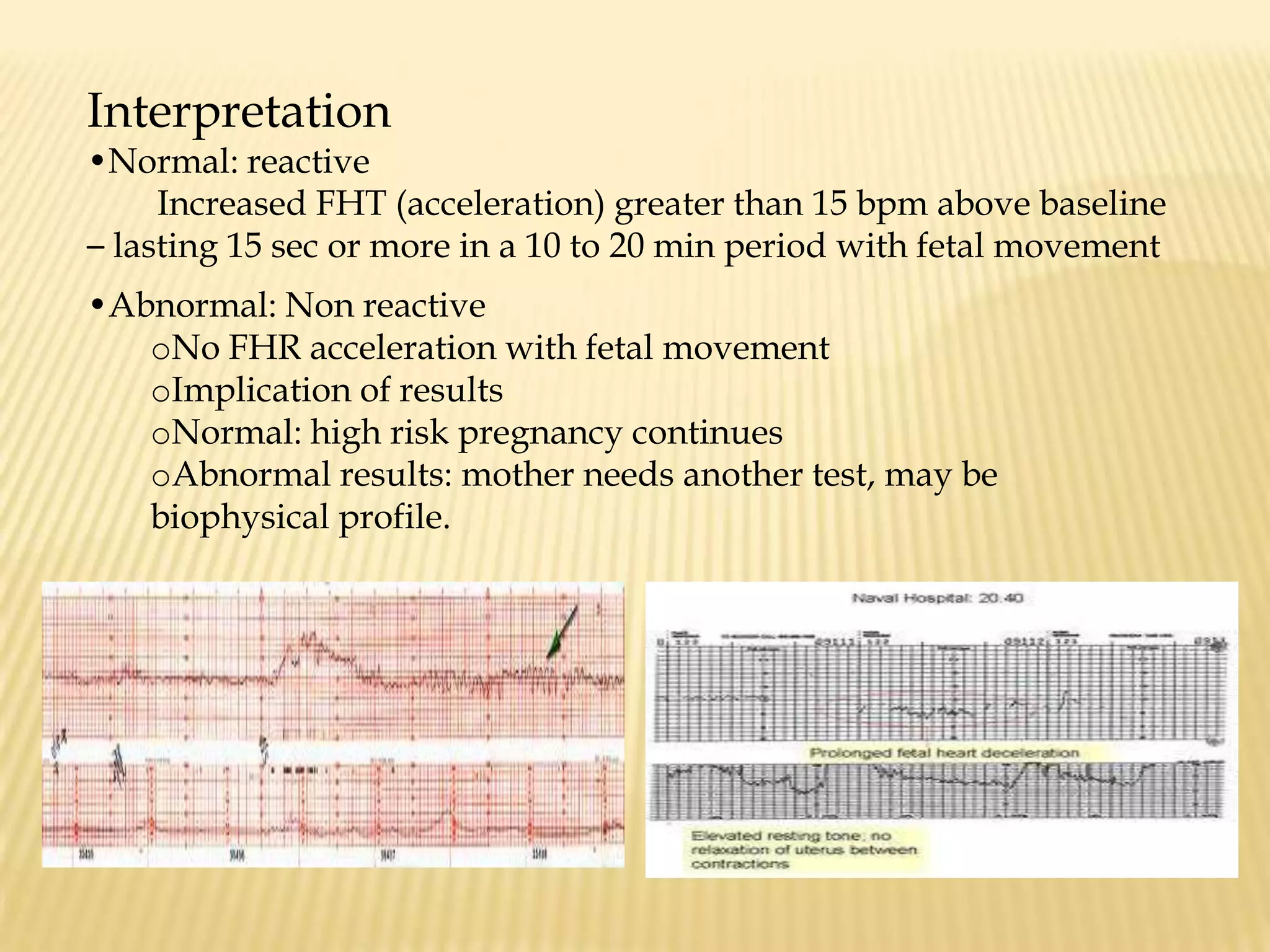
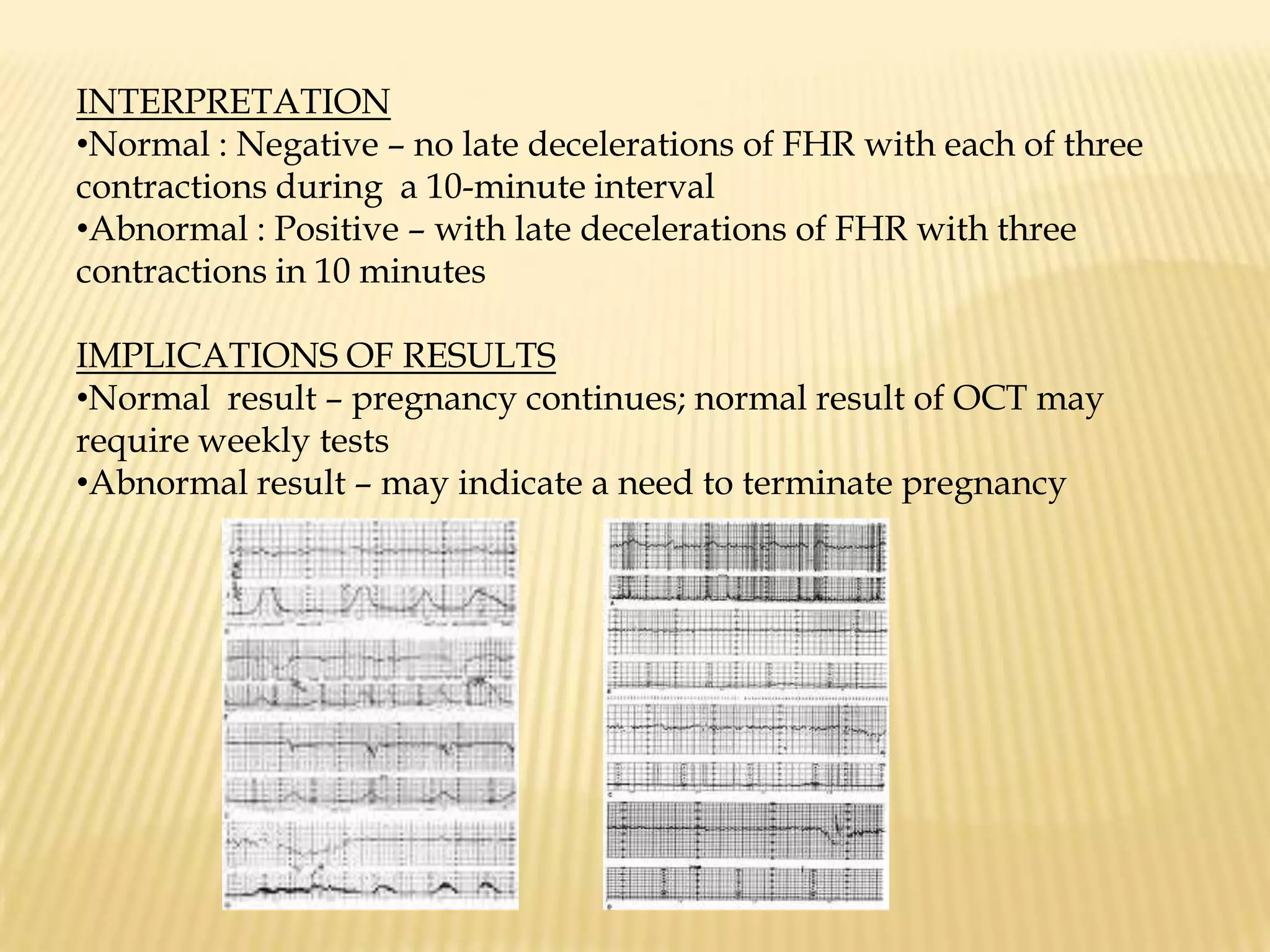
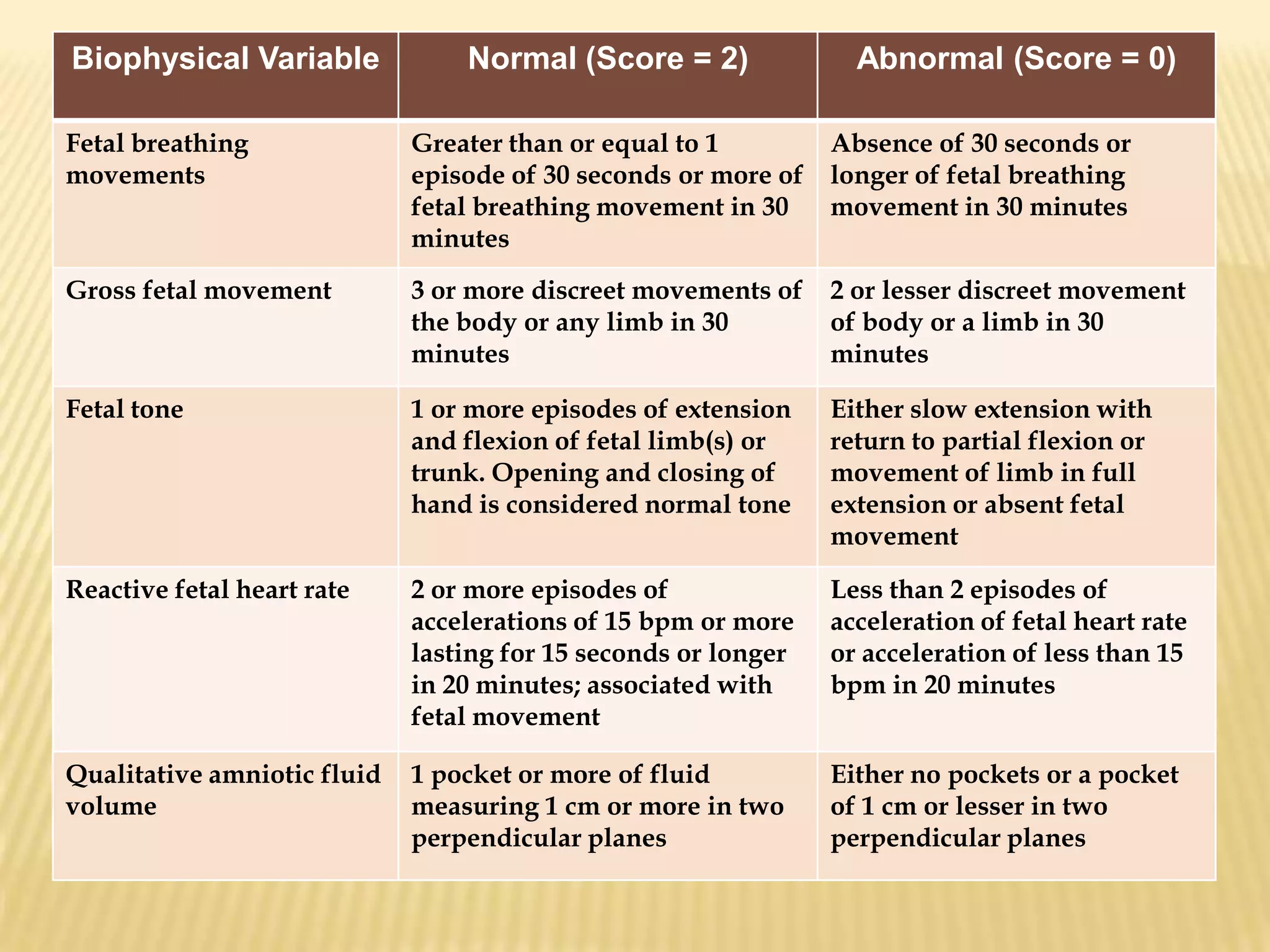
This document summarizes several diagnostic tests used in high-risk pregnancies to determine fetal status, including ultrasonography, fetoscopy, amniocentesis, non-stress testing, biophysical profile, and others. Ultrasonography uses sound waves to detect fetal structures, growth, and abnormalities. Fetoscopy uses a thin scope to visualize the fetus. Amniocentesis extracts amniotic fluid for analysis. Non-stress testing monitors fetal heart rate responses to movement. Biophysical profile combines ultrasound assessment of fetal wellbeing factors into a score. Each test has specific purposes, preparations, risks, implications and interpretations to evaluate fetal health and guide care.