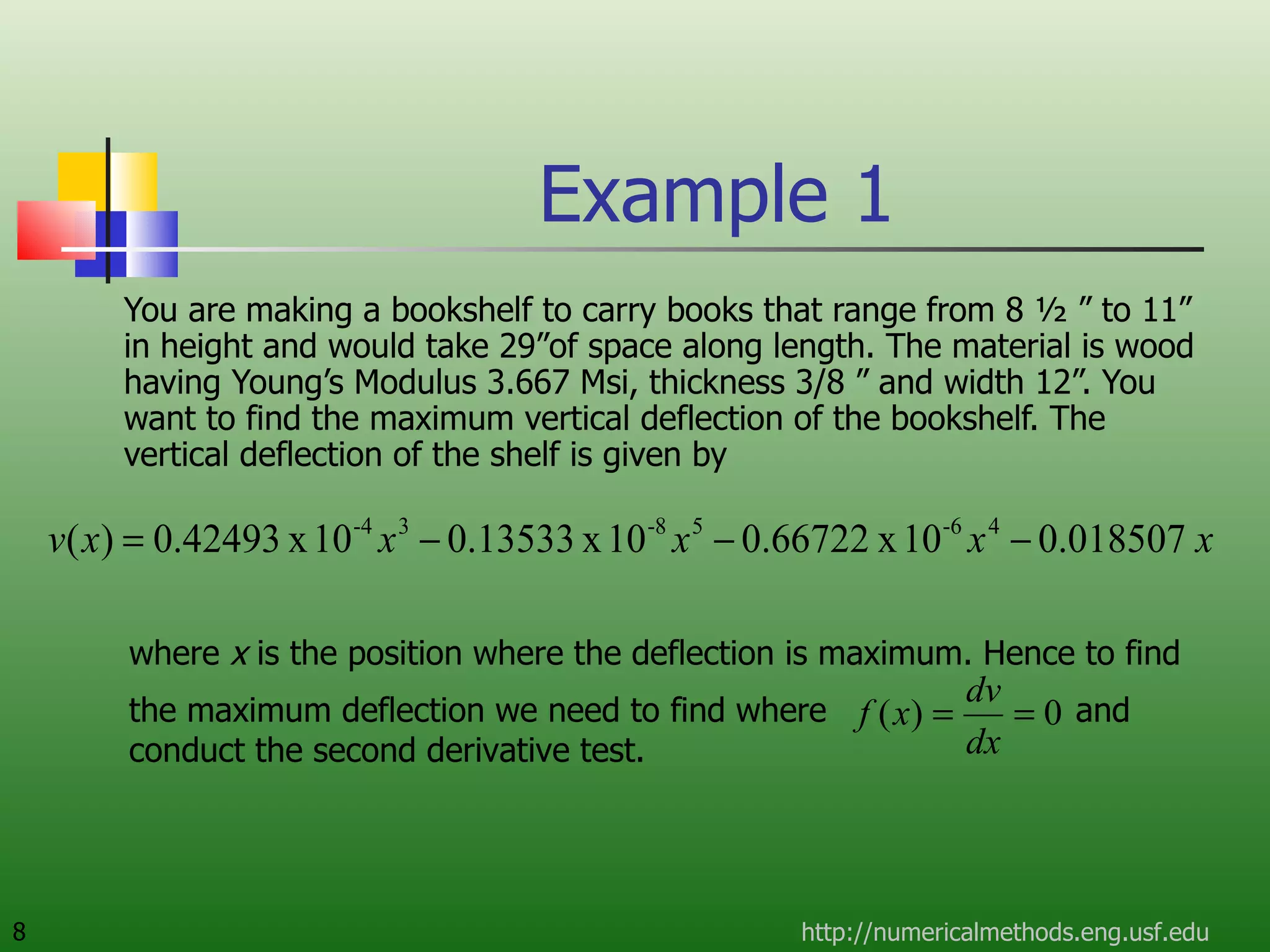
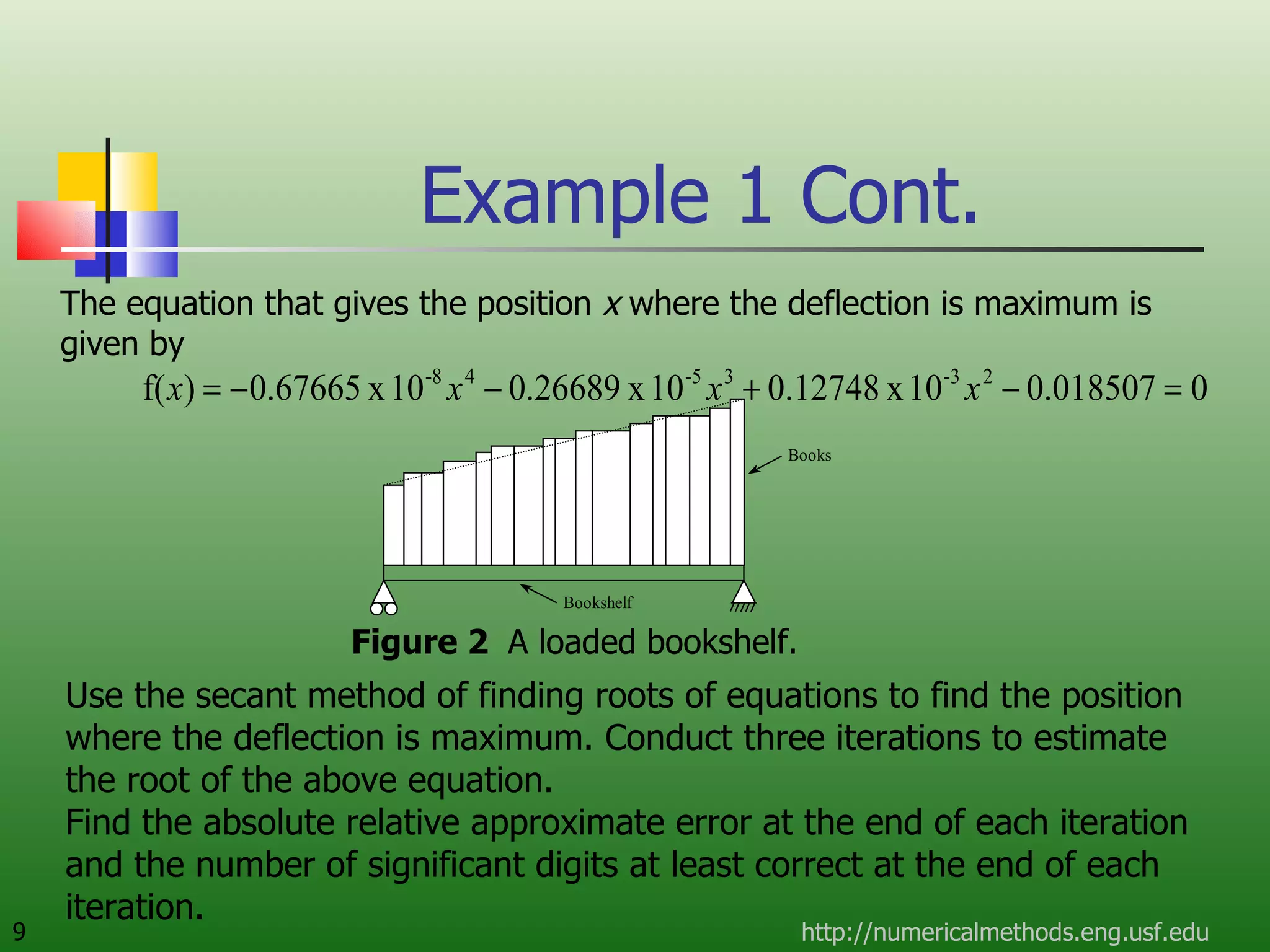
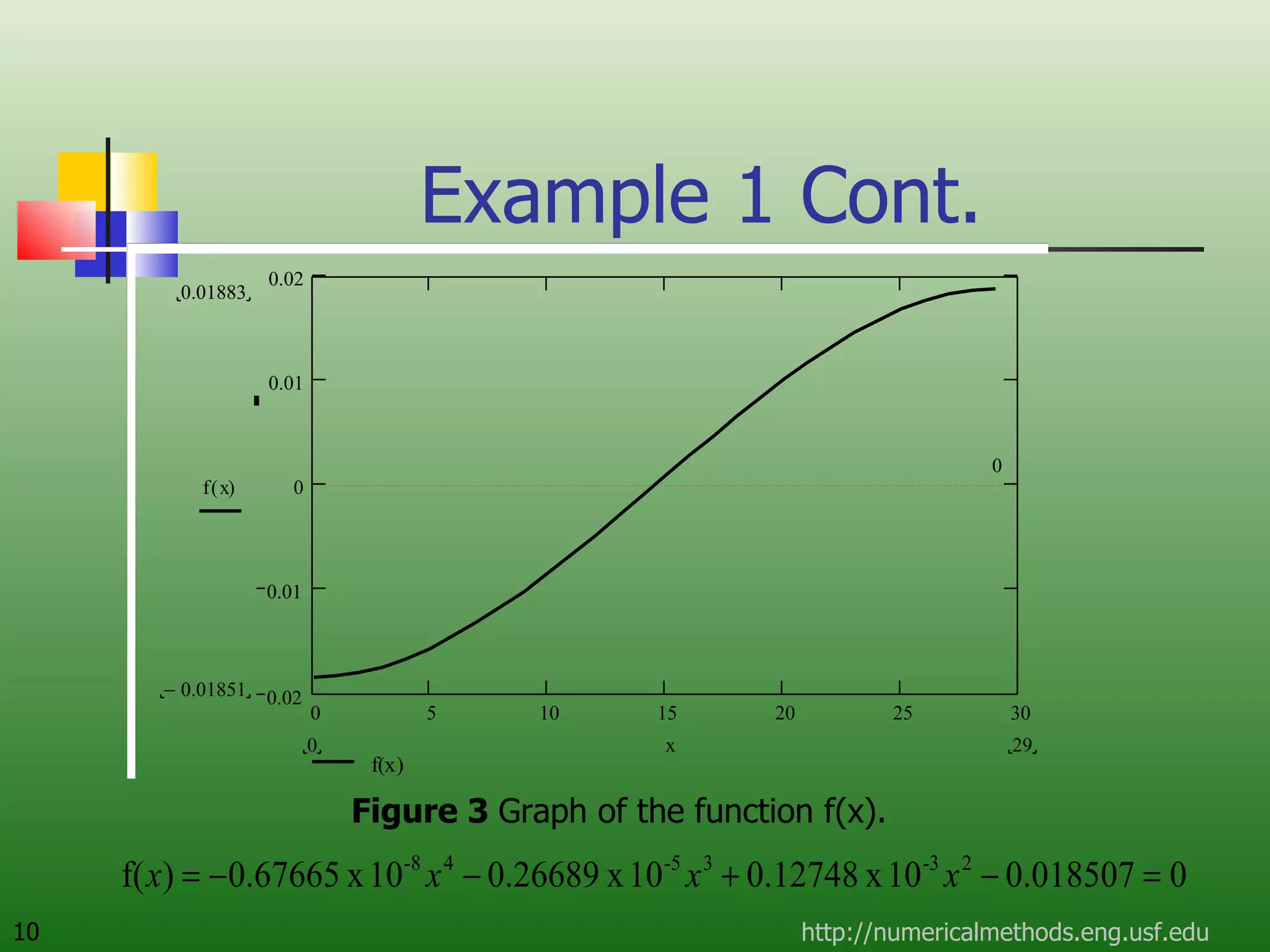
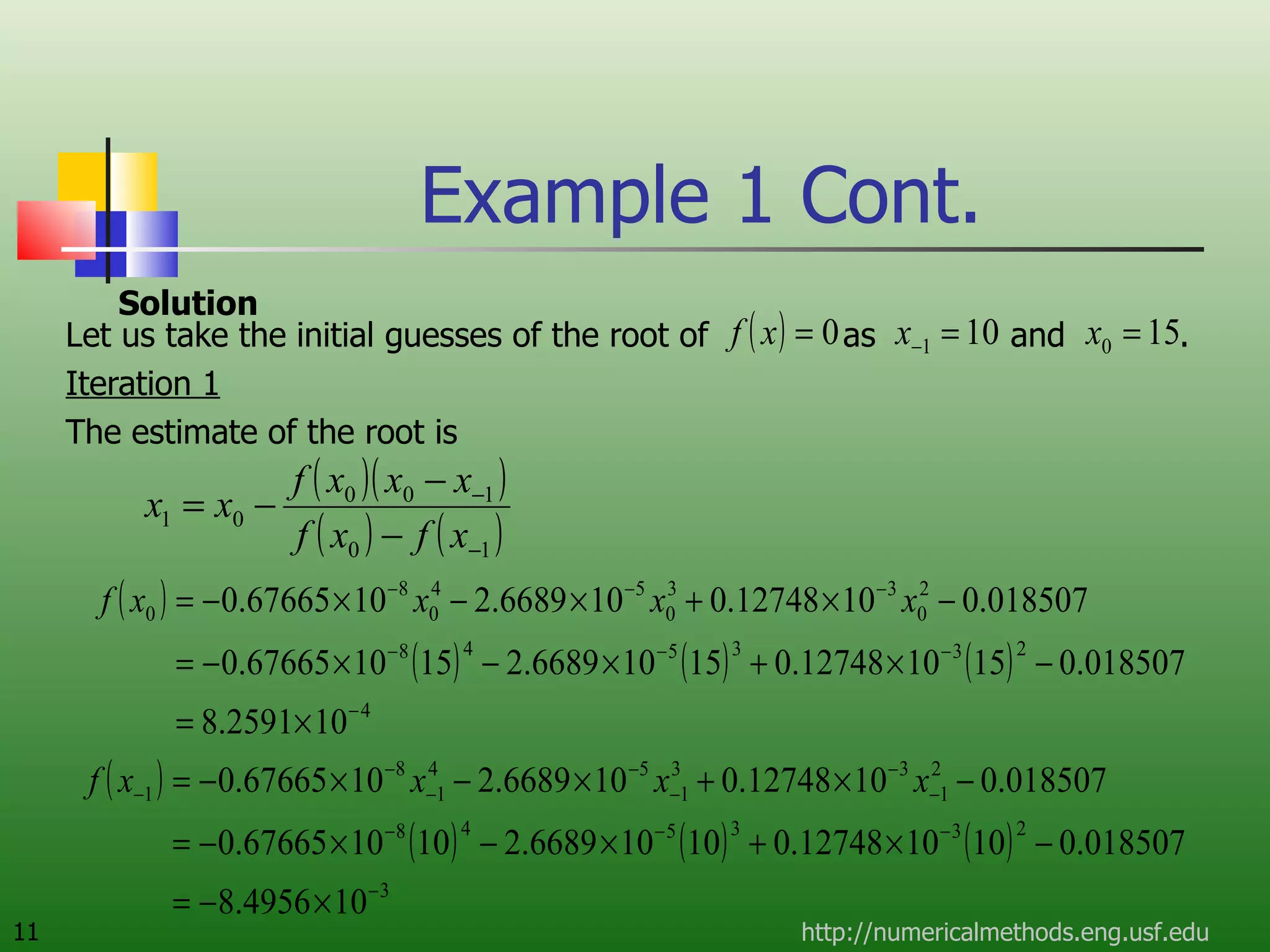
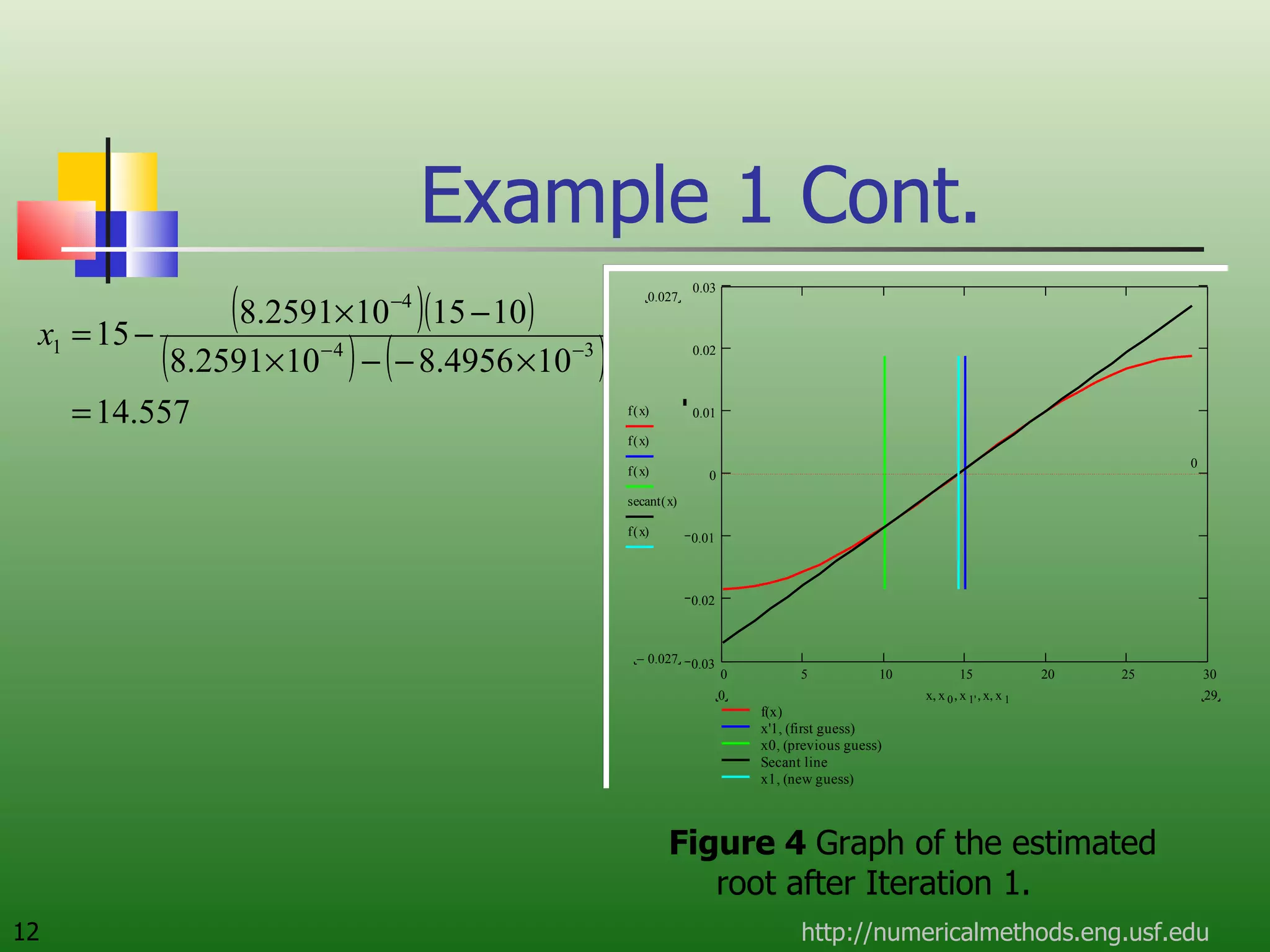
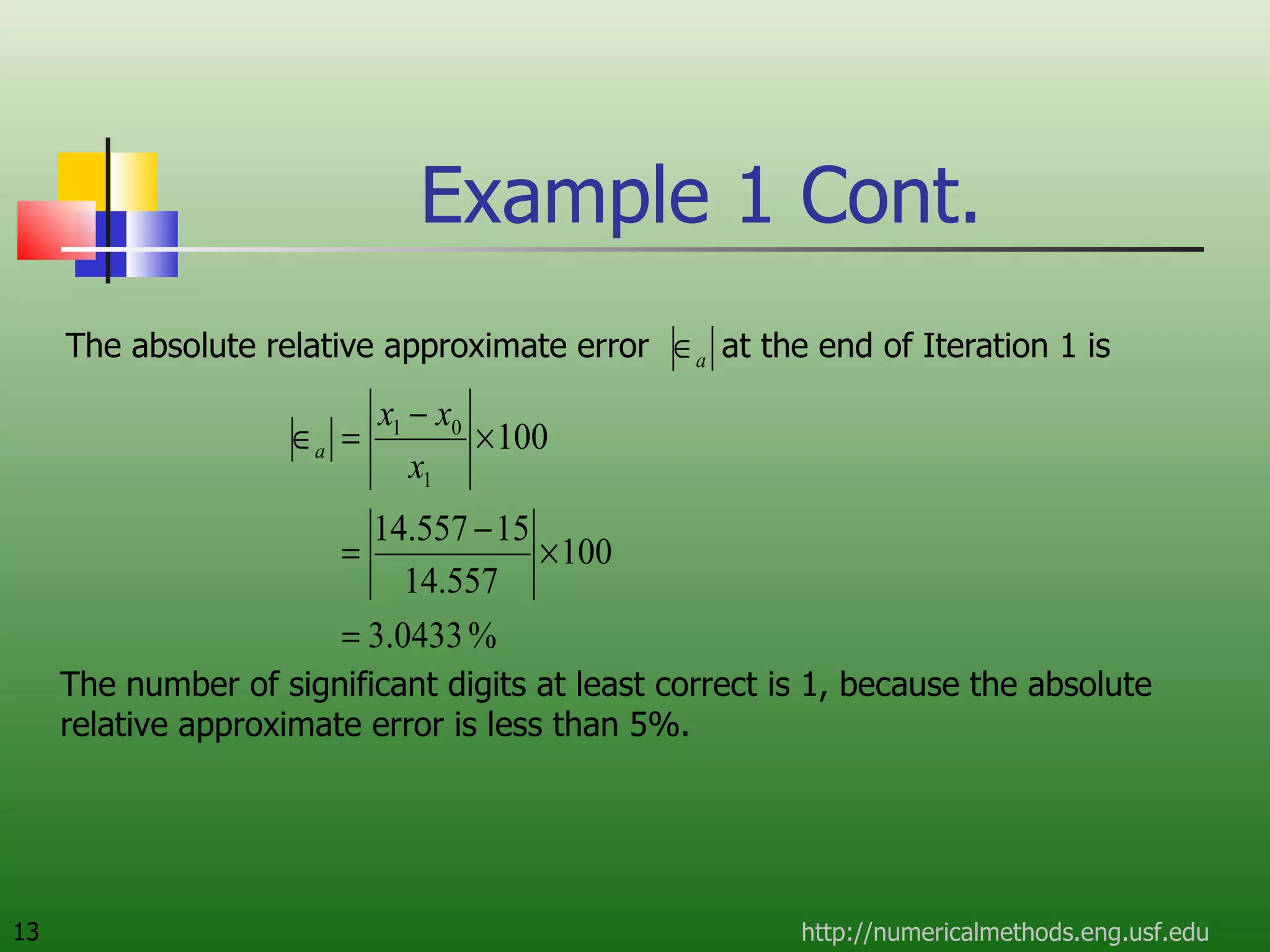
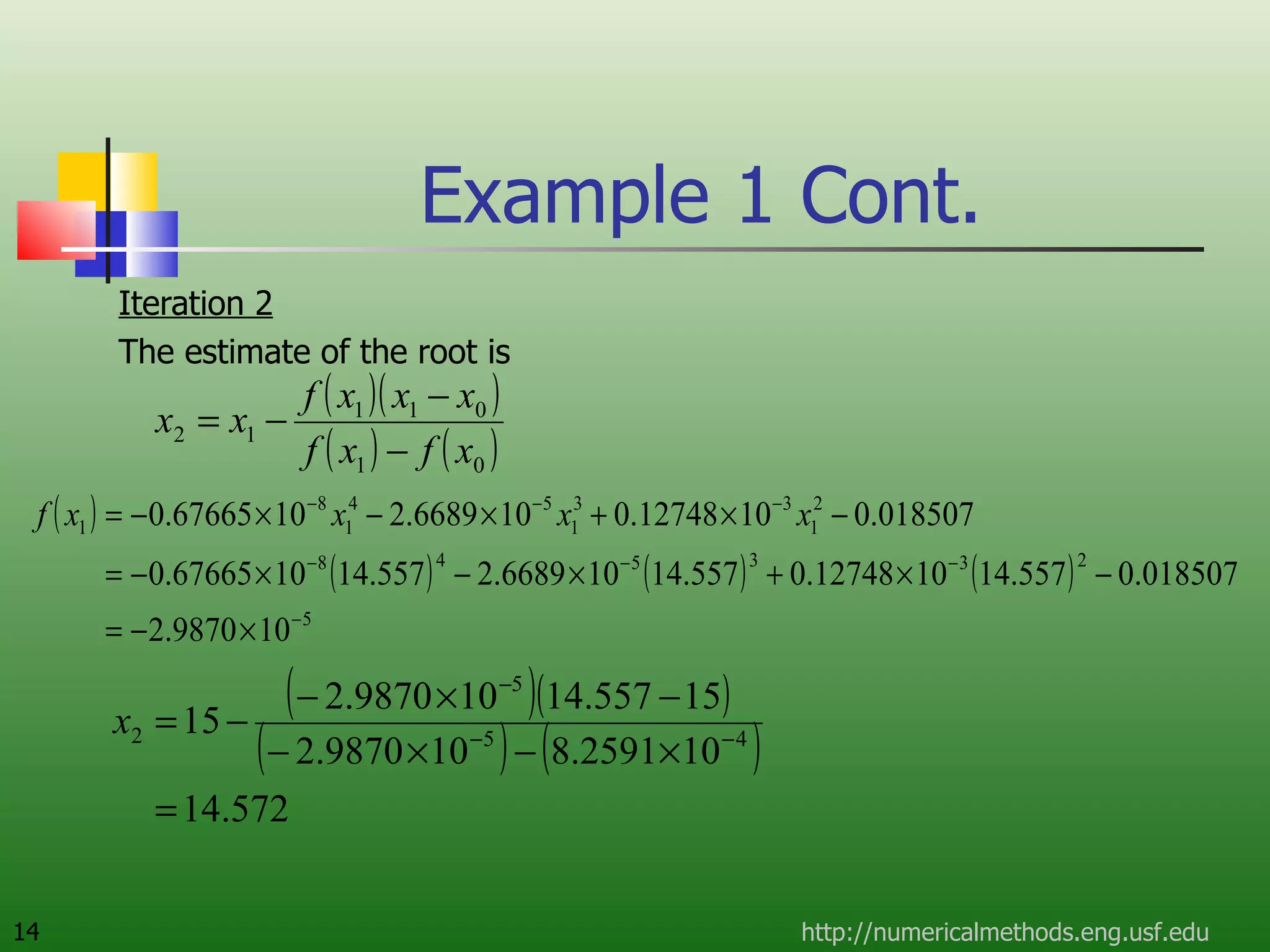
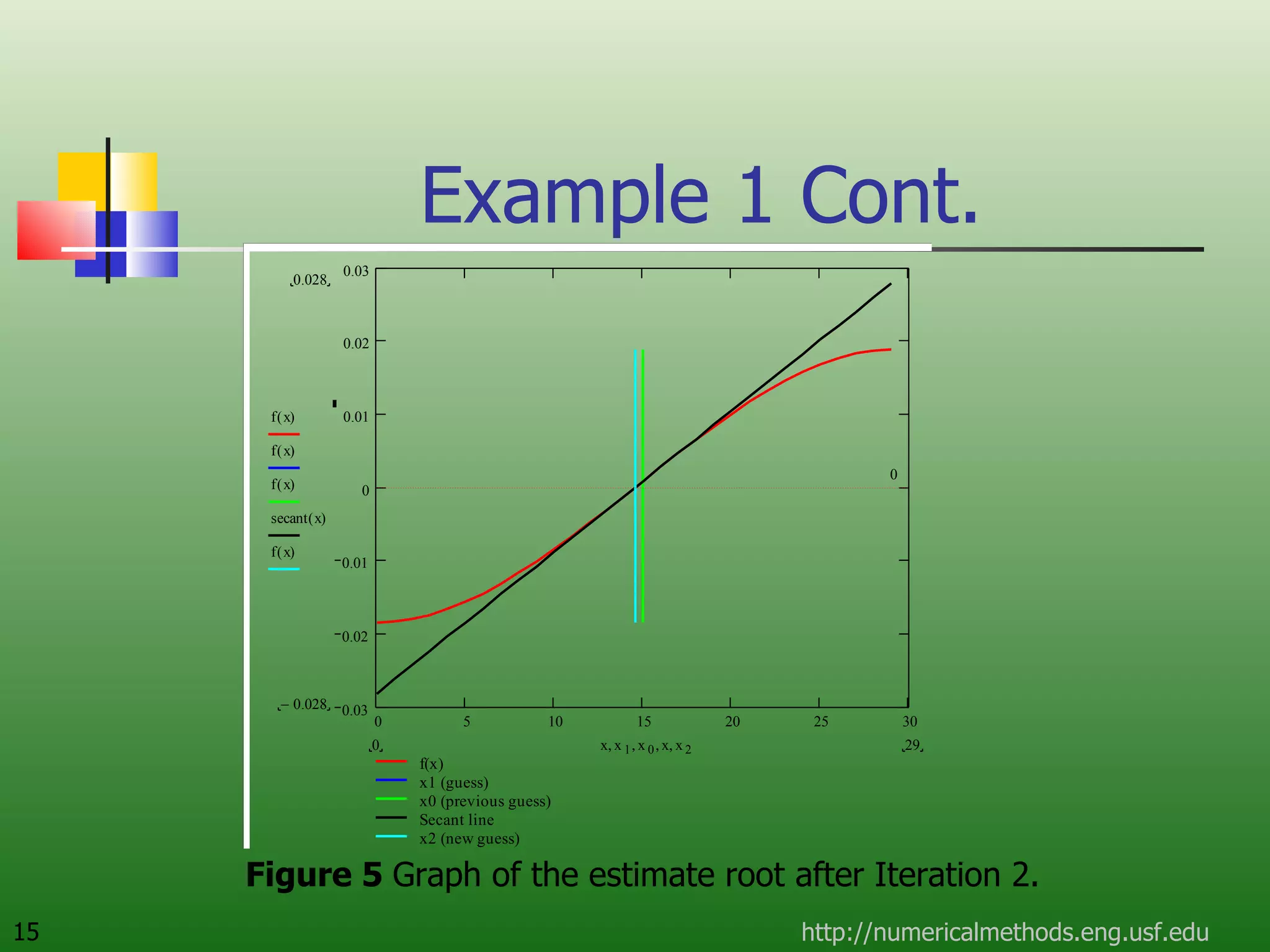
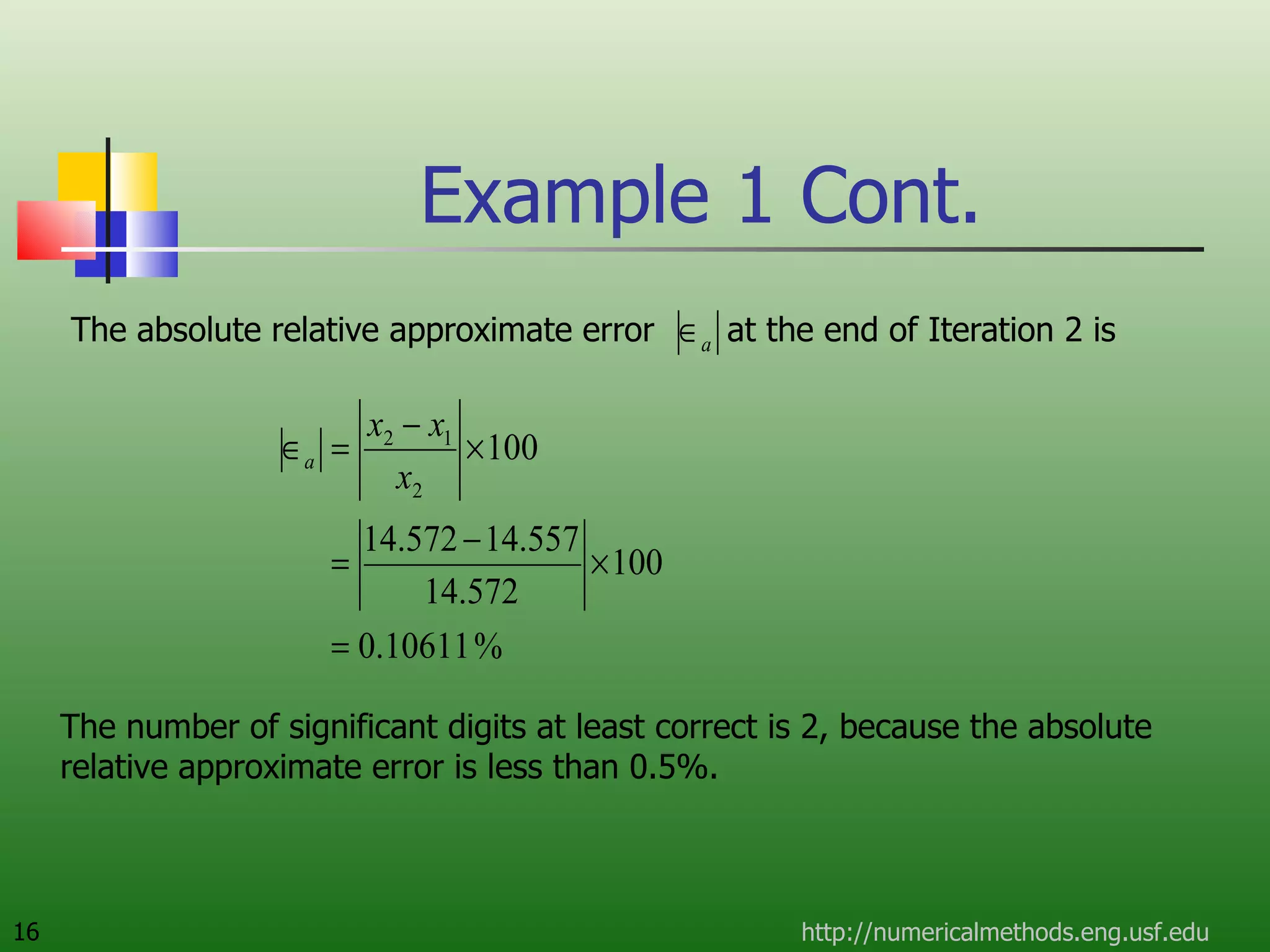
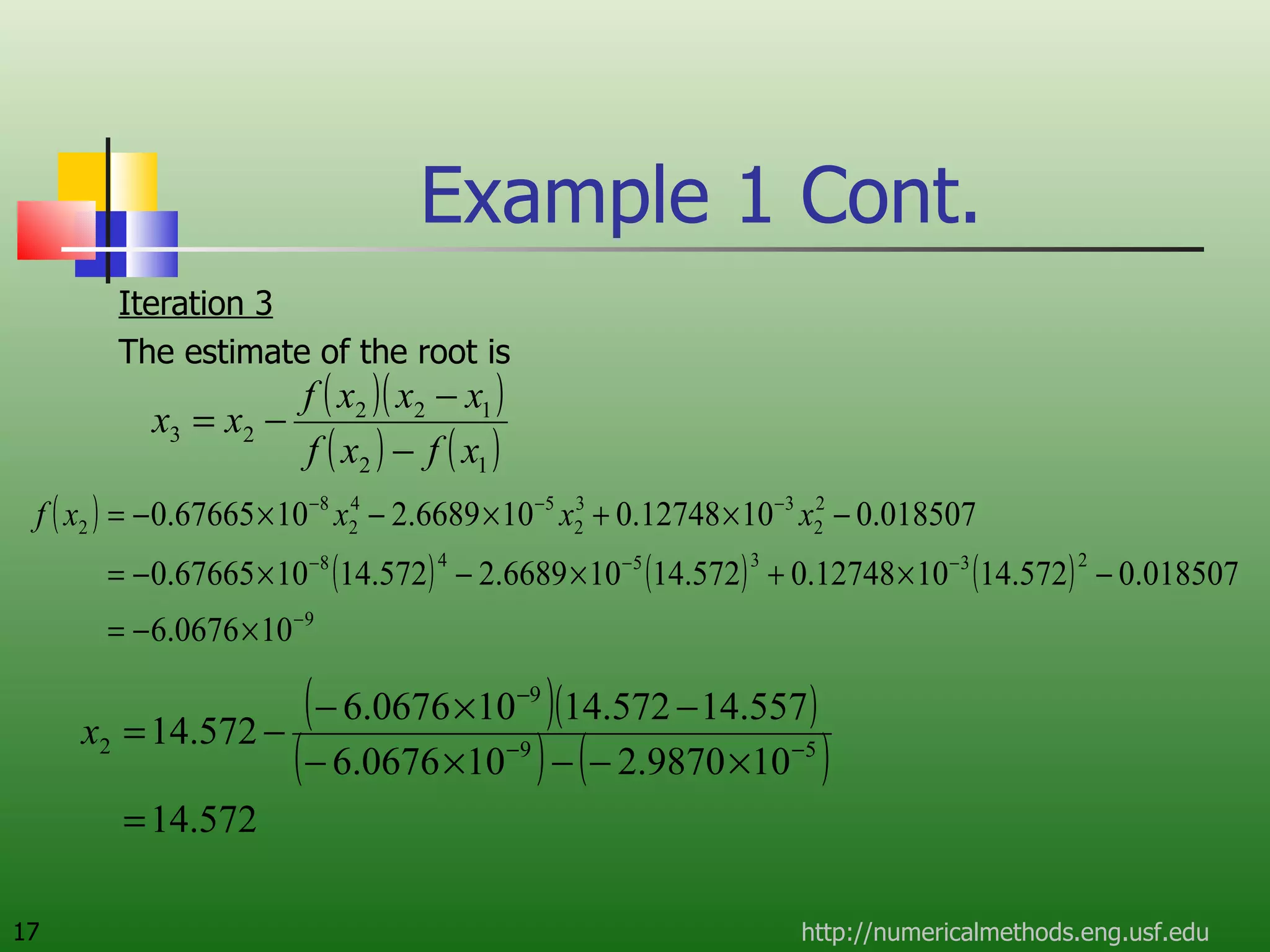
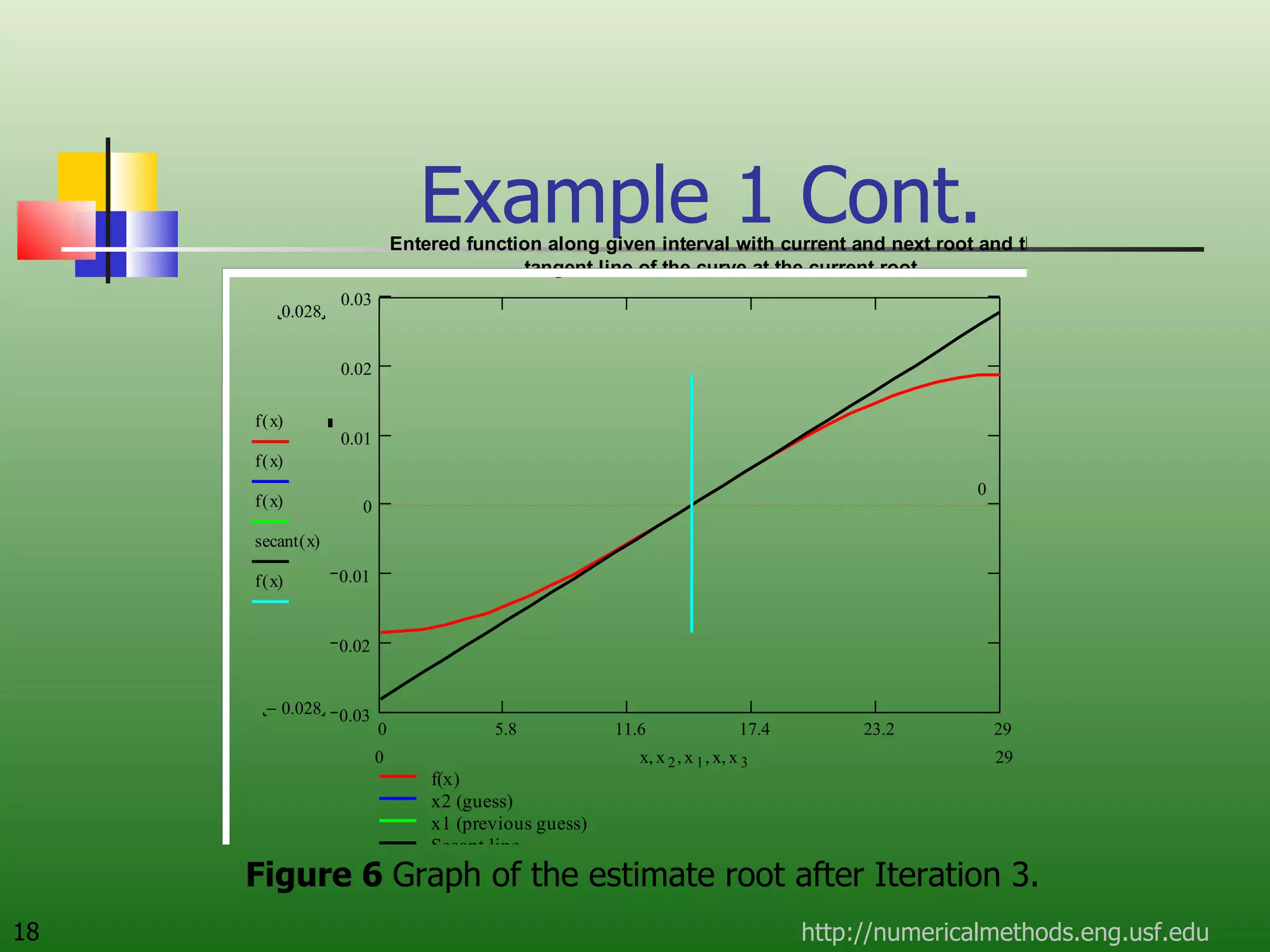
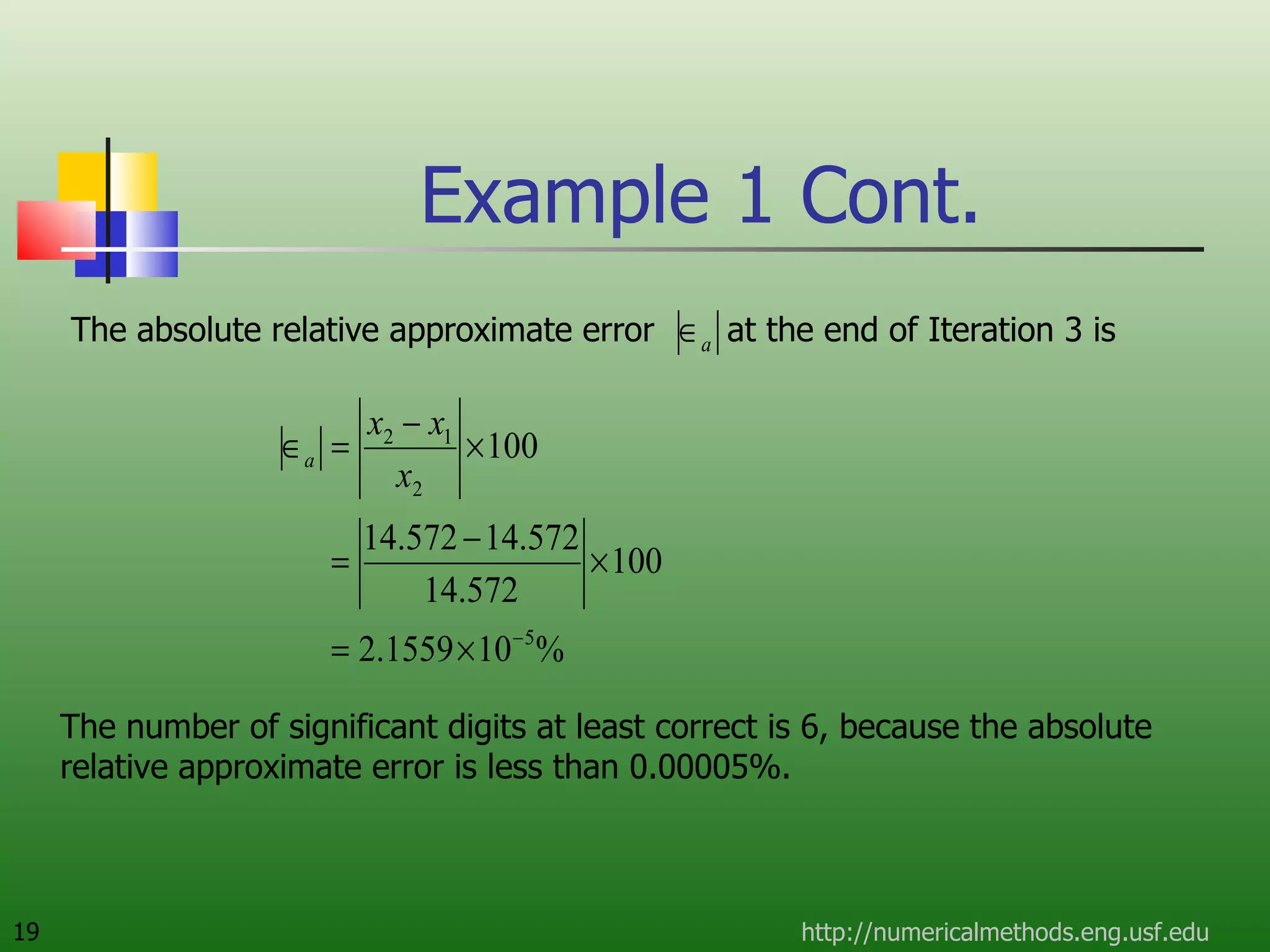
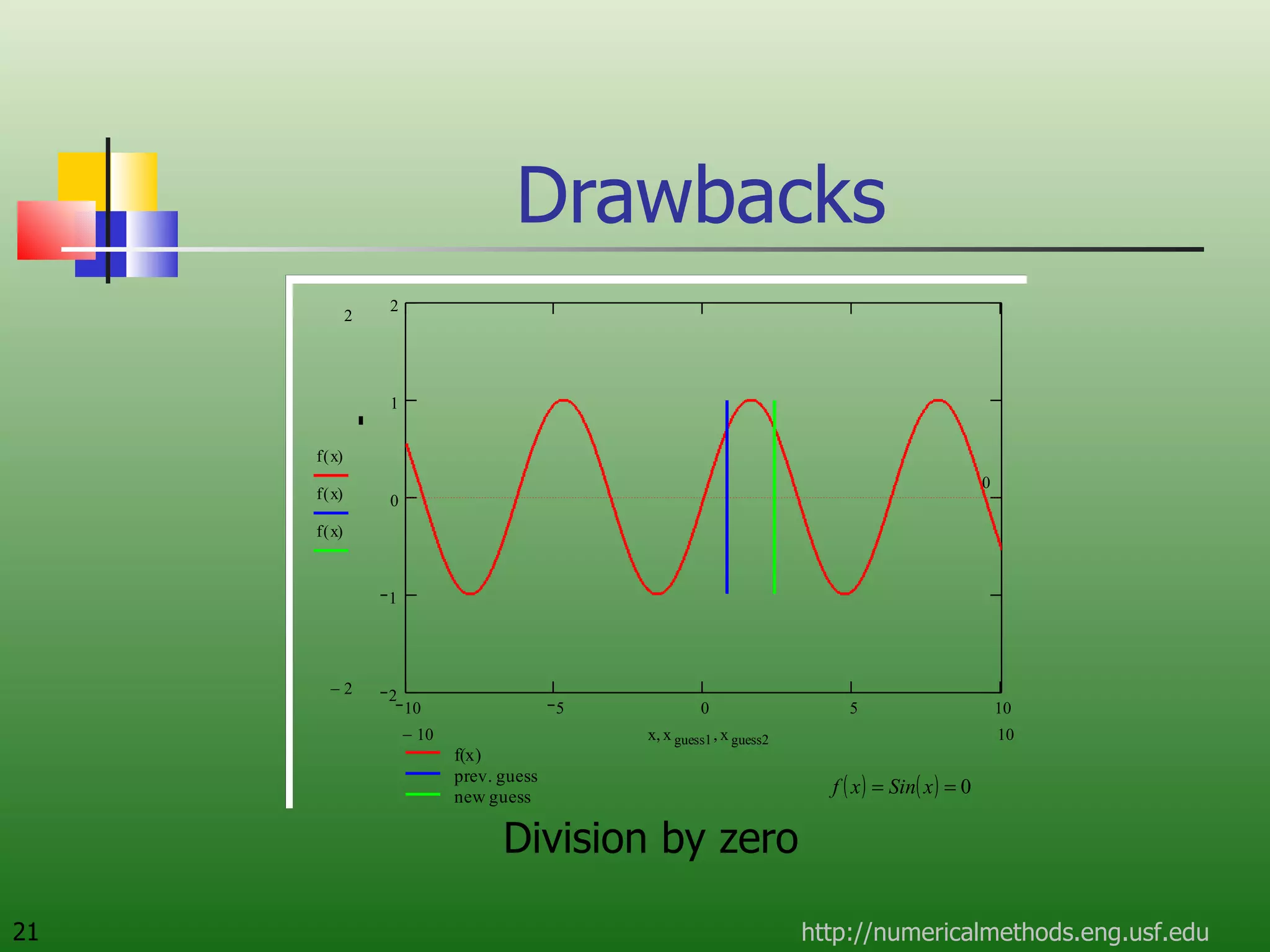
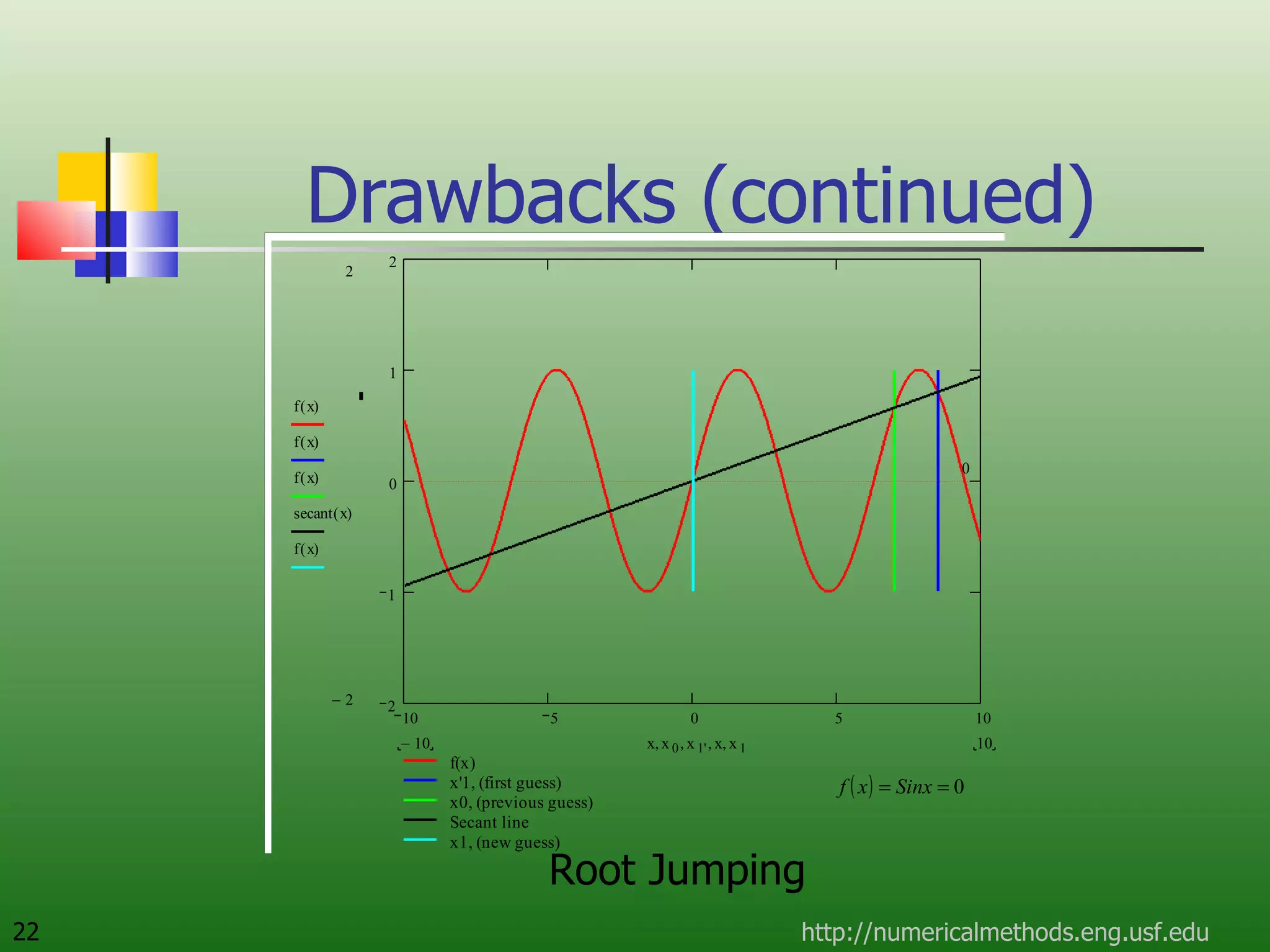
The document discusses the secant method, a root-finding algorithm that approximates the derivative using two points. It derives the secant method from Newton's method and geometry. The document also provides an example of using the secant method to find the maximum deflection of a loaded bookshelf, running through three iterations and calculating the absolute relative approximate error and number of significant digits after each iteration.