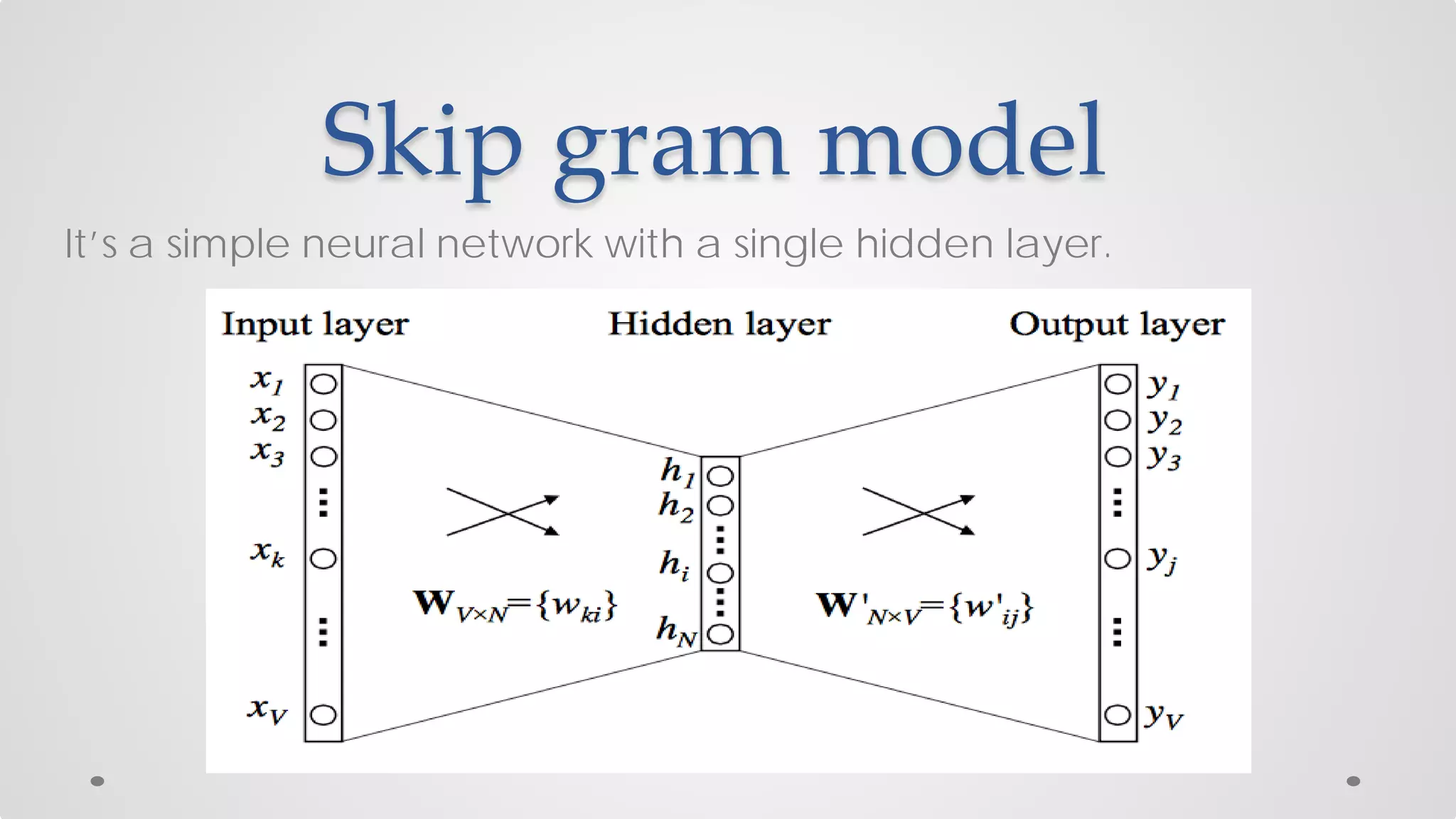
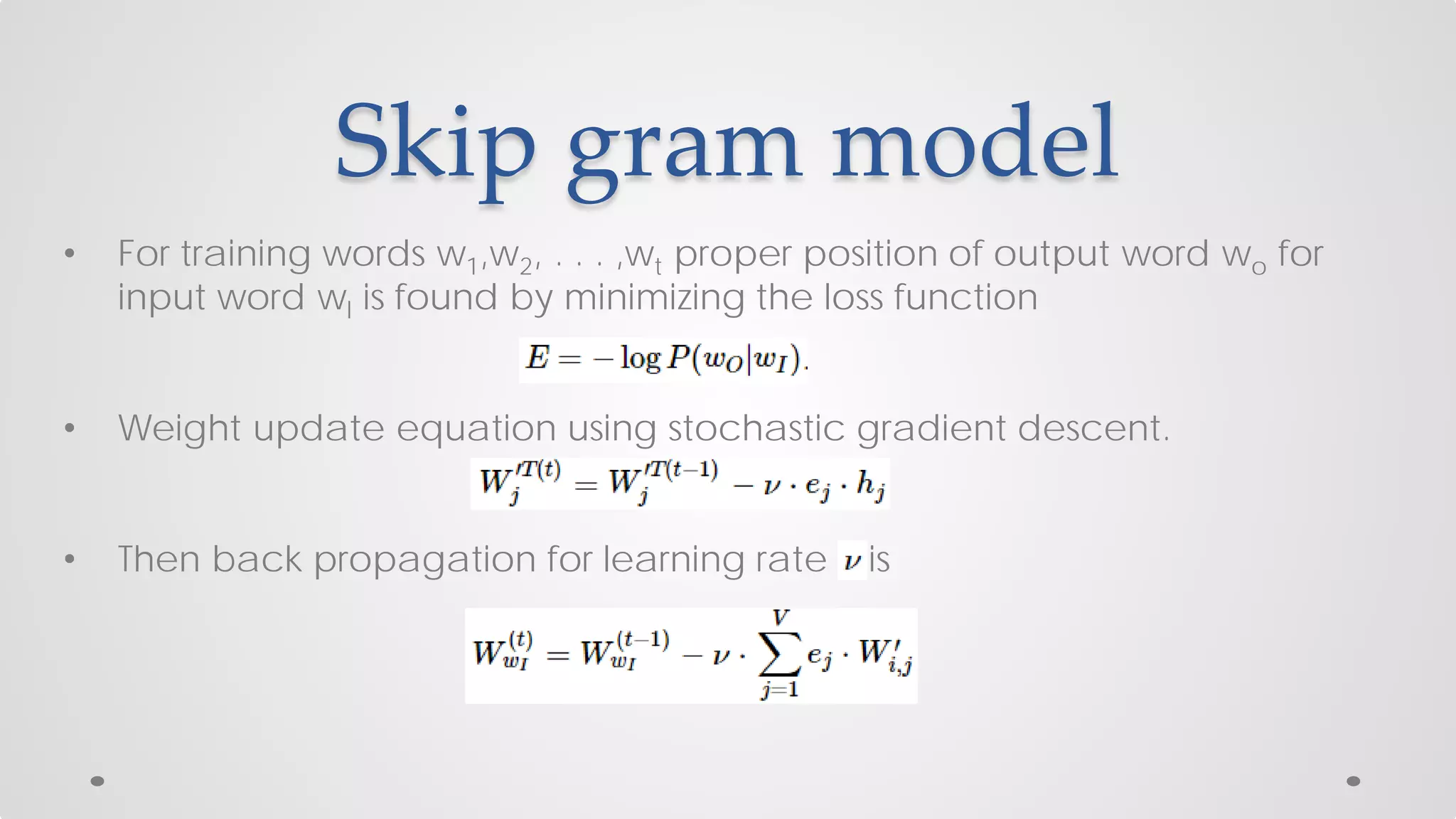
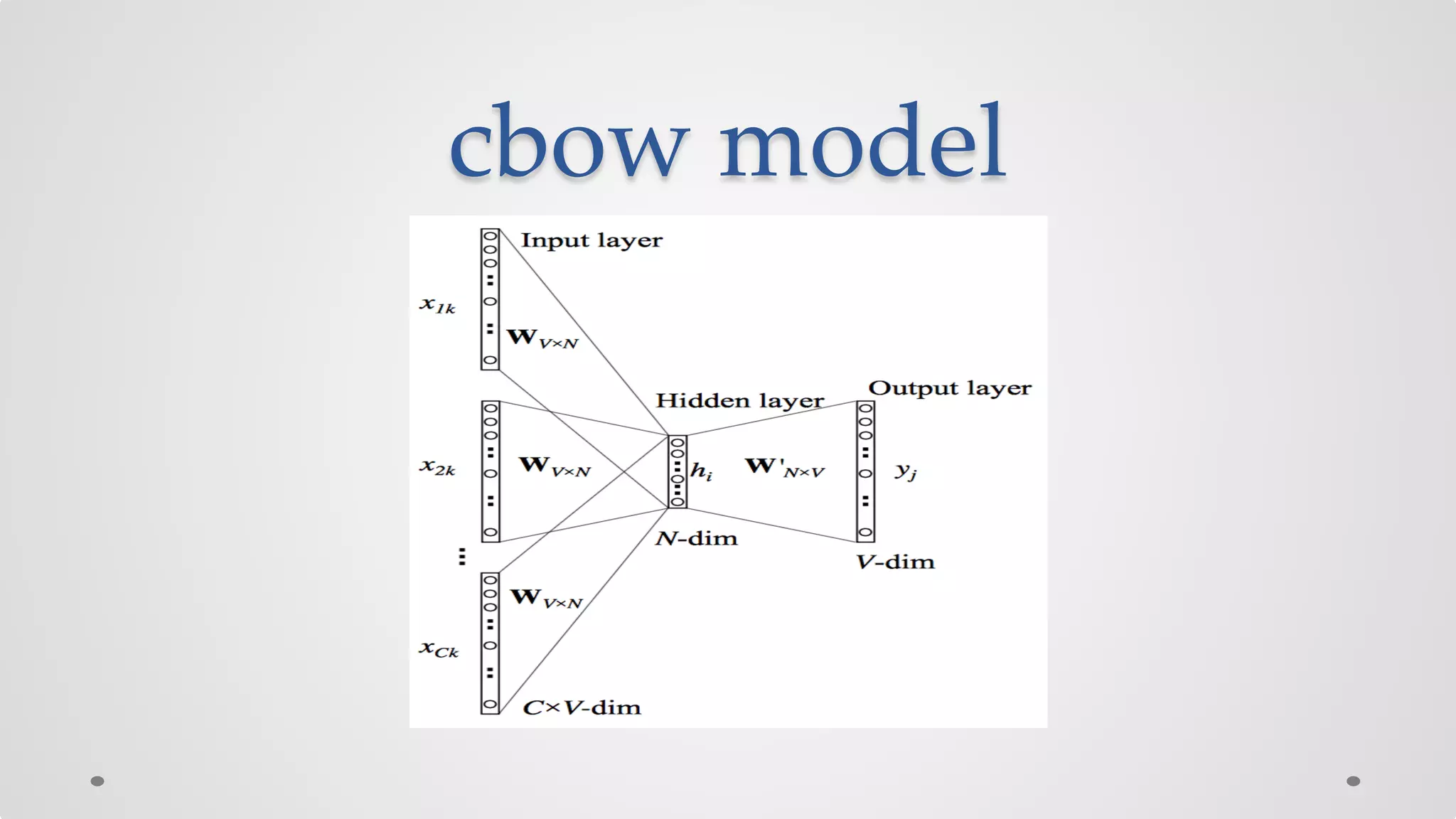
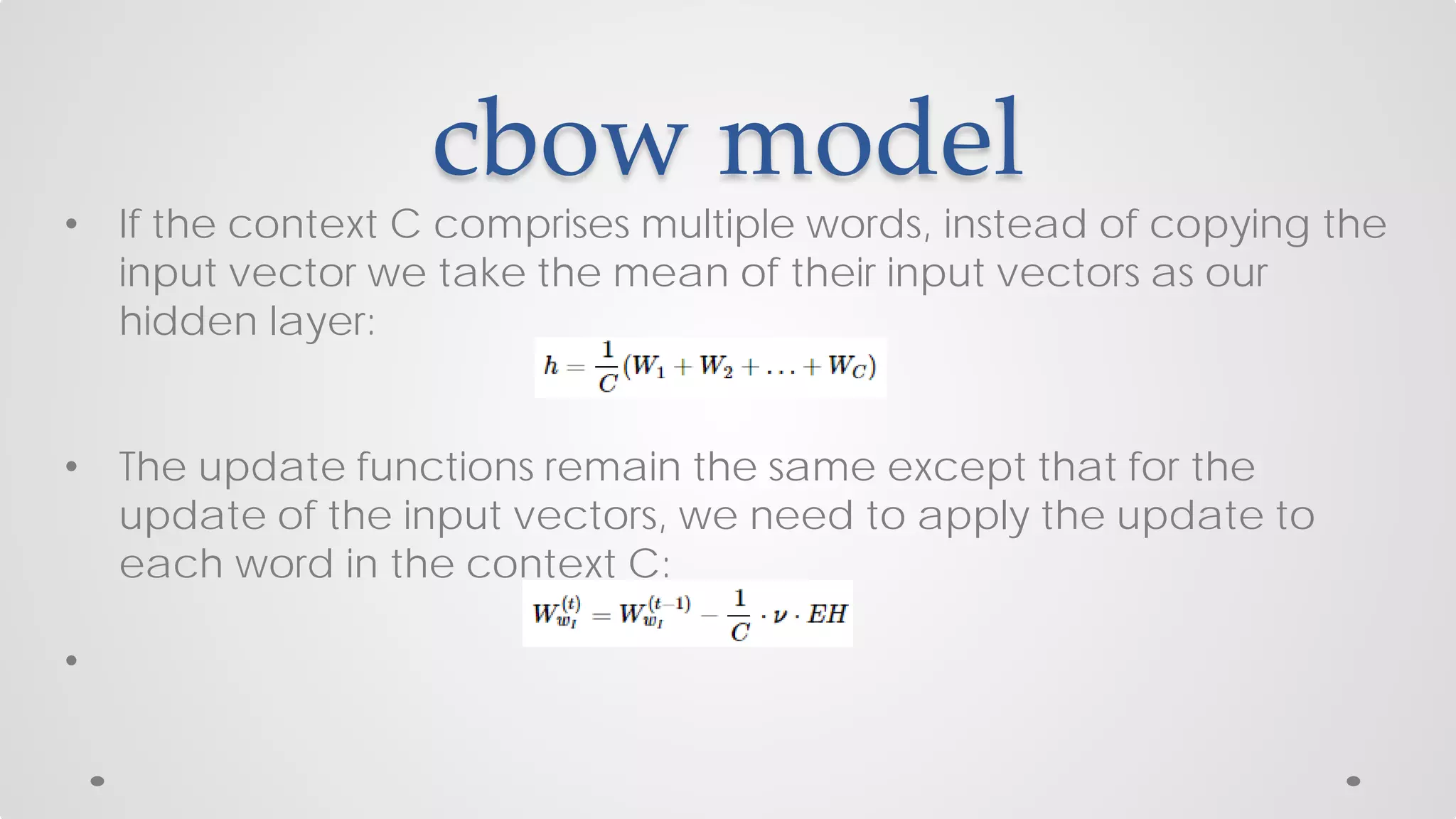
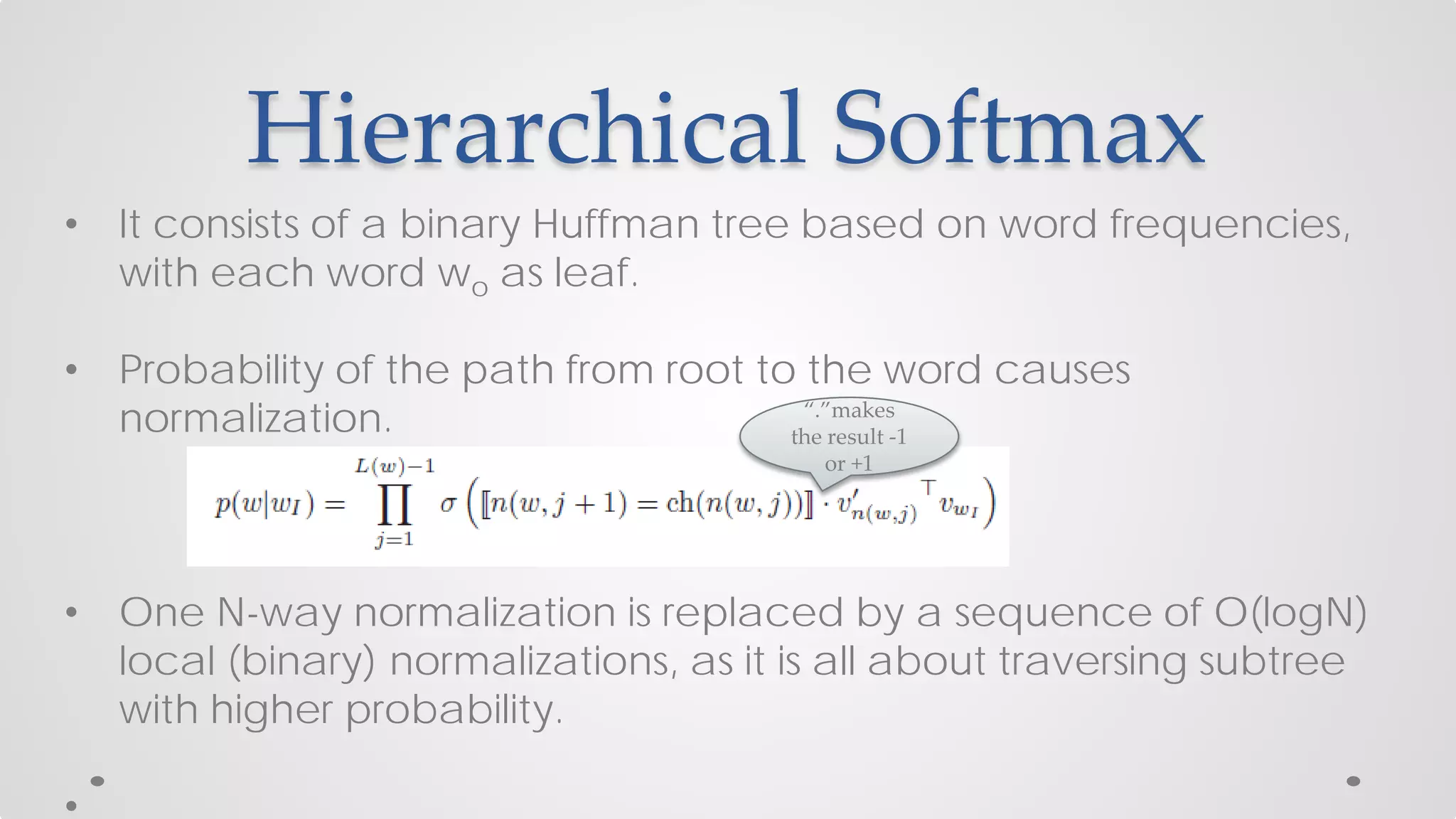
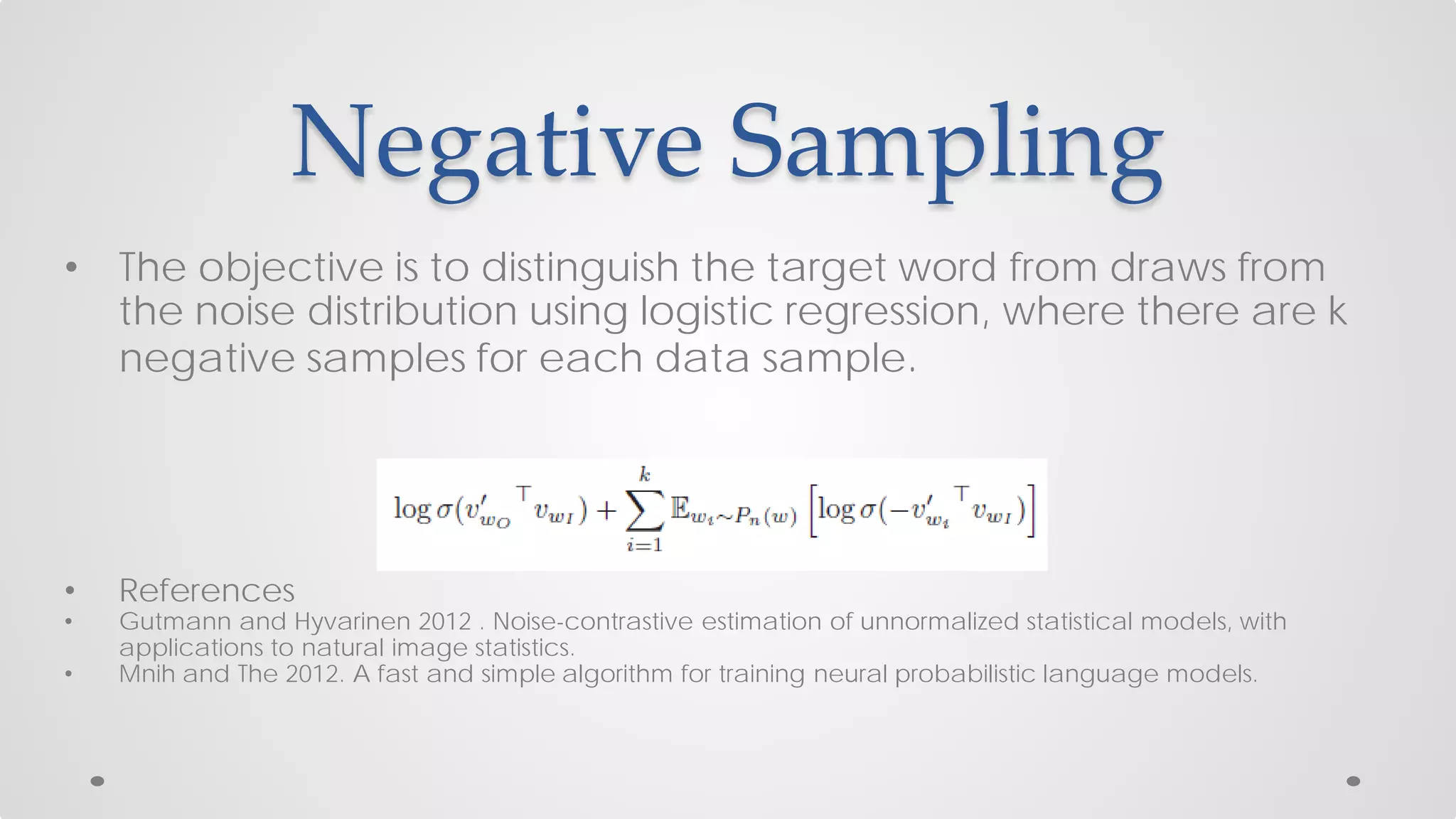
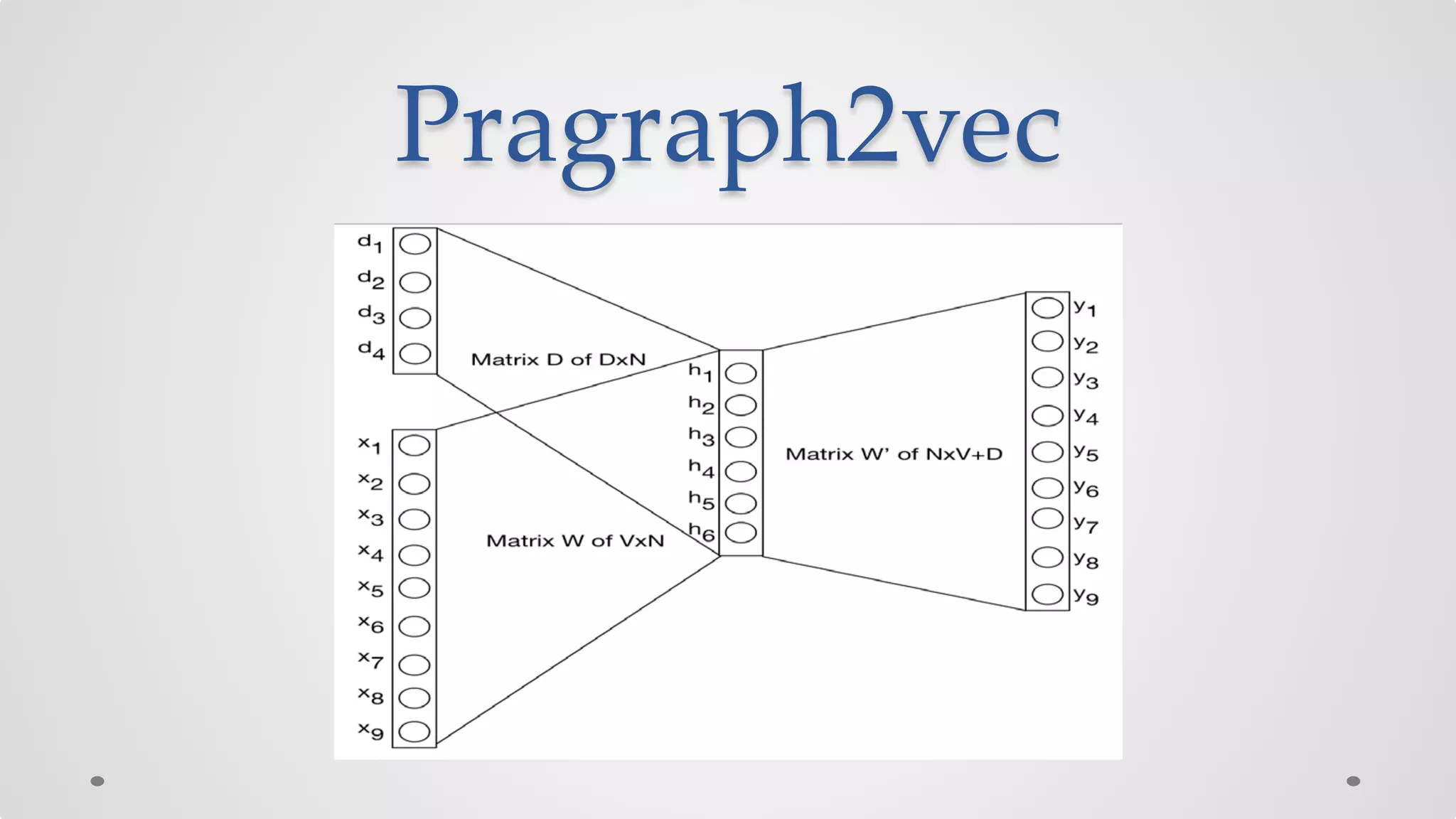
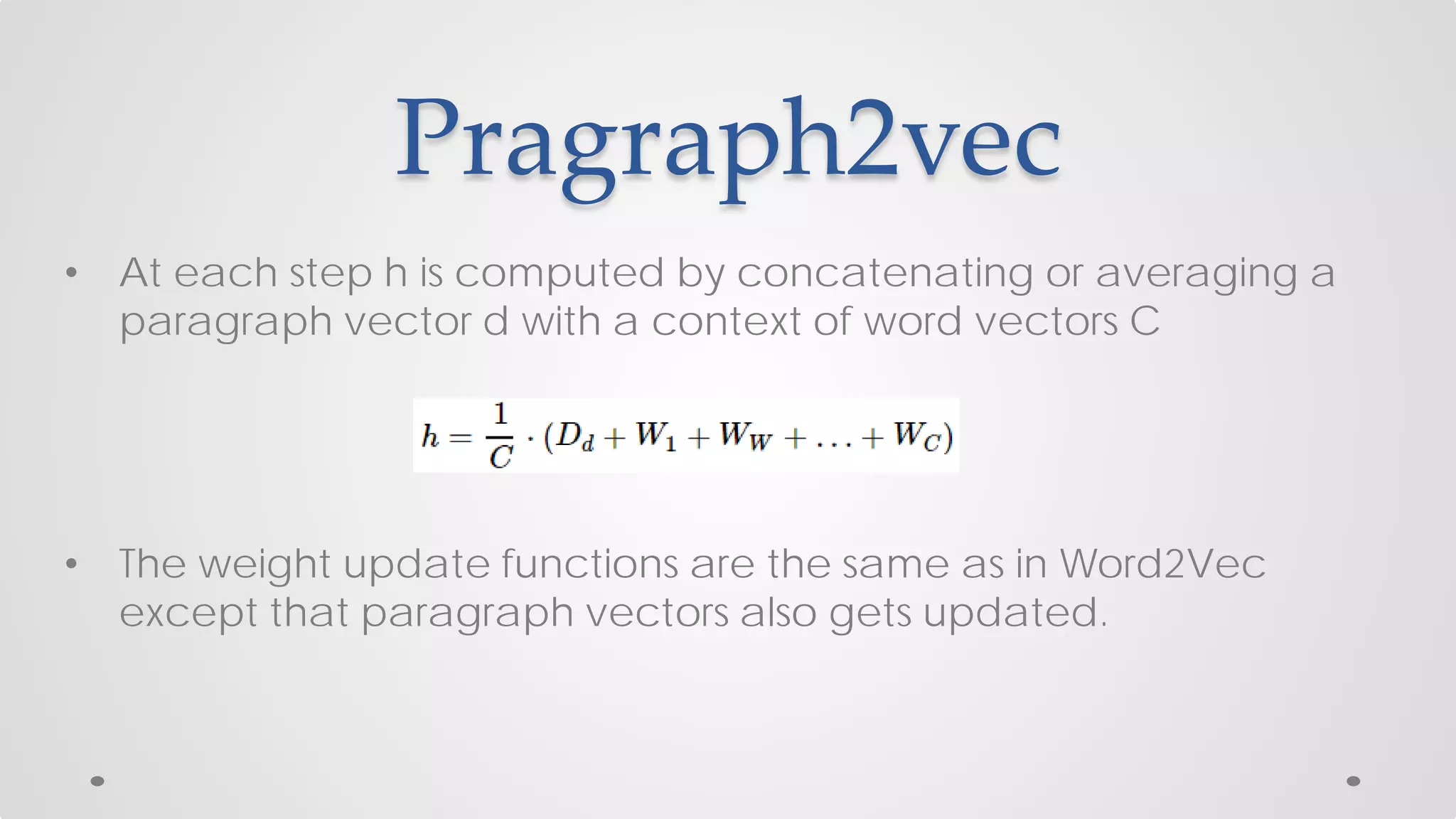
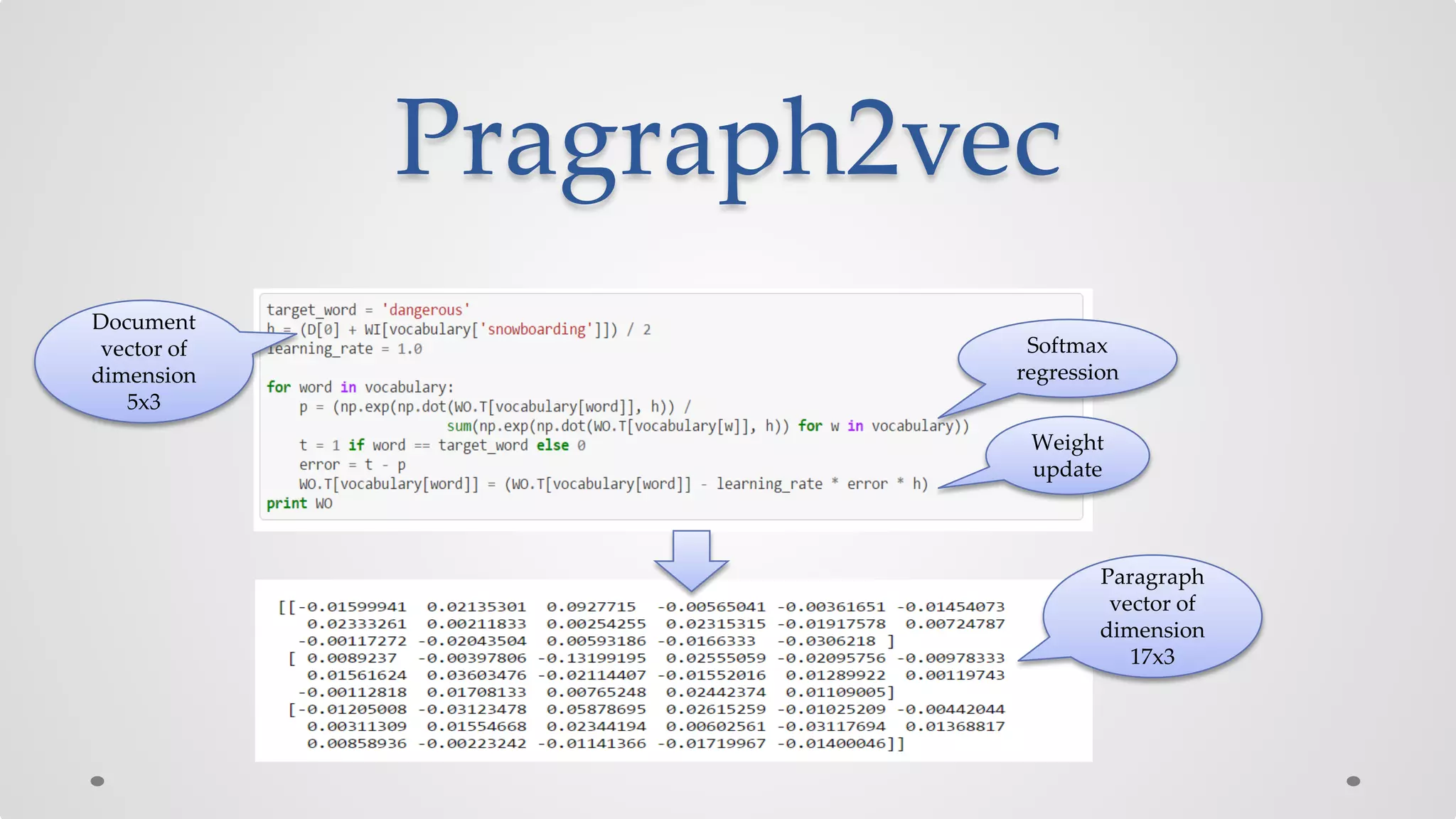
The document discusses various models and techniques in data science and text mining, particularly focusing on vector representations of words and paragraphs using models like word2vec, skip-gram, and CBOW. It explains concepts like softmax regression, hierarchical softmax, and negative sampling, as well as the paragraph vector model (paragraph2vec) for representing variable-length text. Performance comparisons highlight that while paragraph2vec offers higher accuracy in classification tasks, vector averaging is faster, and clustering provides a balance of accuracy and speed.