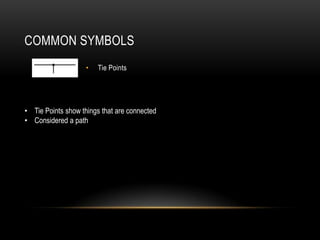
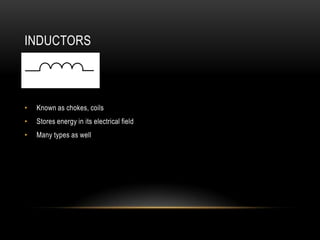
A schematic is a diagram that represents an electrical or mechanical system. It shows how a circuit functions and is used as a roadmap. Common symbols in schematics represent components like resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, batteries, switches, and logic gates. Understanding what each symbol means allows the schematic to show how current flows through the entire circuit.