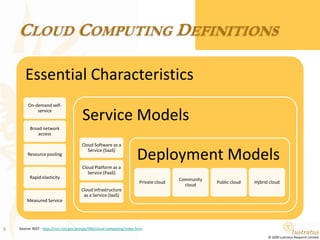
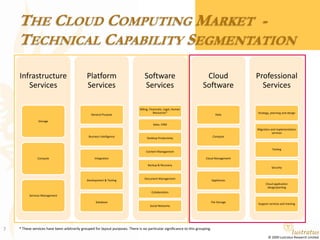
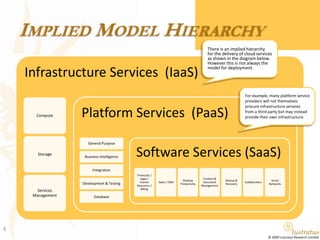
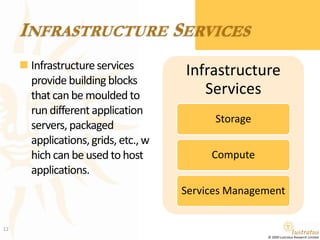
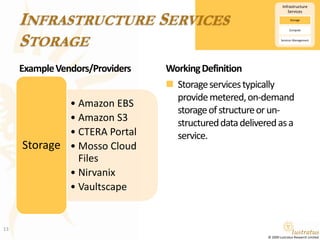
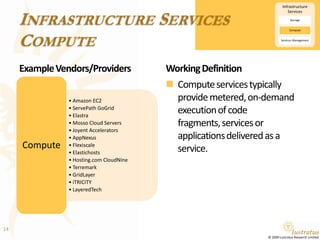
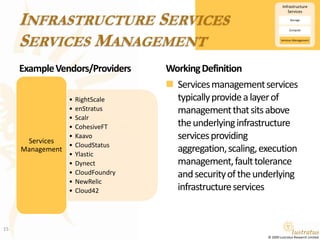
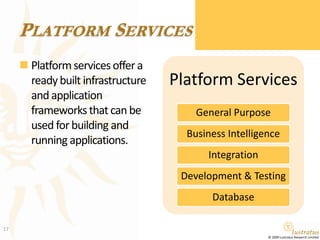
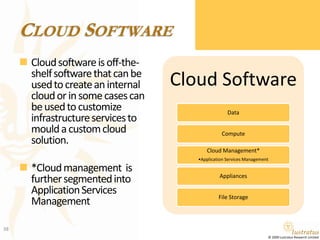
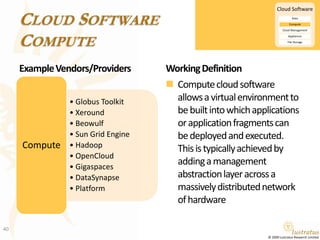
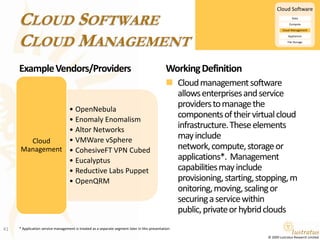
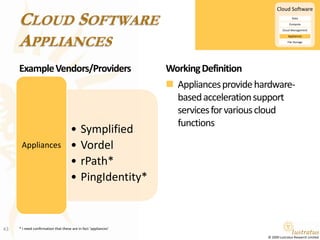
This document presents a foundational draft for competitive intelligence studies on the cloud computing market, focusing on definitions and technical capability segmentation from the perspective of vendors and service providers. It outlines various cloud service categories including infrastructure, platform, and software services, along with example vendors. The material is intended for non-commercial feedback and may evolve in future iterations.