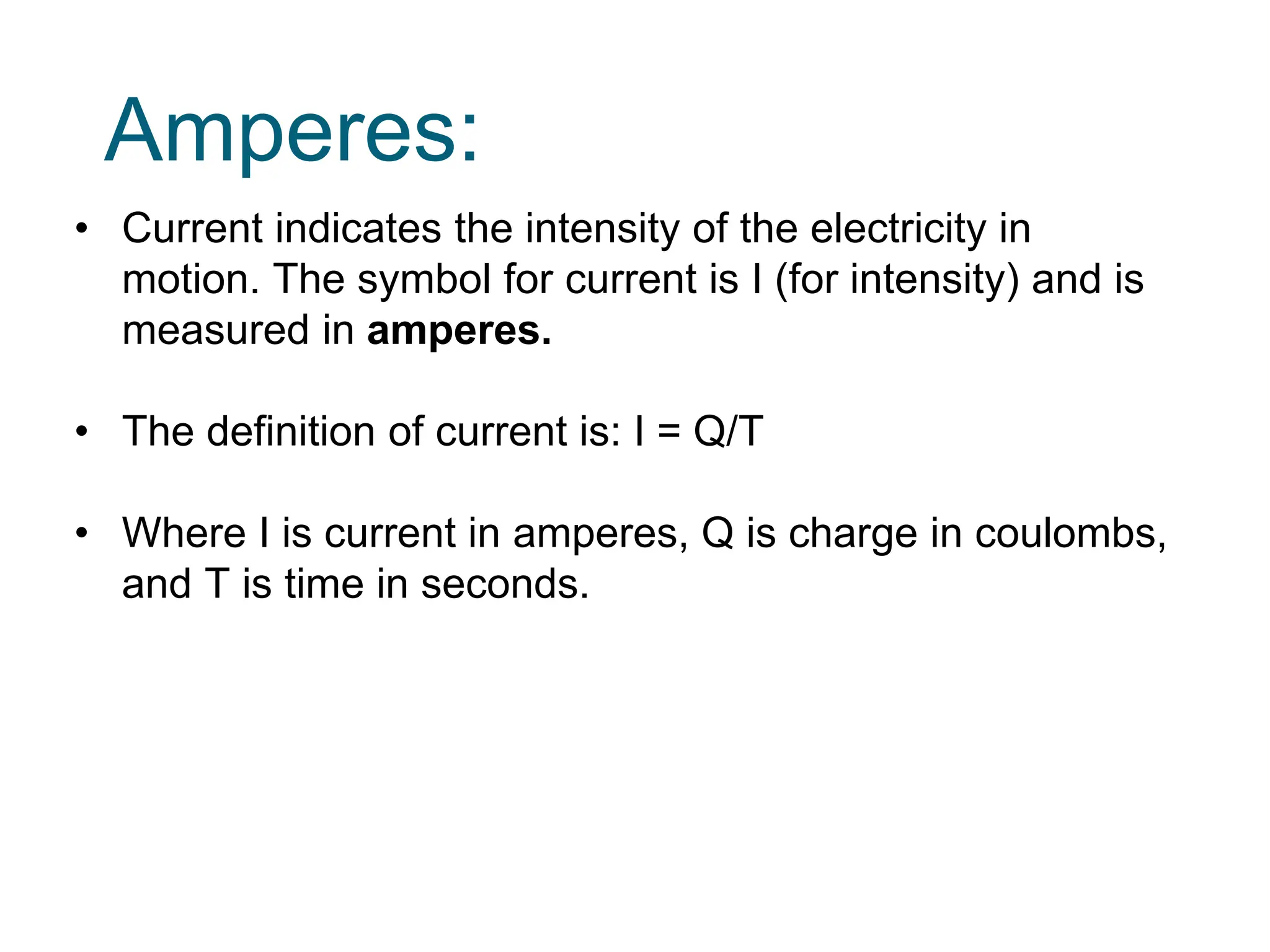
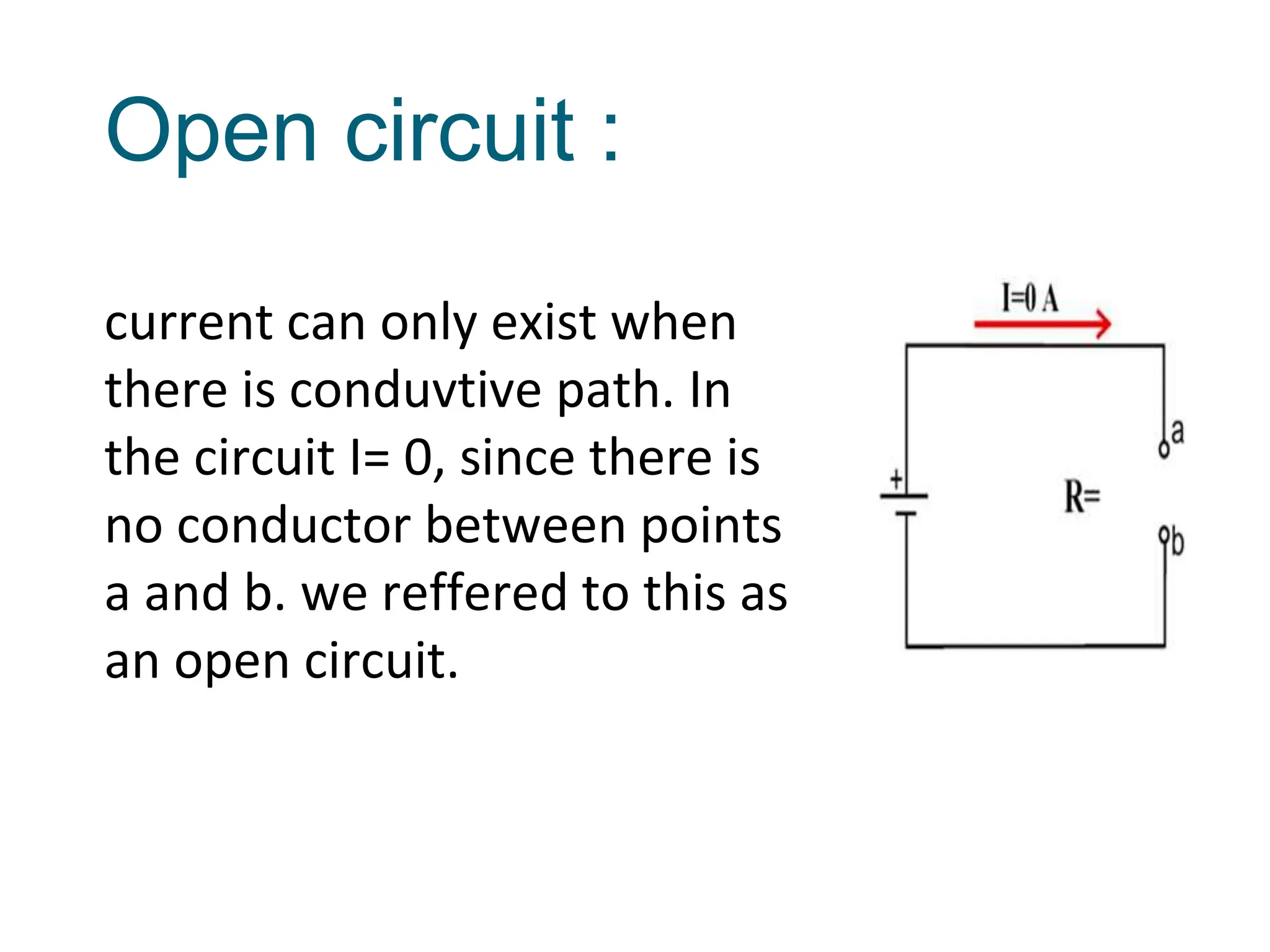
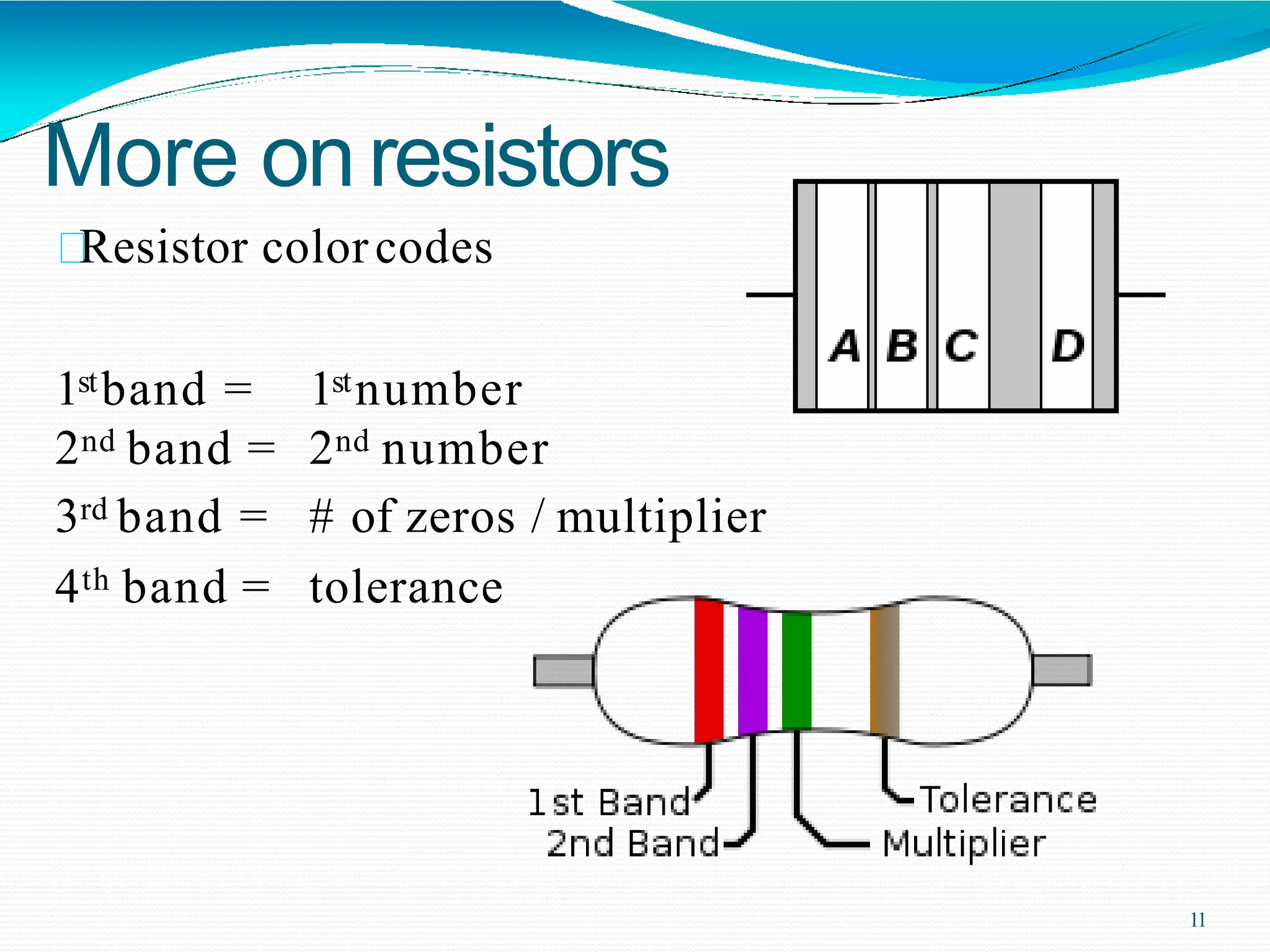
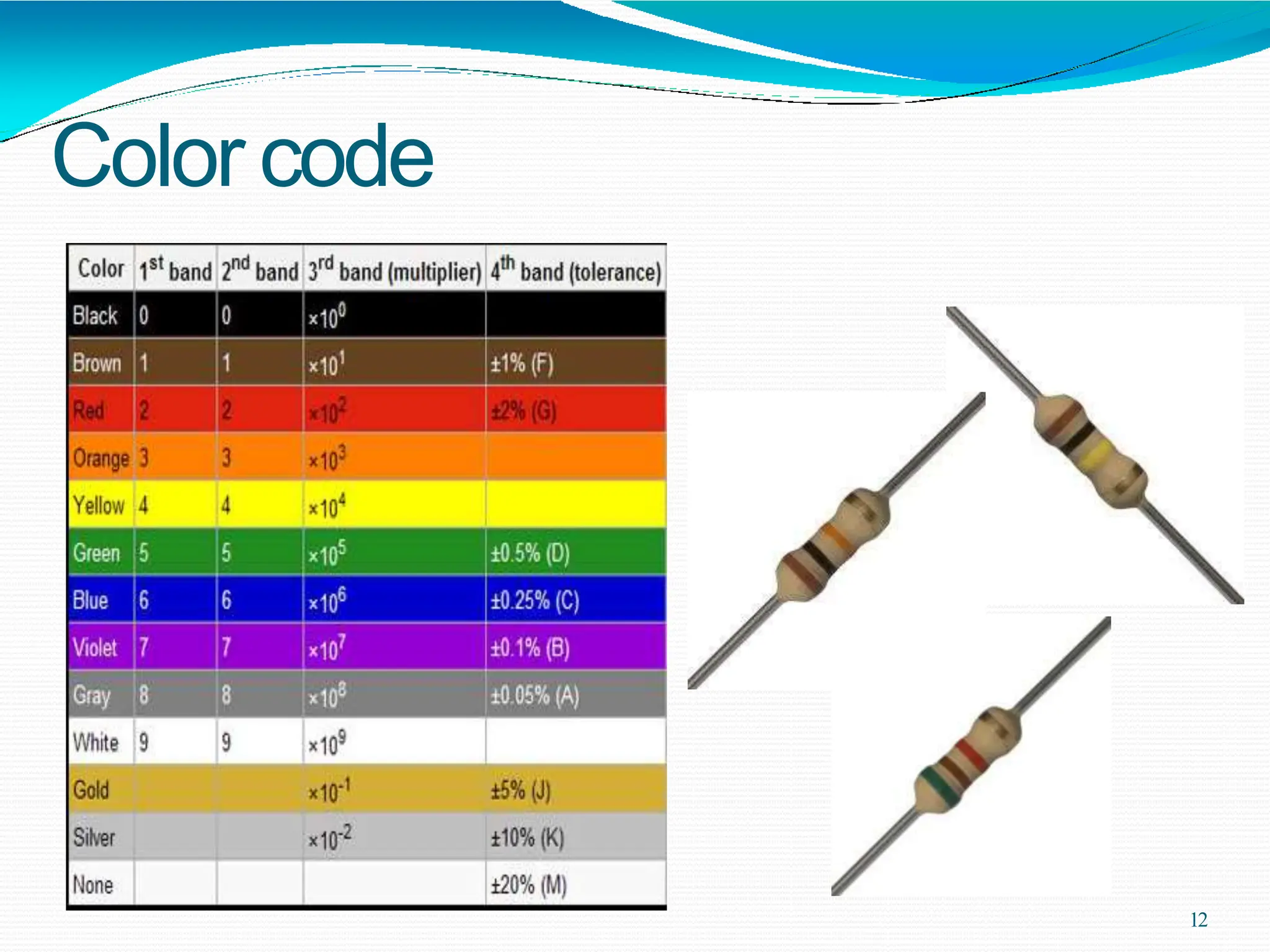
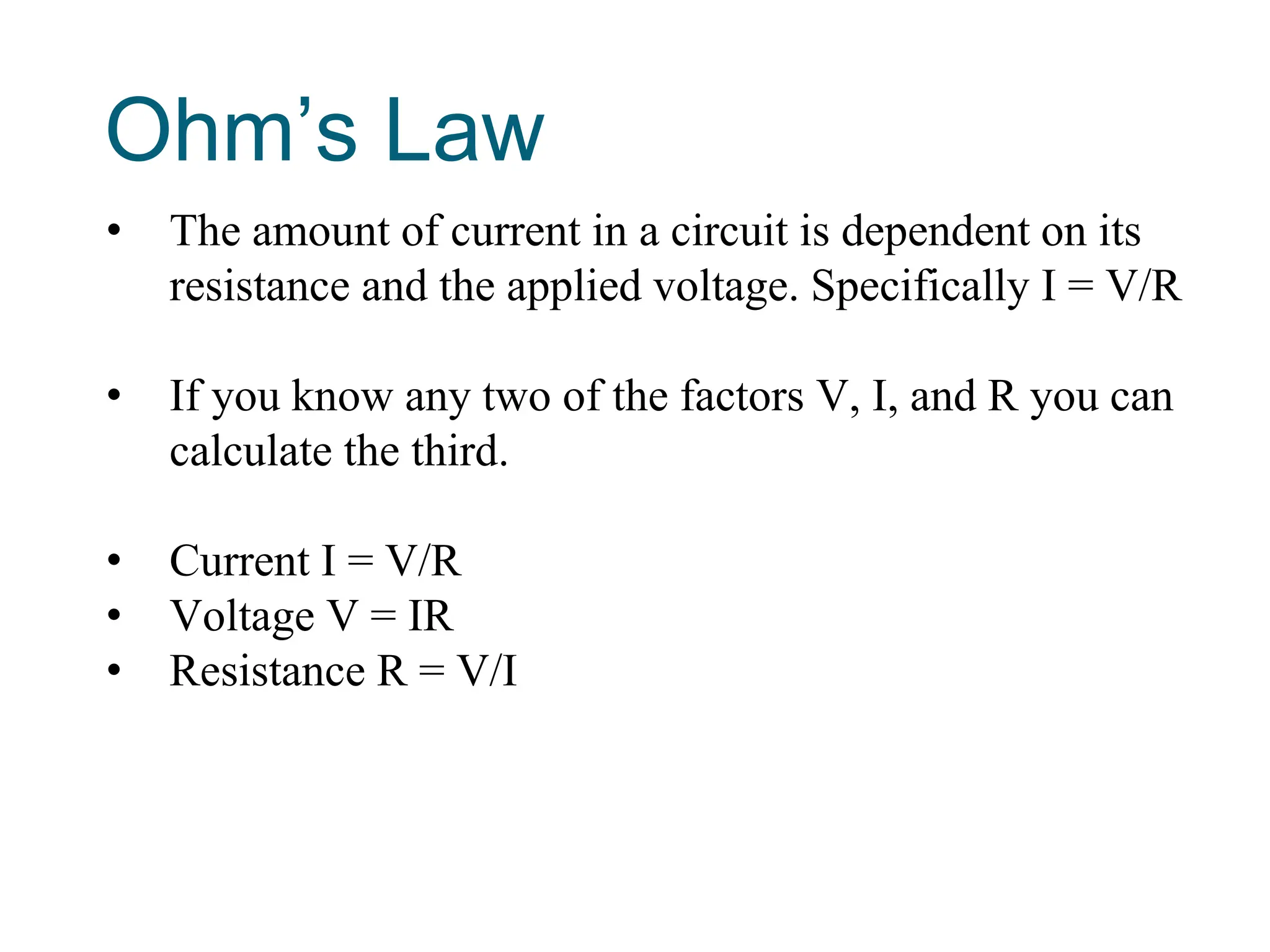
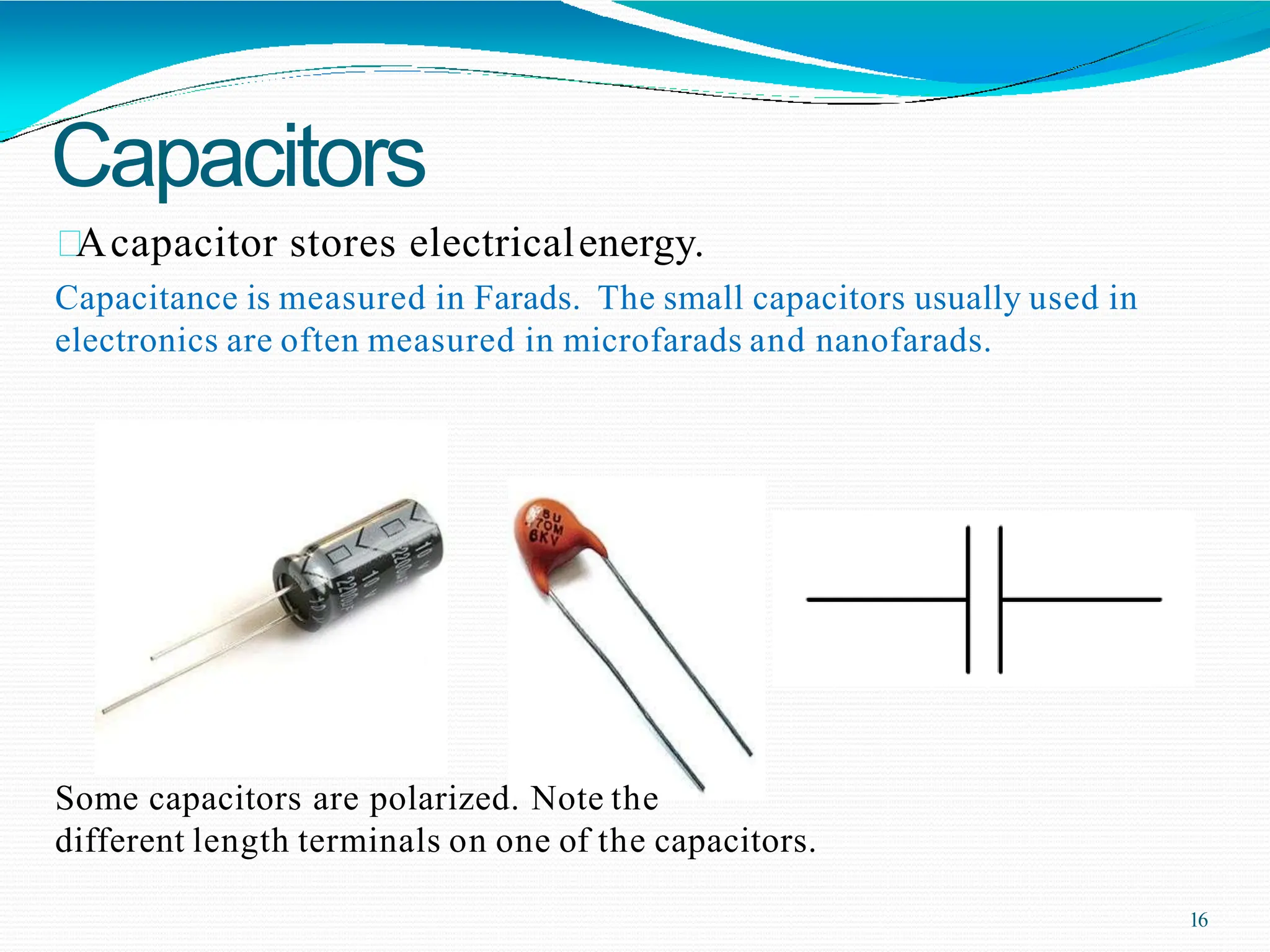
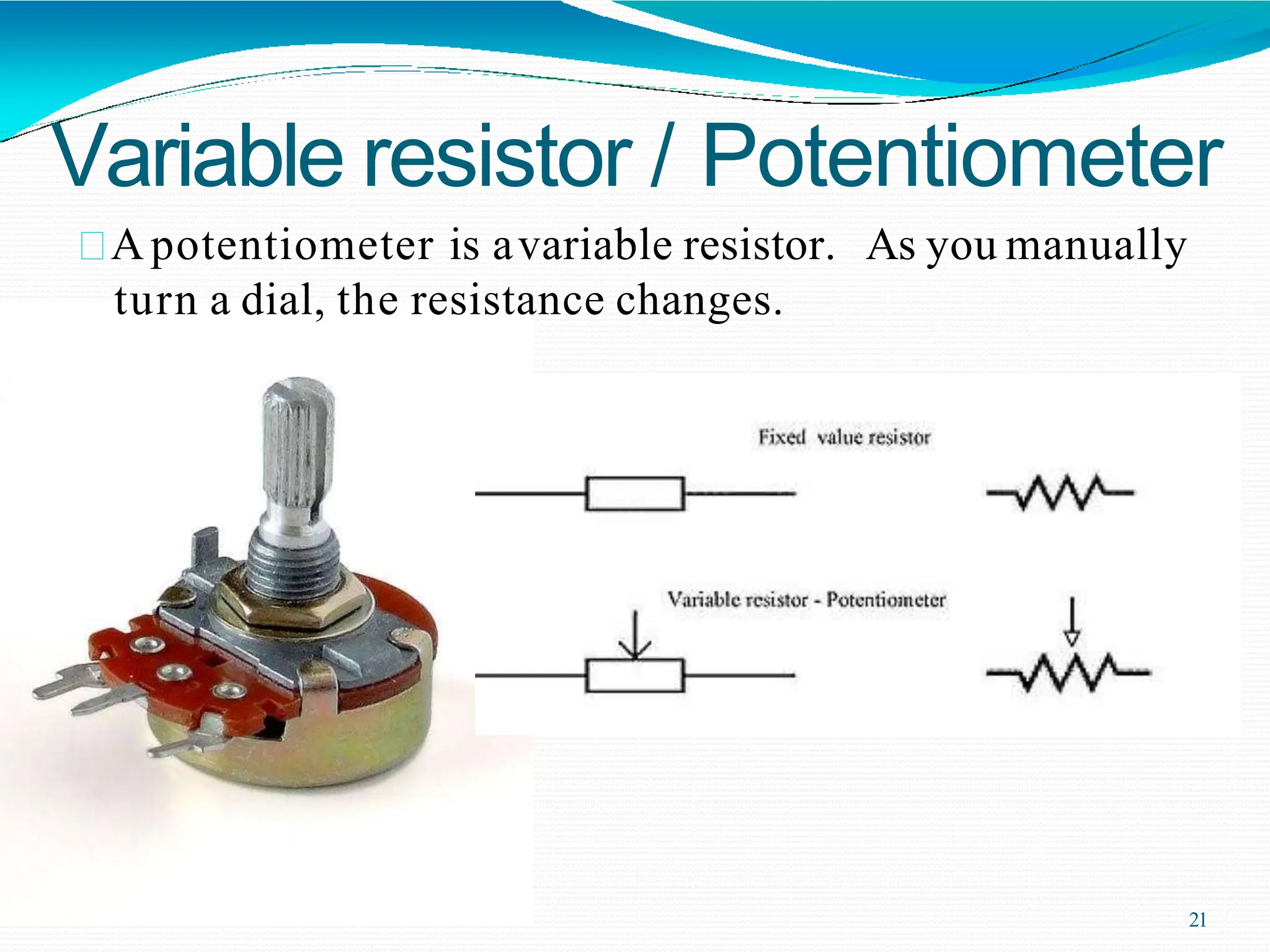
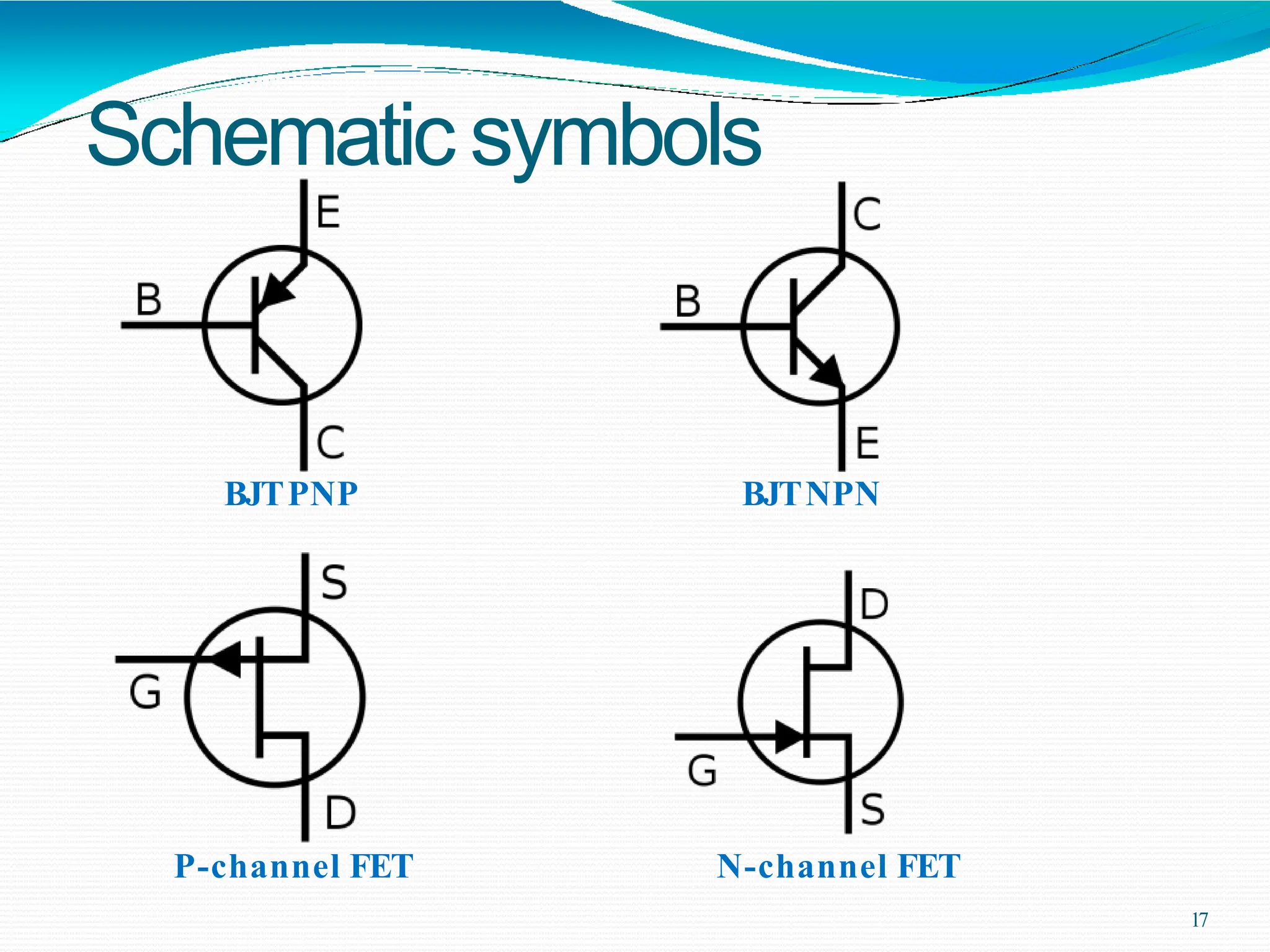
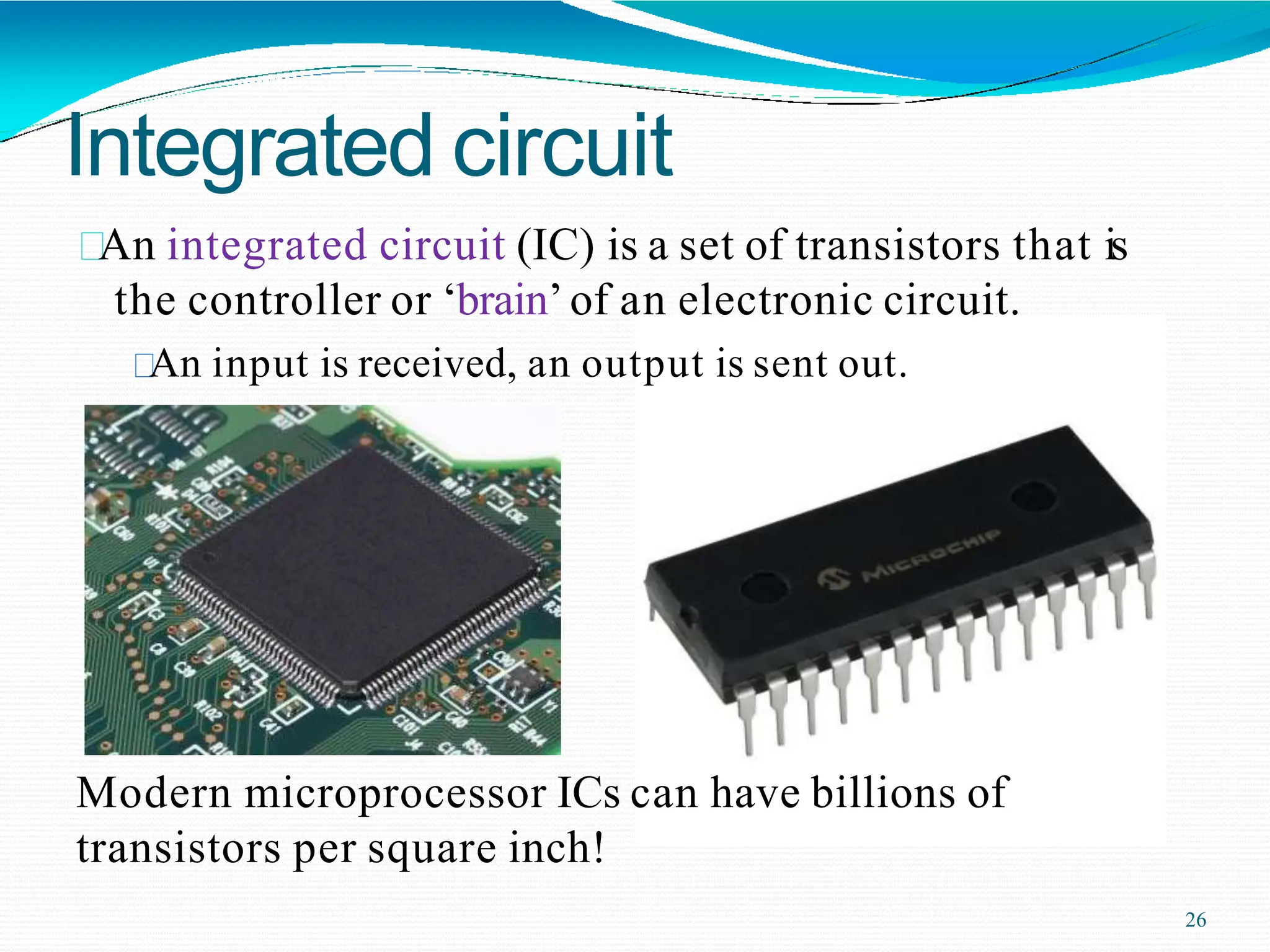
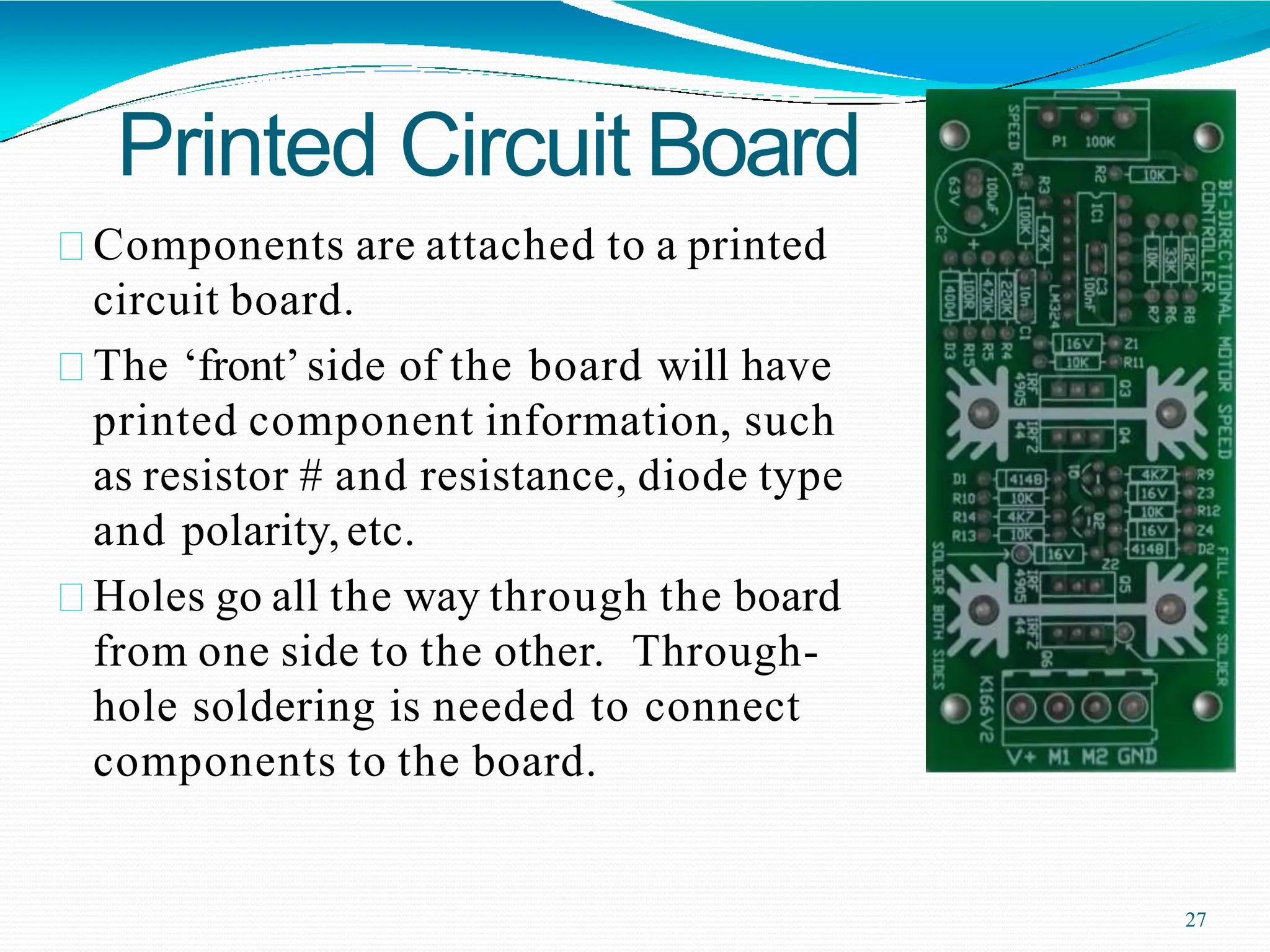
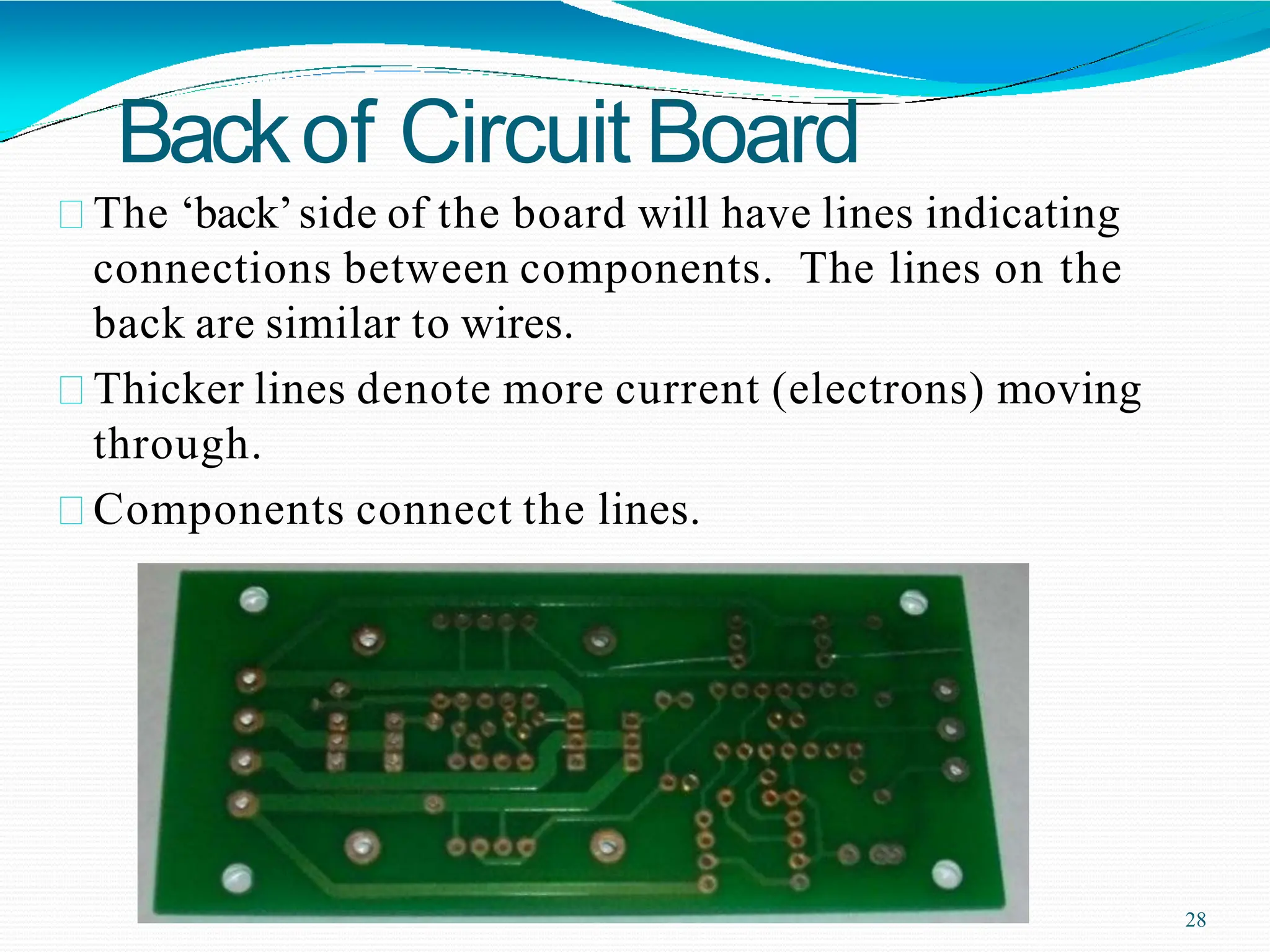
Potential difference (voltage) enables the flow of charge (current) through conductors. Voltage is measured in volts, current in amperes, and their relationship is defined by Ohm's law. Circuits allow current to flow in a closed path, and their basic components - resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors - each control current in different ways. Integrated circuits combine many transistors to process electronic signals and power. Printed circuit boards provide a platform to connect these components via conductive pathways.