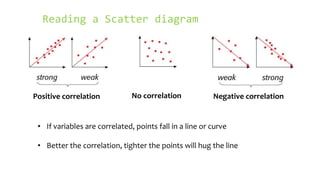
This document discusses scatter plots and their uses:
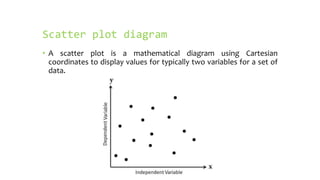
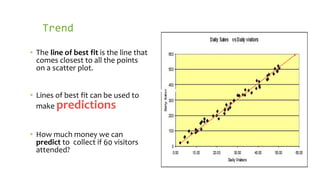
- A scatter plot displays values for two variables using Cartesian coordinates to show their relationship. It can identify if variables are correlated and the strength of their relationship.
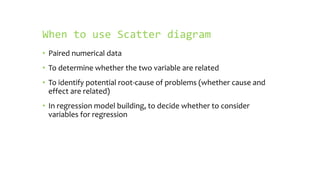
- Scatter plots are used to analyze paired numerical data and determine if variables are related or have a cause-and-effect relationship. They are also used in regression model building.
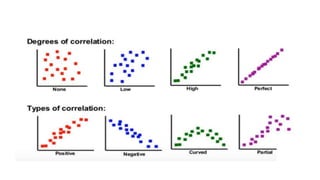
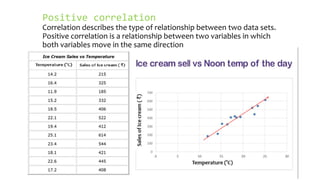
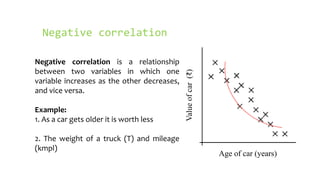
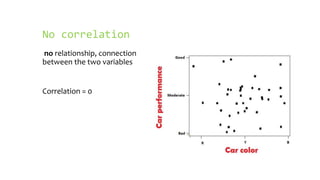
- Positive correlation means variables increase together, while negative correlation means one decreases as the other increases. No correlation means there is no relationship between the variables.