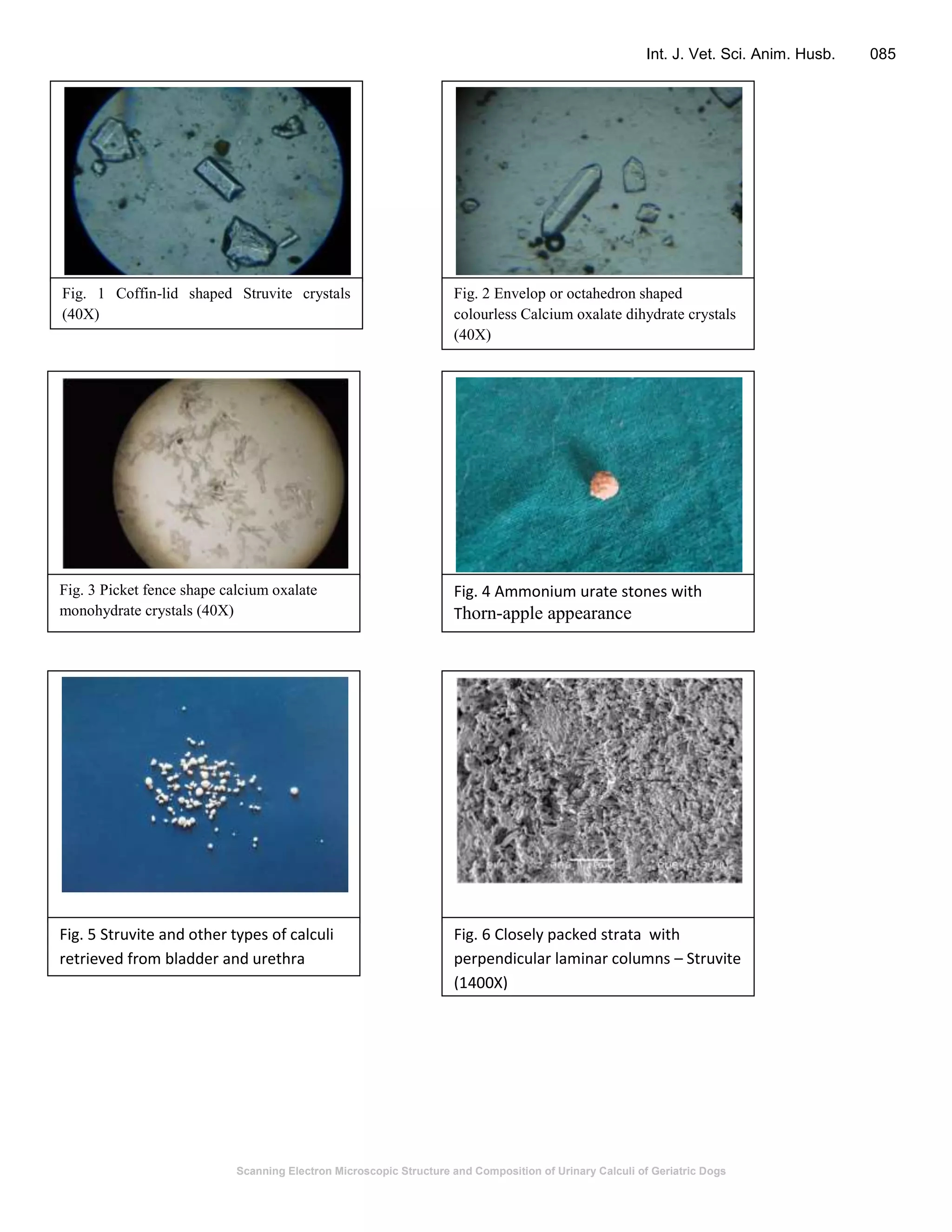
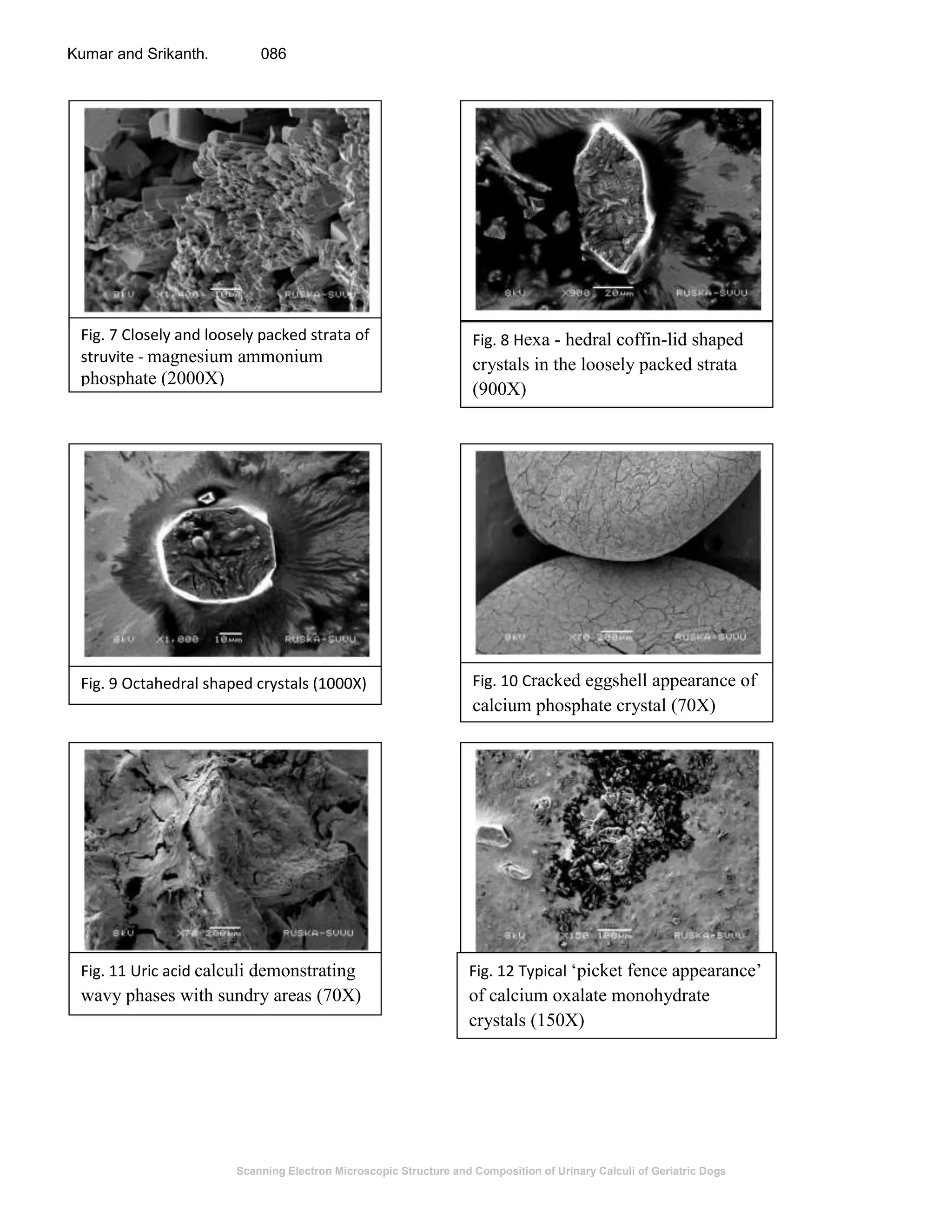
This document summarizes a study on the scanning electron microscopic structure and chemical composition of urinary calculi (stones) found in geriatric dogs. Microscopic examination of urine samples revealed increased numbers of blood cells, epithelial cells, pus cells, casts, bacteria and crystals of various shapes, predominantly struvite, calcium oxalate dihydrate and monohydrate, and ammonium urate. Scanning electron microscopy showed perpendicular columnar strata of struvite crystals and wavy phases of uric acid. Chemical analysis identified calcium phosphate, calcium oxalate and urea stones. The study characterized the microscopic and electron microscopic appearance of crystals and chemical composition of urinary calculi in geriatric dogs.