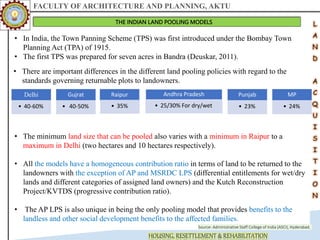
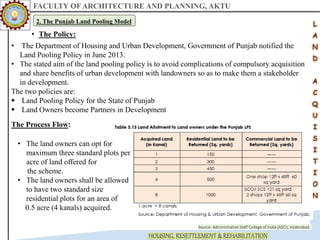
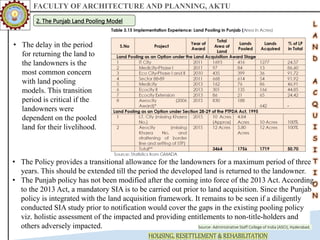
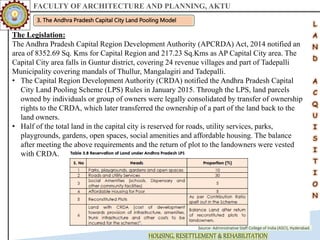
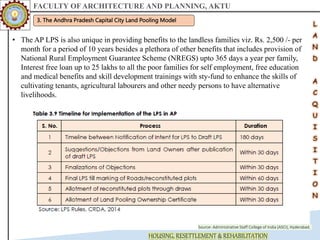
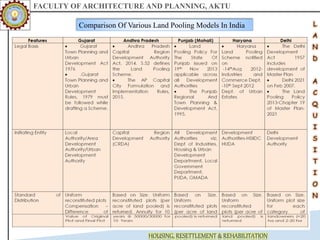
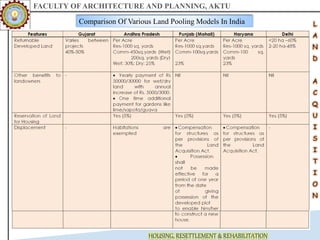
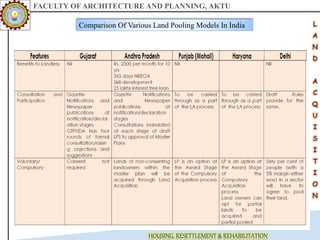
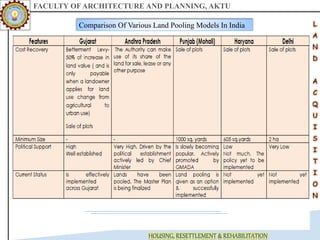
The document discusses various land acquisition models and practices in India, focusing on land pooling, which allows landowners to collectively hand over their land for infrastructure development while retaining rights to a portion post-development. It examines the principles of compulsory land acquisition, emphasizes the benefits and social implications of land pooling, and compares different models used in states like Gujarat, Punjab, and Andhra Pradesh. The advantages include reduced government costs and increased land use efficiency, although challenges such as delays and compensation issues are noted.