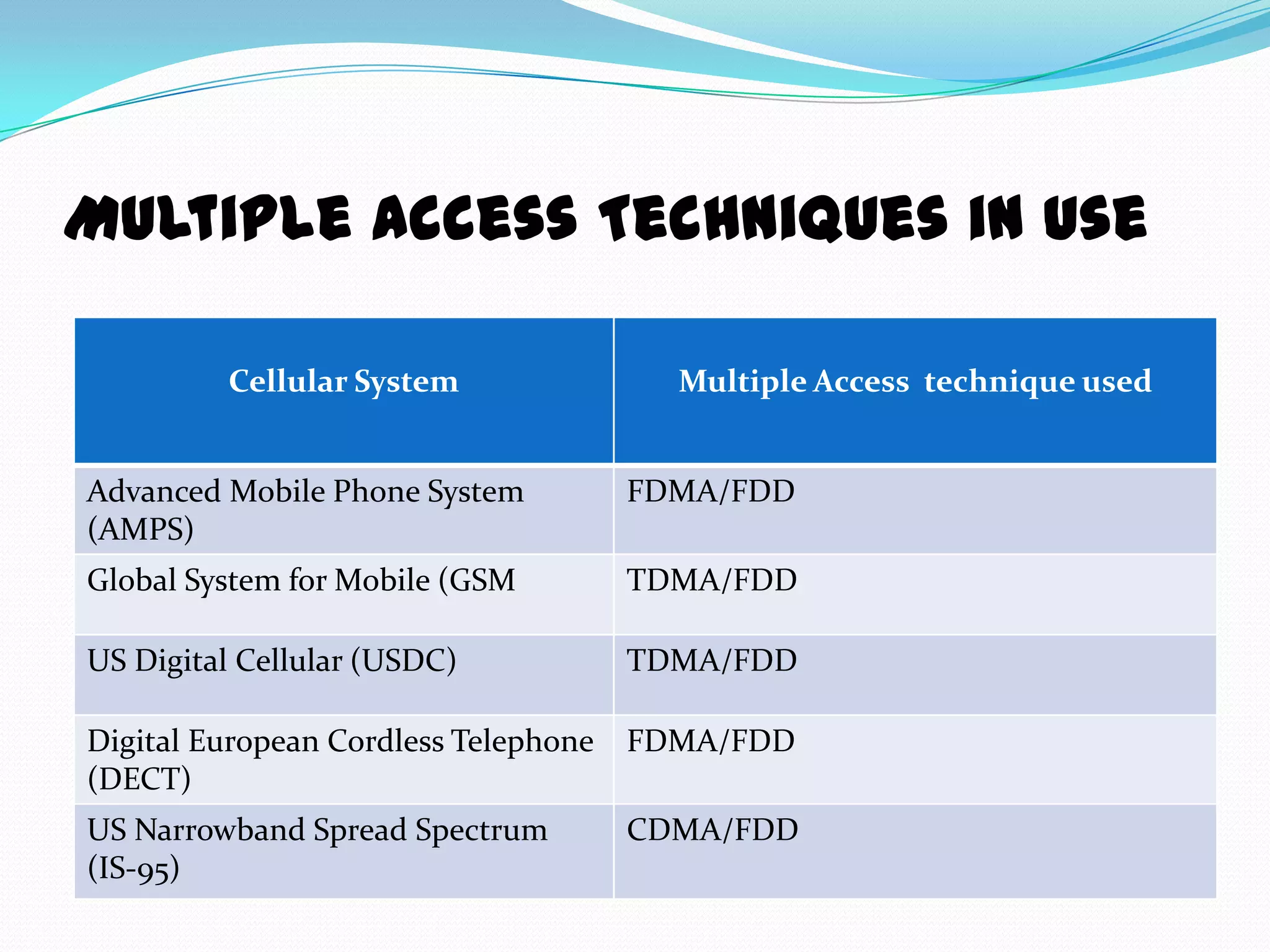
This document discusses multiple access techniques for wireless communication. It describes frequency division duplexing (FDD) and time division duplexing (TDD) for sharing radio spectrum. The main multiple access techniques are described as frequency division multiple access (FDMA), time division multiple access (TDMA), and code division multiple access (CDMA). FDMA allocates different frequency bands to each user, TDMA divides the available time into time slots and allocates one slot per user, and CDMA uses pseudo-random codes to distinguish users transmitting simultaneously on the same frequency. Common cellular systems like AMPS, GSM, and IS-95 are cited as examples.