This document discusses various classes of antidepressant drugs, including their mechanisms of action, structures, and metabolic pathways. It begins by defining depression and outlining the current hypotheses for its causes. The main classes of antidepressants covered are monoamine reuptake inhibitors, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and receptor antagonists. Specific drug examples like tricyclic antidepressants, SSRIs, SNRIs, and MAOIs are discussed in detail regarding their structures, pharmacological properties, and metabolic pathways. Adverse effects of tricyclic antidepressants are also reviewed.




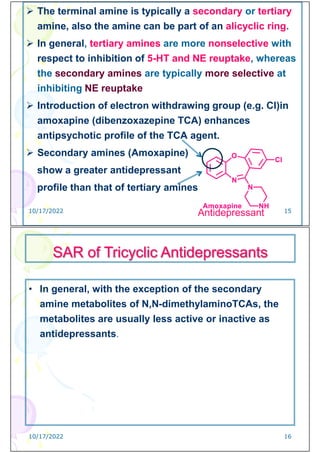
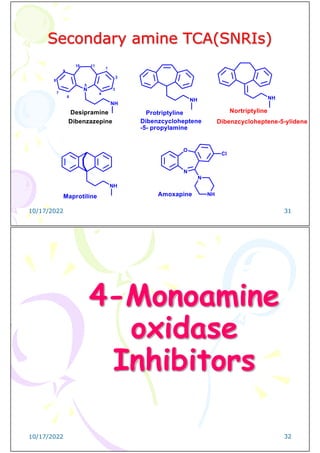
![SAR of Tricyclic Antidepressants
TCA have in common a tricyclic ring structure
consisting of a central six membered or more
commonly a seven –membered ring flanked by two
benzene rings held in a skewed arrangement. This
tricyclic bulky structure lacks coplanarity
N
N
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11
R
5-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine HCl
Imipramine R=CH3
Desipramine R=H
10/17/2022 9
Ring Nitrogen atom is not required for
antidepressant activity, replacement with sp3 or sp2
carbon enhances antidepressant activity.
The side chain must be three carbon atoms ,either
saturated (propyl) or unsaturated (propylidine)
NH
Protriptyline
SAR of Tricyclic Antidepressants
N
N
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11
R
Imipramine
Amitriptyline
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4th-year-medicinal-chemistry-3rd-lecture1-240226191703-68b2eee3/85/4th-Year-Medicinal-Chemistry-3rd-Lecture-1-pdf-5-320.jpg)





![2-Selective Seretonin Reuptake Inhibitors
(SSRIs)
• Fluoxetine (Prozac)
N-methyl-3-phenyl-3-
[4-(trifluoromethyl) phenoxy]-
propan-1-amine
Monosubstitution in 4 position of phenoxy gp with
electron withdrawing gp (CF3)results in selective
inhibition of 5HT
Disubstitution 2,3 or 3,4 results in loss of SERT
selectivity
Metabolism : N-demethyl compound(Nor fluoxetine)is
as potent as the parent compound and more
selective SERT inhibitor
O
HN
CF3
10/17/2022 29
SSRIs(Fluoxetine cont.)
• Both enantiomer(R,S) display
similar affinities for SERT .
• The S- enantiomer is 100 times more selective
for SERT rather than NET
• If the para substituent is
moved to the ortho
position and substituted
by methoxy group,
a SNERI is obtained as in Nisoxetine.
• Fkuoxetine is Used in ttt of bulimia nervosa nisoxetine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4th-year-medicinal-chemistry-3rd-lecture1-240226191703-68b2eee3/85/4th-Year-Medicinal-Chemistry-3rd-Lecture-1-pdf-15-320.jpg)


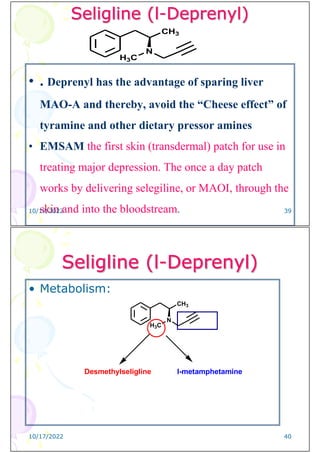
![Third
generation
MAOI
(Reversible,
Preferential)
10/17/2022 41
Moclobemide
•
• 4-Fluoro-N-[2-(N-morpholino)ethyl]benzamide
• Moclobamide is a reversible MAO inhibitor ,thereby
increasing conc. of 5-HT, NE and other
Catecholamines in the synaptic cleft and in the
storage sites
N
H
N O
F
O
10/17/2022 42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4th-year-medicinal-chemistry-3rd-lecture1-240226191703-68b2eee3/85/4th-Year-Medicinal-Chemistry-3rd-Lecture-1-pdf-21-320.jpg)
