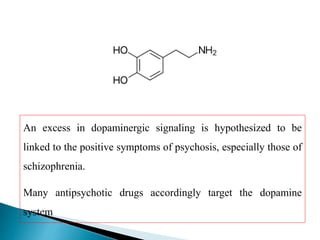
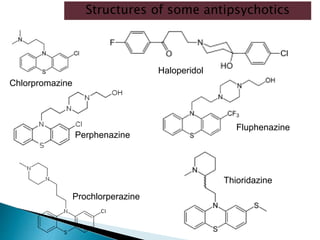
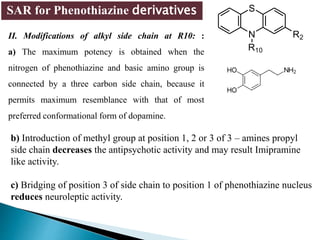
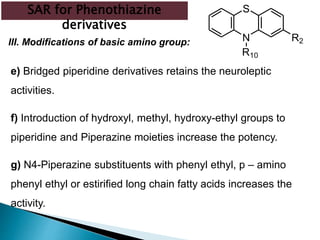
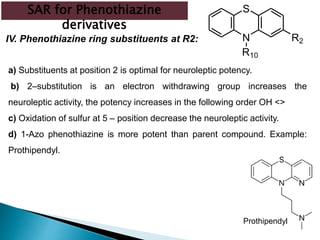
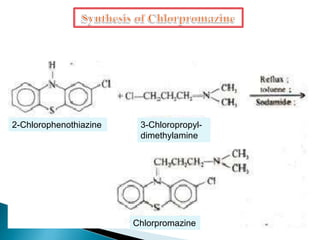
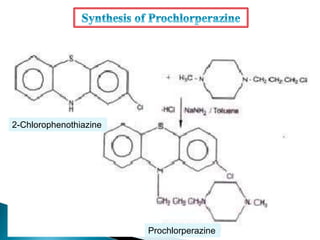
Tranquilizers are drugs that calm anxiety and help sleep by acting on the central nervous system. They are often called depressants because they suppress CNS activity and slow the body down. Tranquilizers are used to treat mental illnesses involving psychoses, which are behavioral disorders characterized by disturbances like hallucinations and delusions. Minor tranquilizers treat anxiety while major tranquilizers treat psychoses like schizophrenia. An excess of dopamine signaling is linked to psychotic symptoms, so many antipsychotic drugs target the dopamine system. First and second generation antipsychotics differ in their mechanisms of action and side effect profiles.