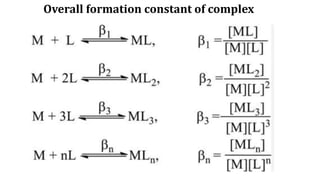
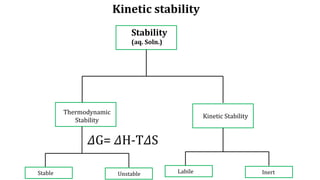
The document discusses the naphelauxetic effect, which is a decrease in the Racah parameter value when a complex is formed. It then discusses various factors that affect the stability of complexes, including thermodynamic stability measured by formation constants, the nature of the central metal ion and ligands, the chelate effect, and kinetic stability. Thermodynamic stability depends on free energy change and favors complexes with higher formation constants, while kinetic stability refers to how rapidly a complex breaks down in solution.