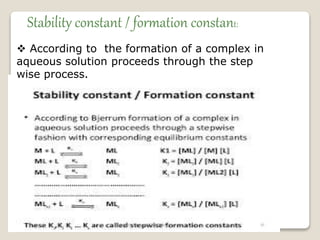
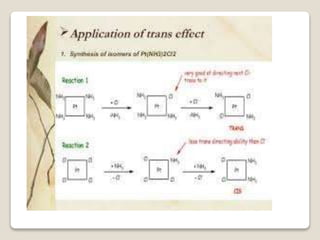
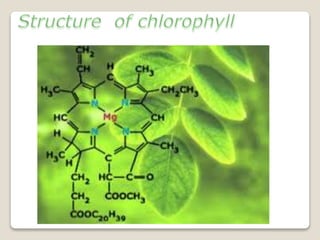
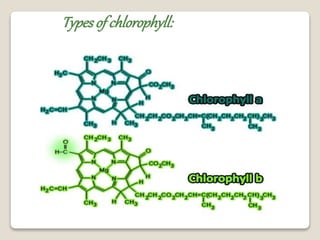
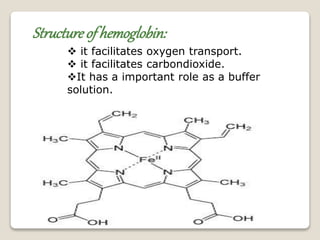
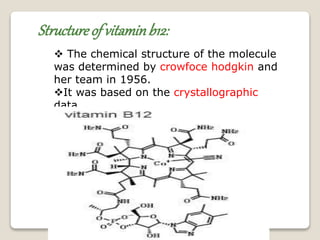
This document discusses coordination chemistry, including the concepts of labile and inert complexes, factors that affect stability and lability, and theories of the trans effect. It also briefly outlines the structures of chlorophyll, hemoglobin, and vitamin B12. Labile complexes rapidly exchange ligands while inert complexes exchange ligands slowly. Stability is influenced by factors like the metal ion size and charge, as well as ligand properties. The polarization and pi-bonding theories explain the trans effect, in which ligands trans to certain others make that site more reactive.