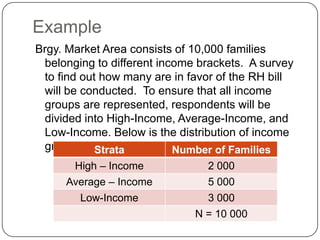
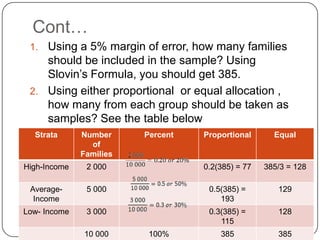
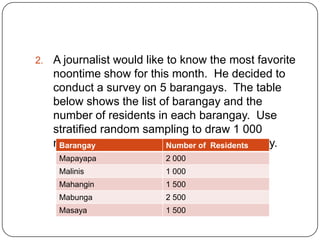
Here are the steps to solve this problem using stratified random sampling:
1. Divide the population into strata based on the barangays.
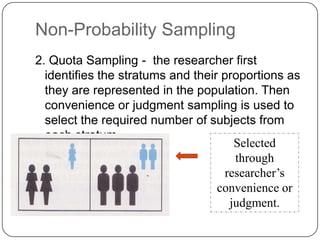
2. Calculate the sample size for each stratum proportionately based on the total sample size (1000 residents) and population size of each stratum.
3. Randomly select the calculated sample size from each stratum.
Barangay Population Proportion of sample Sample size
Mapayapa 2,000 0.2 200
Malinis 1,000 0.1 100
Mahangin 1,500 0.15 150
Mabunga 2,500 0.25 250