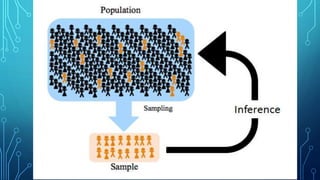
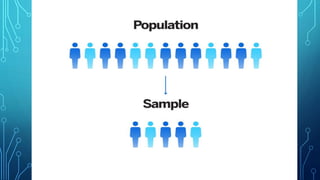
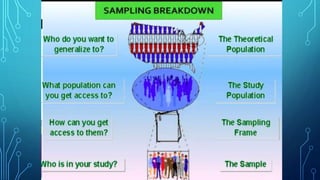
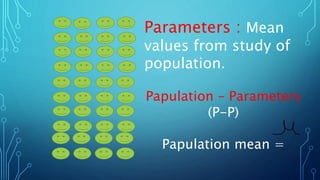
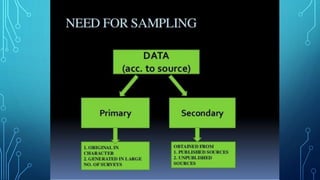
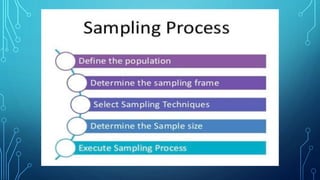
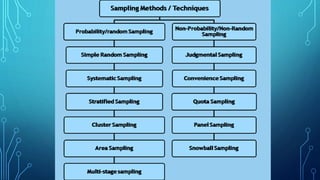
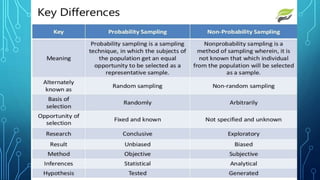
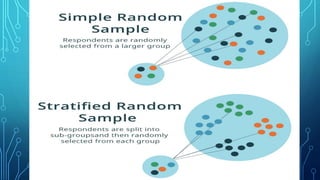
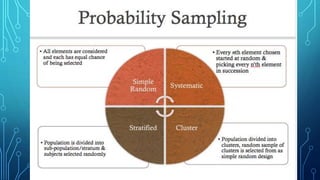
The document discusses the concepts of population, sampling frames, and the various types of sampling units used in research. It highlights the differences between probability and non-probability sampling methods and emphasizes the importance of representativeness and sample size. Additionally, it mentions the necessity of using primary data collection when secondary data is unavailable.