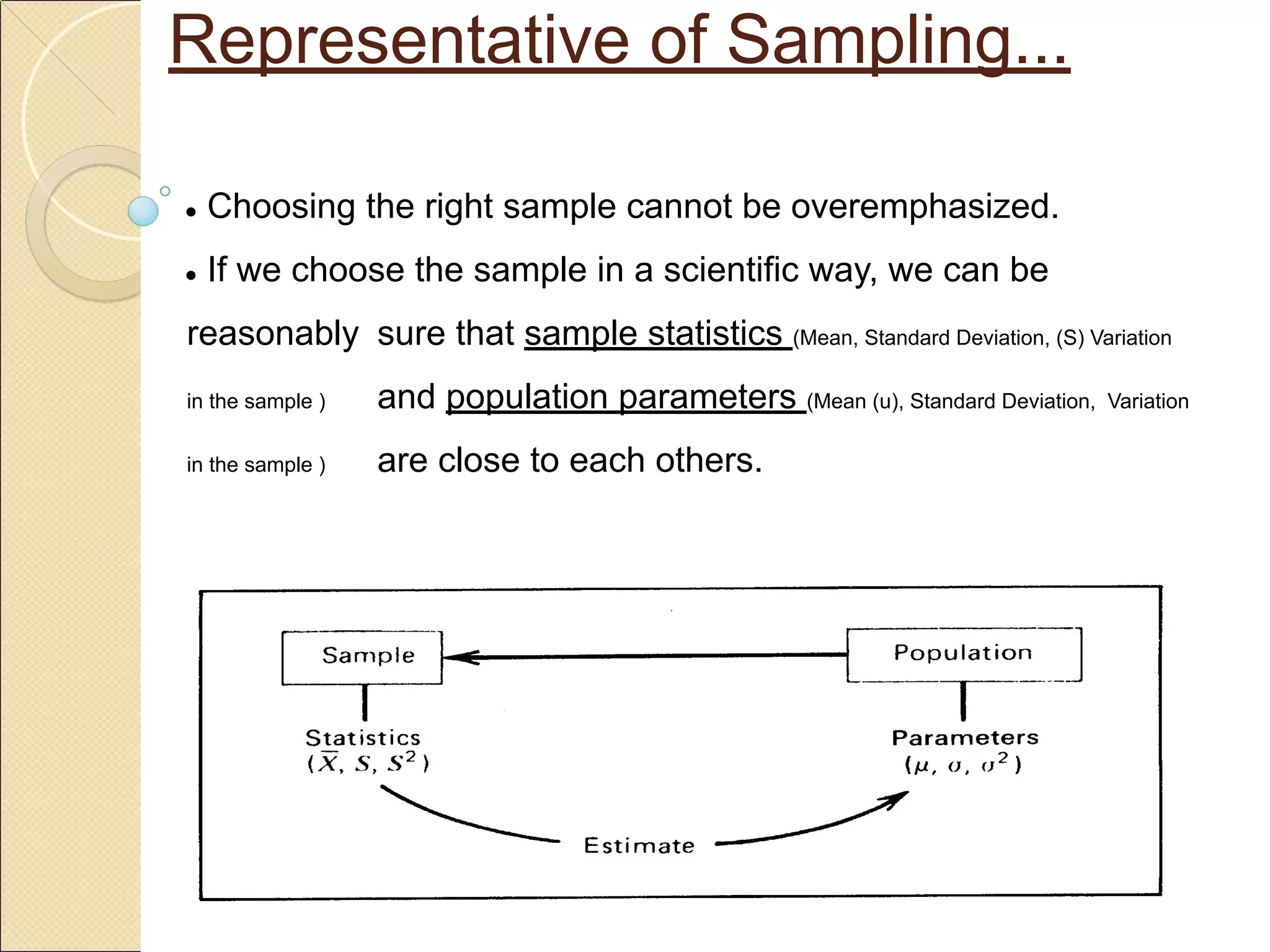
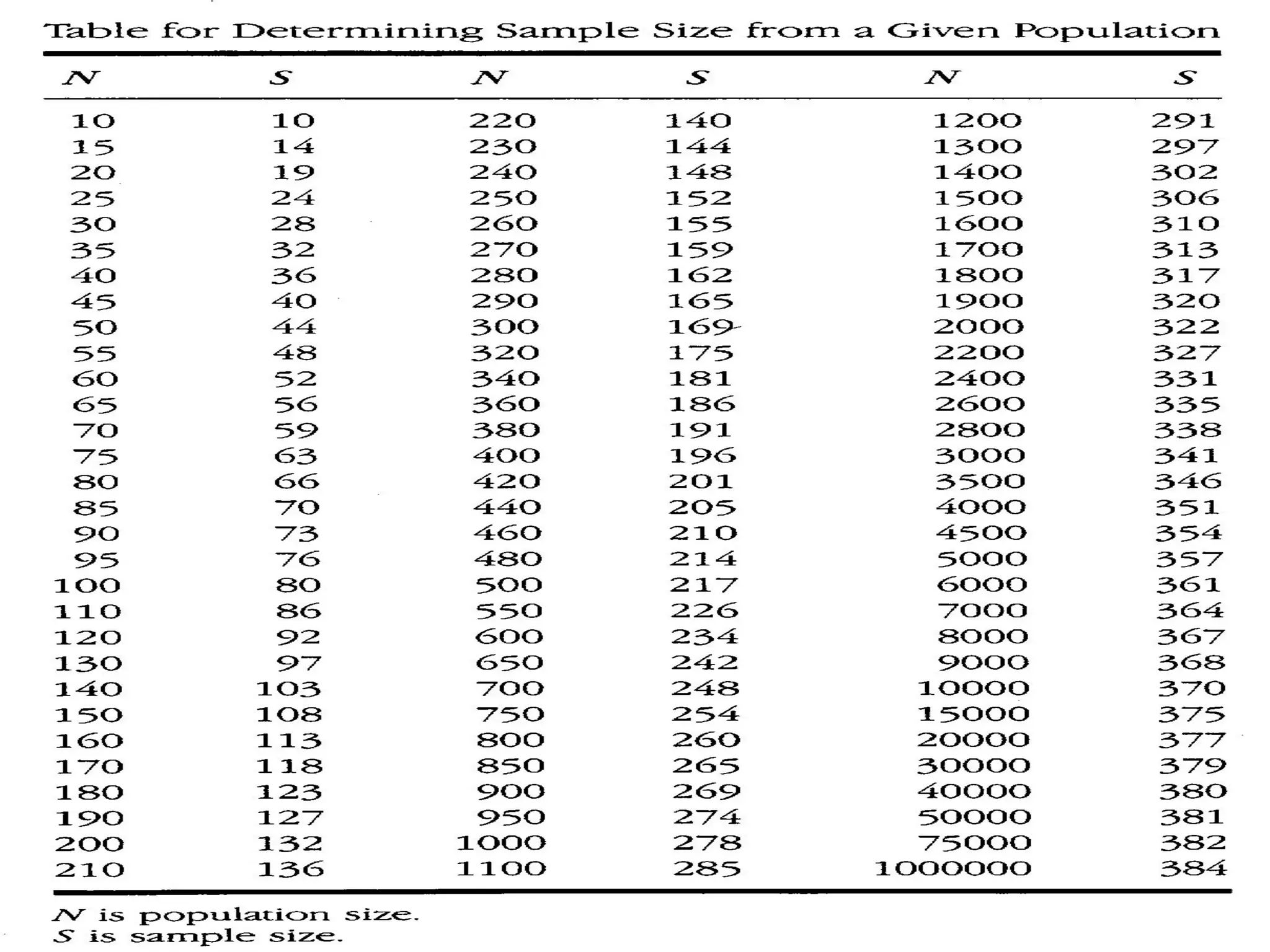
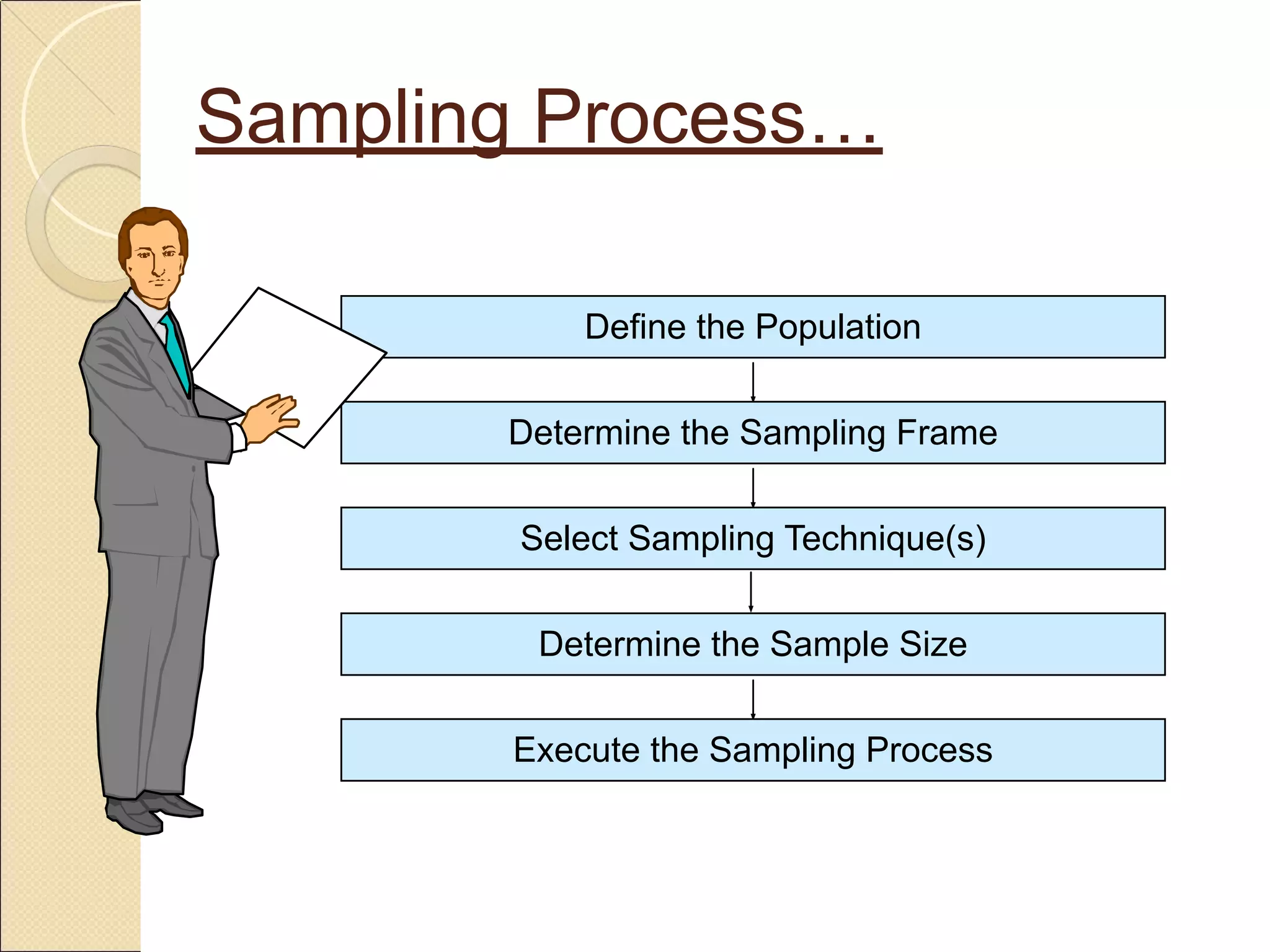
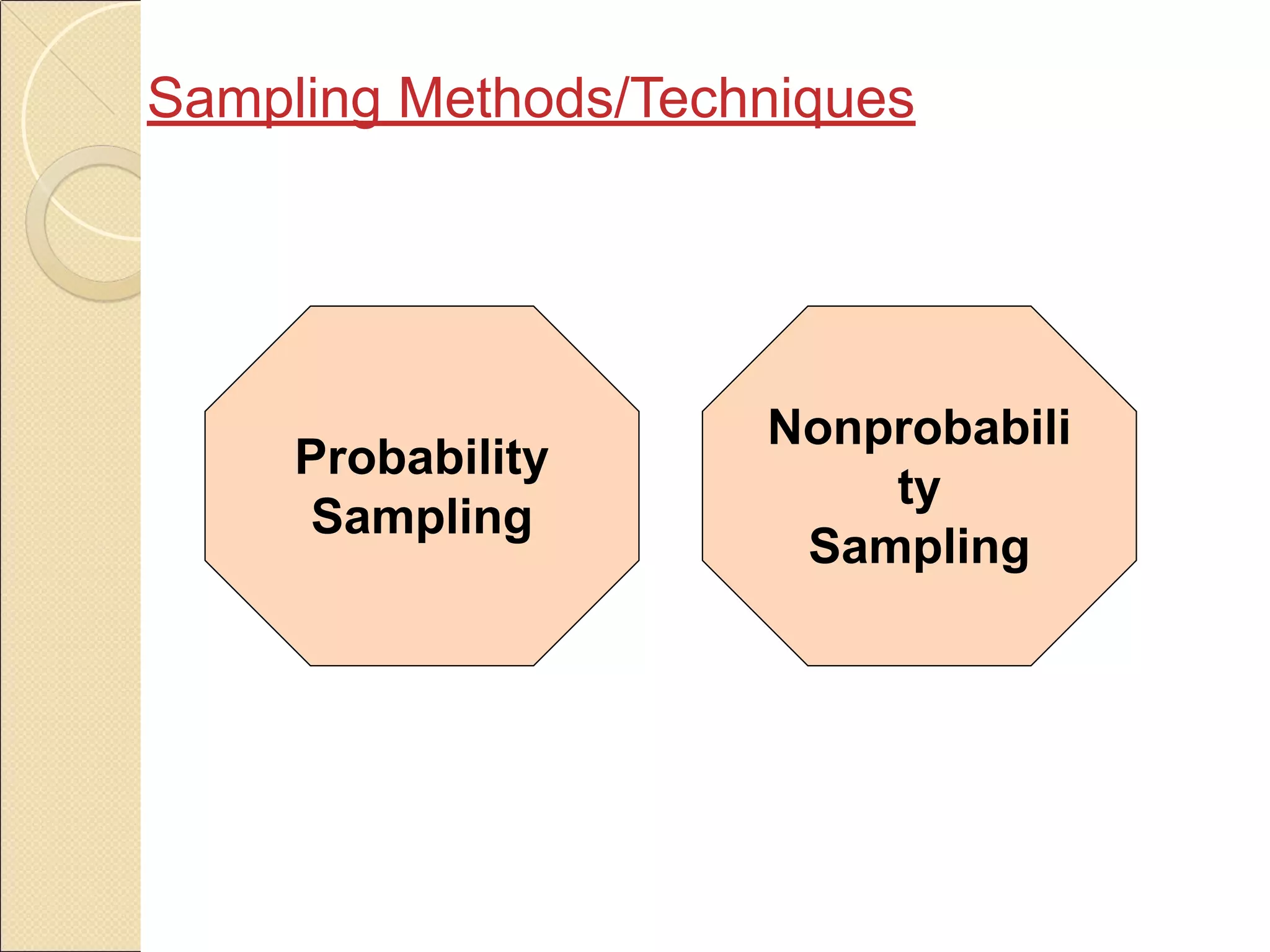
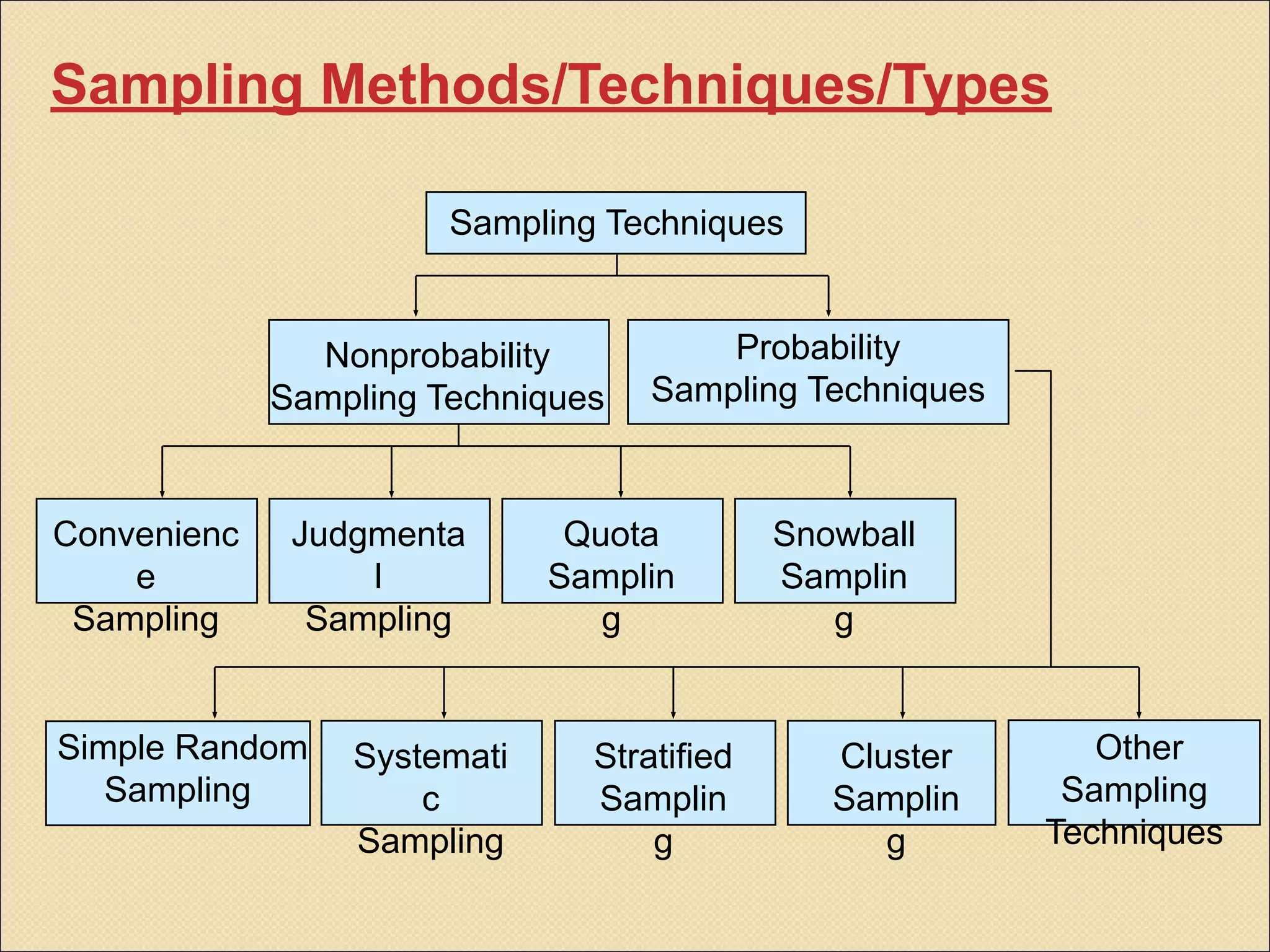
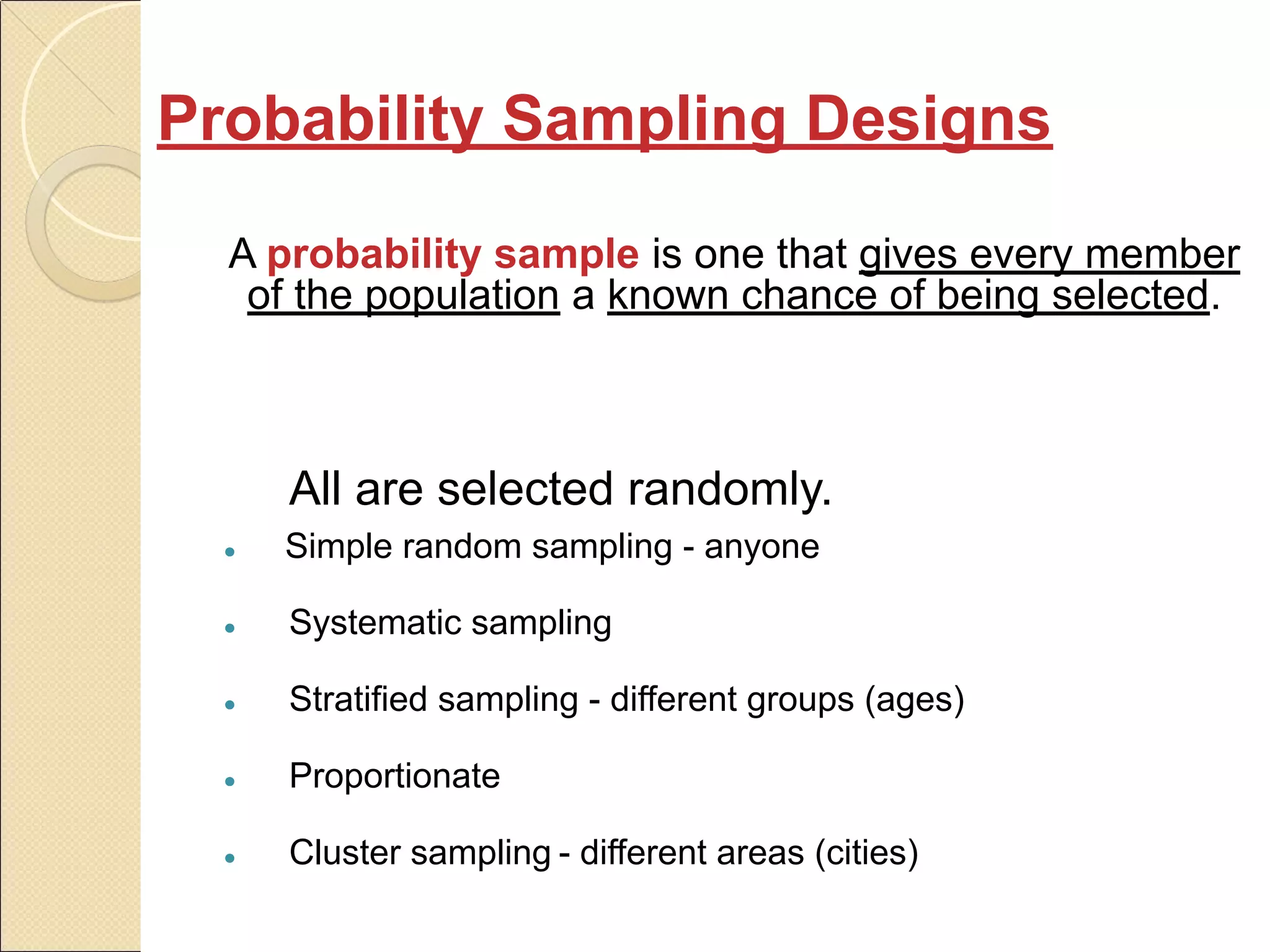
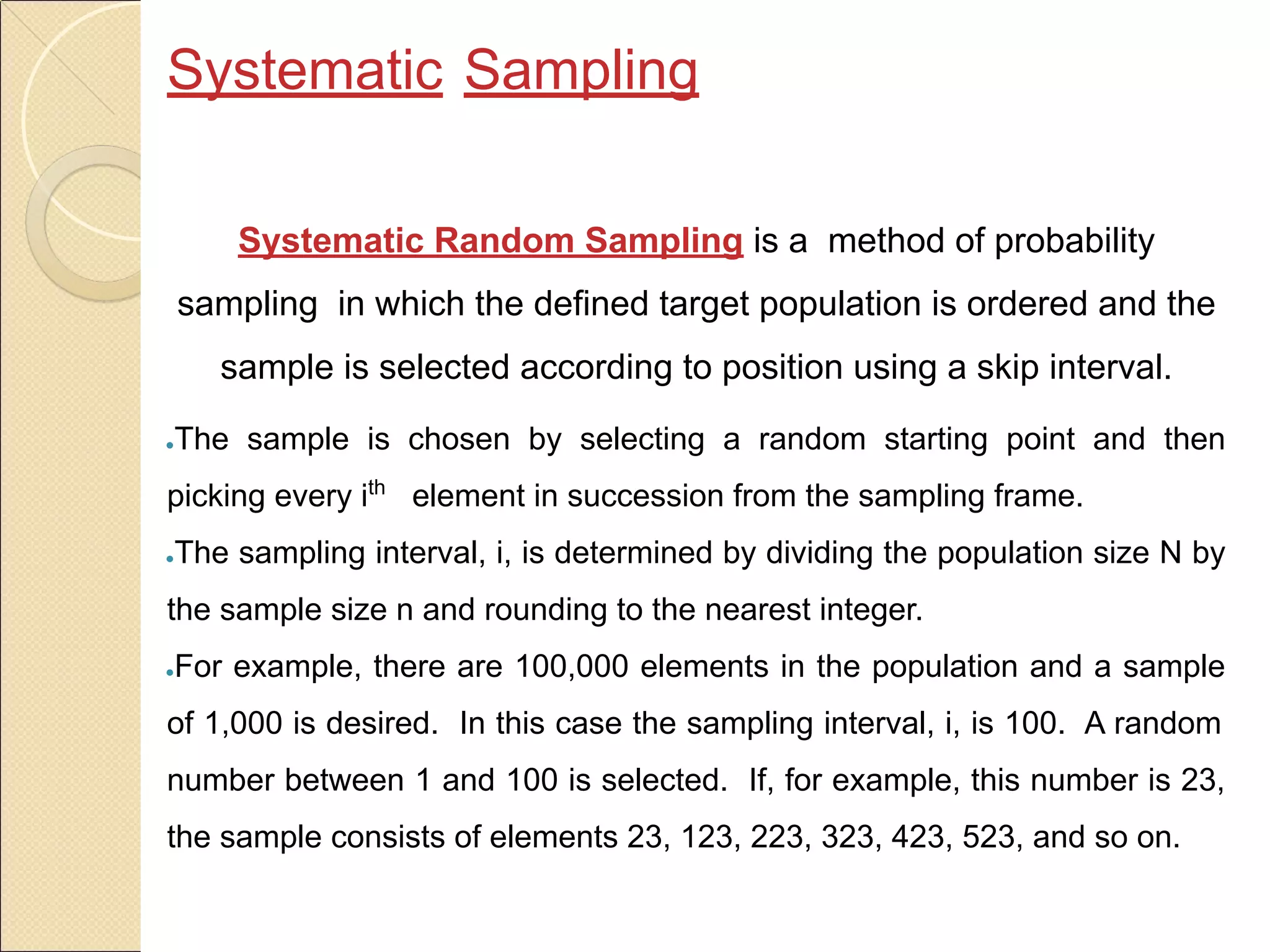
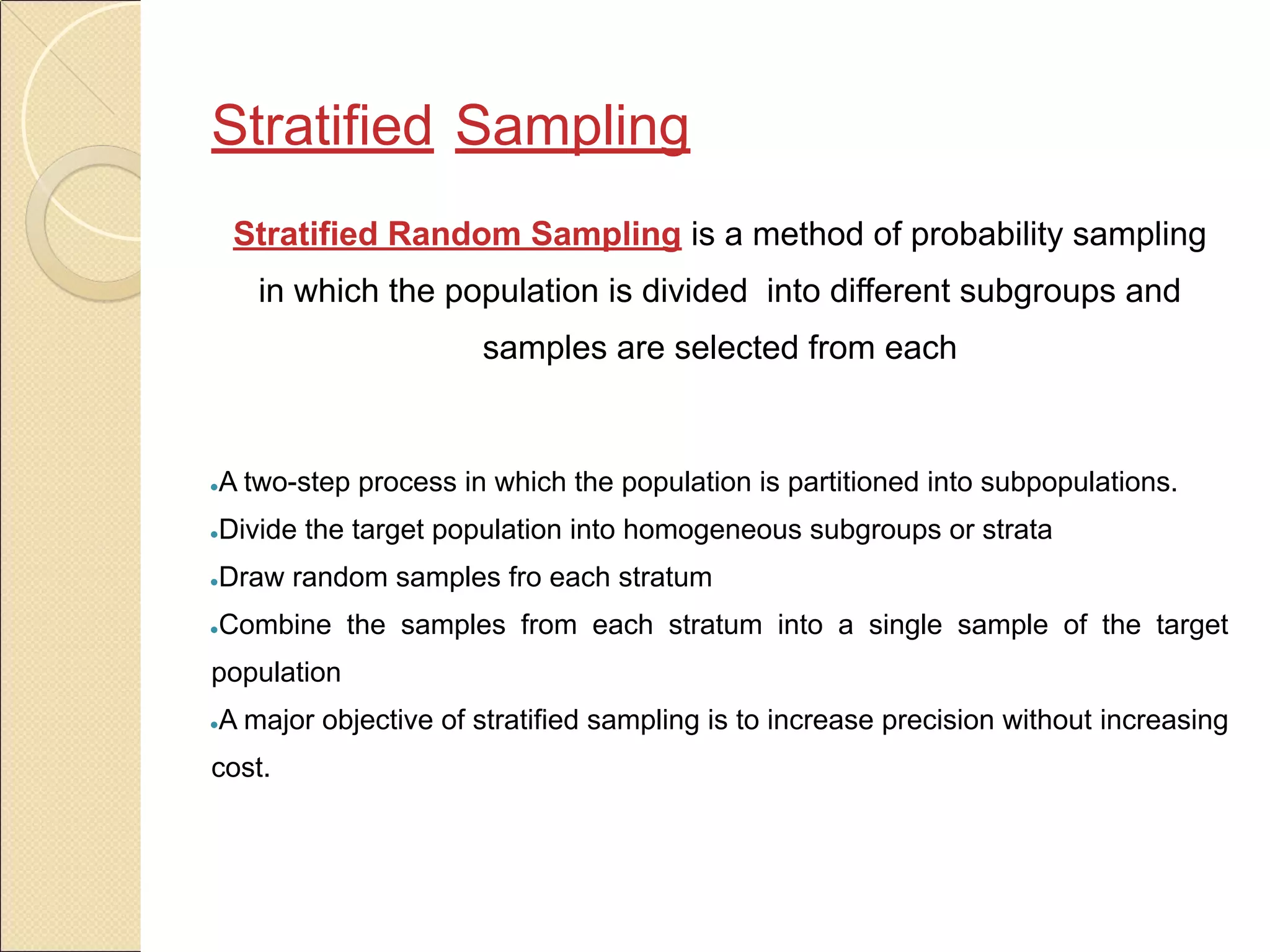
Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of a larger population to gather information about the whole population. It allows researchers to make inferences about the characteristics of the entire population based on a representative sample. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, where every member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected; and non-probability sampling, where samples are selected in a non-random manner. Common probability sampling techniques include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Common non-probability techniques include convenience sampling, judgmental sampling, and quota sampling.