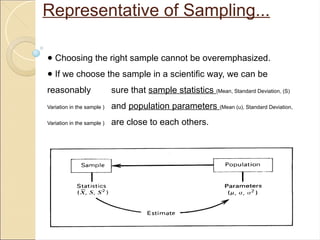
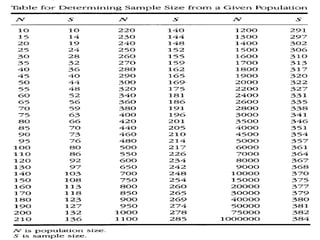
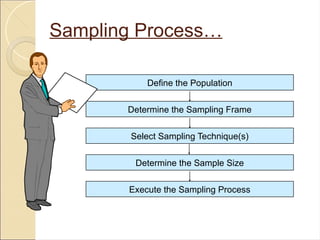
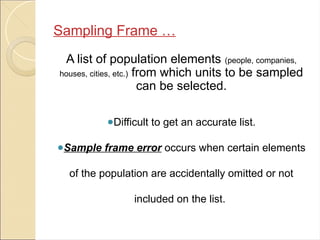
Sampling Techniques in Statistics
Sampling techniques are methods used to select a subset of individuals or observations from a larger population for the purpose of statistical analysis. The goal of sampling is to obtain a representative sample that accurately reflects the characteristics of the population, allowing researchers to make inferences about the population based on the sample data.
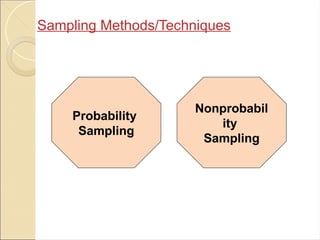
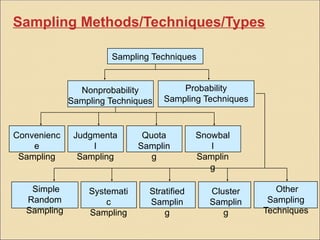
Types of Sampling Techniques
There are several types of sampling techniques, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common sampling techniques include:
1. *Random Sampling*: Random sampling involves selecting individuals or observations from the population using a random process, such as a random number generator. This technique ensures that every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
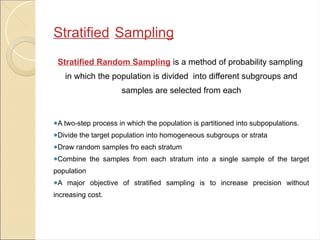
2. *Stratified Sampling*: Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into distinct subgroups or strata and then sampling from each stratum. This technique is useful when the population is heterogeneous and the researcher wants to ensure that each subgroup is adequately represented.
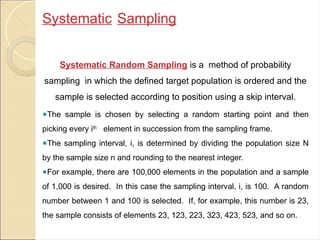
3. *Systematic Sampling*: Systematic sampling involves selecting individuals or observations from the population at regular intervals, such as every 10th individual. This technique is useful when the population is large and a random sample is not feasible.
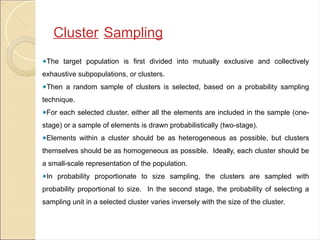
4. *Cluster Sampling*: Cluster sampling involves selecting groups or clusters of individuals or observations from the population and then sampling from each cluster. This technique is useful when the population is spread out over a large geographic area.
5. *Convenience Sampling*: Convenience sampling involves selecting individuals or observations that are easily accessible or convenient to study. This technique is often used in exploratory studies or pilot studies.
6. *Purposive Sampling*: Purposive sampling involves selecting individuals or observations that are specifically chosen for their relevance to the research question. This technique is often used in qualitative research studies.
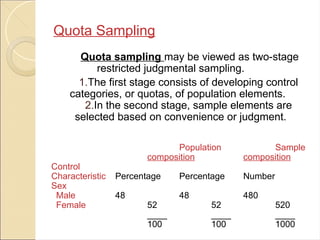
7. *Quota Sampling*: Quota sampling involves selecting individuals or observations that meet specific criteria or quotas, such as age, sex, or occupation. This technique is often used in market research studies.
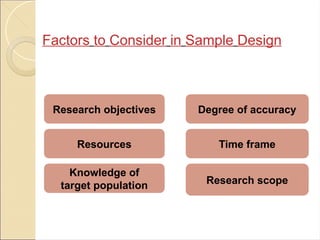
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sampling Techniques
Each sampling technique has its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the advantages of sampling techniques include:
- *Cost-effective*: Sampling techniques can be more cost-effective than studying the entire population.
- *Time-efficient*: Sampling techniques can be more time-efficient than studying the entire population.
- *Increased accuracy*: Sampling techniques can provide more accurate results than studying the entire population, especially when the population is large and diverse.
Some of the disadvantages of sampling techniques include:
- *Sampling bias*: Sampling techniques can be subject to sampling bias, which occurs when the