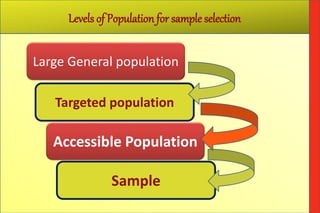
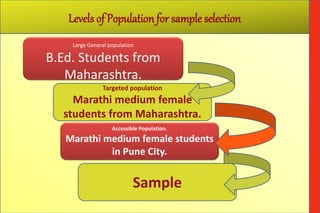
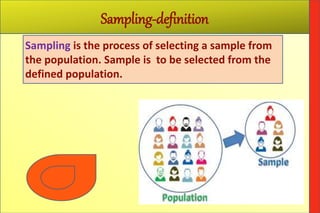
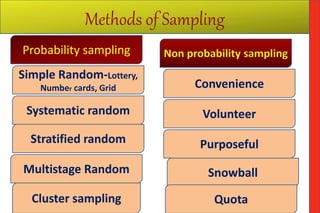
The document defines 'population' as a group of individuals or entities relevant to a sampling study, referred to as the 'universe,' which can be configured based on various characteristics. It explains the importance of selecting a representative 'sample' from the population through proper sampling methods to minimize bias and ensure accurate analysis. The document outlines the sampling process, including steps such as defining the population, listing it, selecting a sample, and highlights different sampling methods, both probability and non-probability.