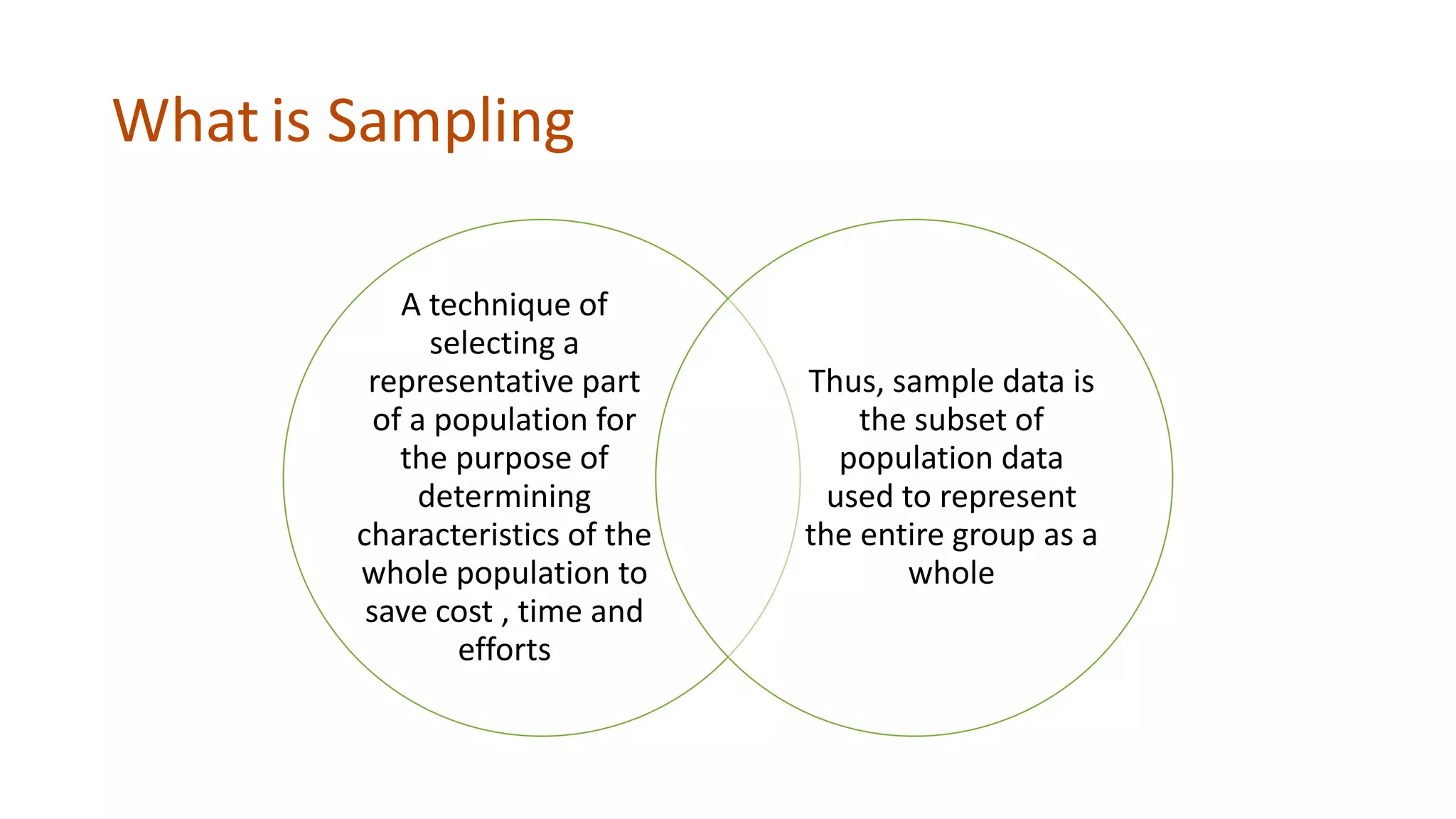
This document discusses sampling techniques used in data analysis. It defines sampling as selecting a subset of data to represent a larger population. Two common sampling methods are described:
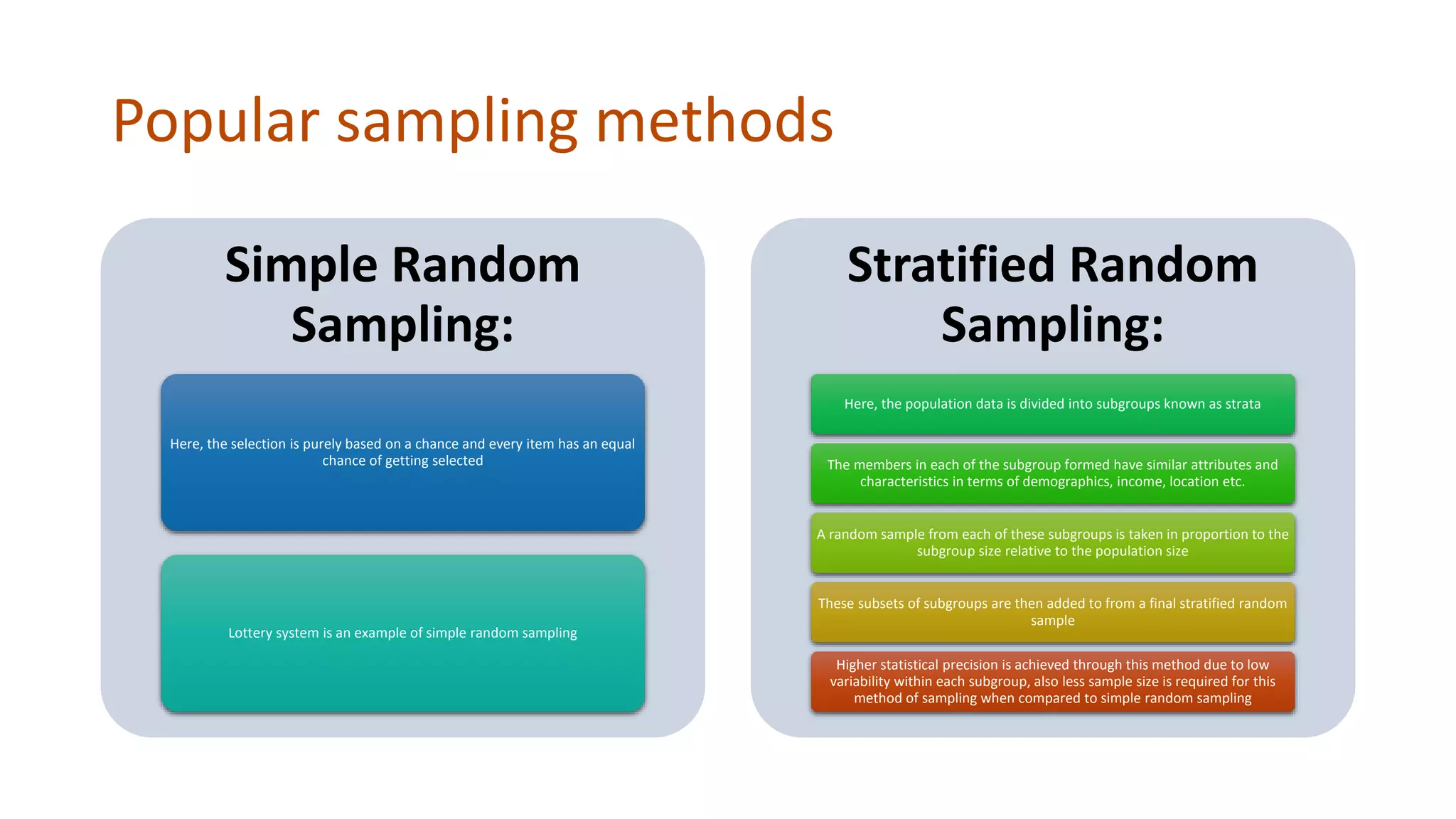
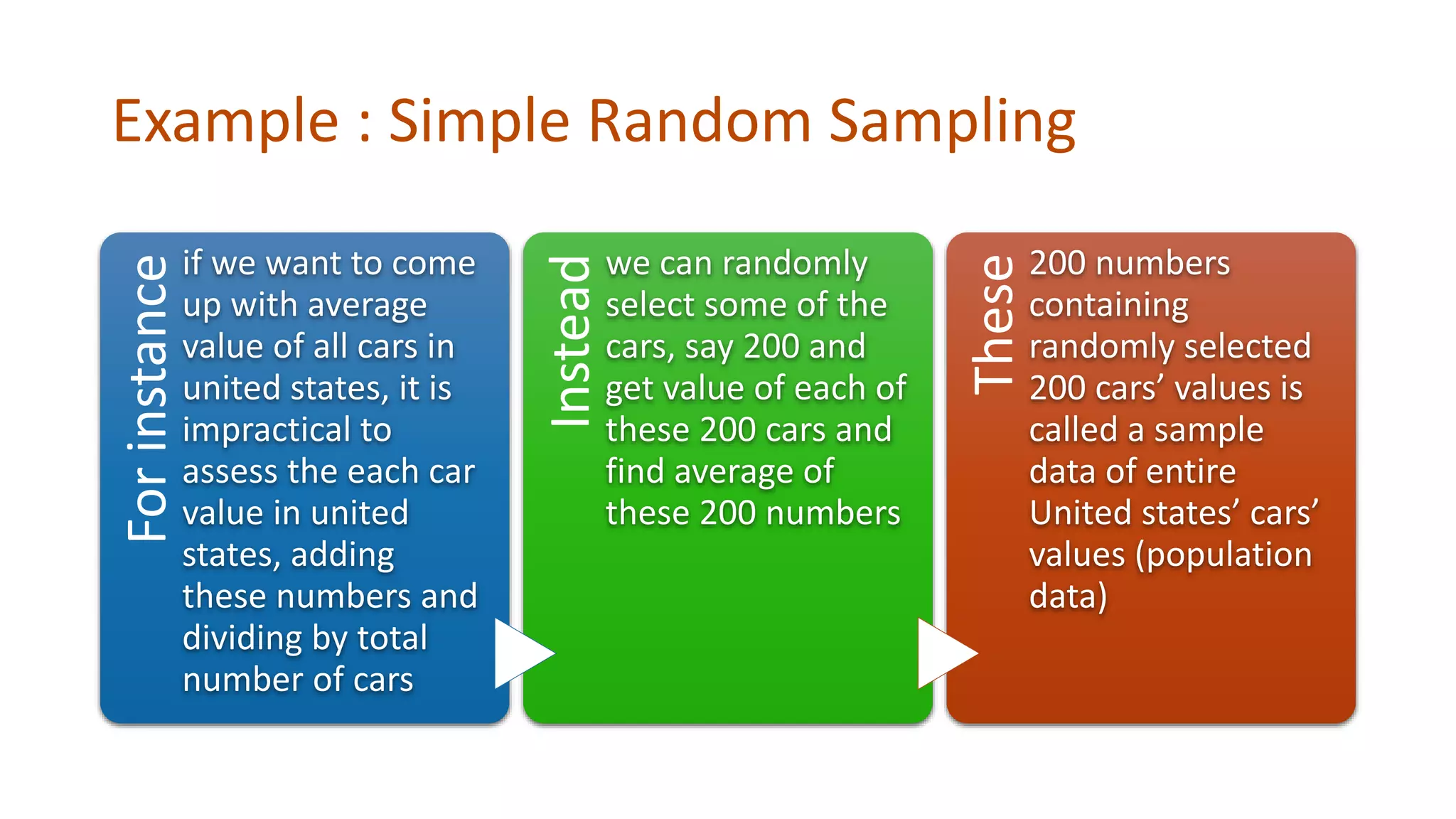
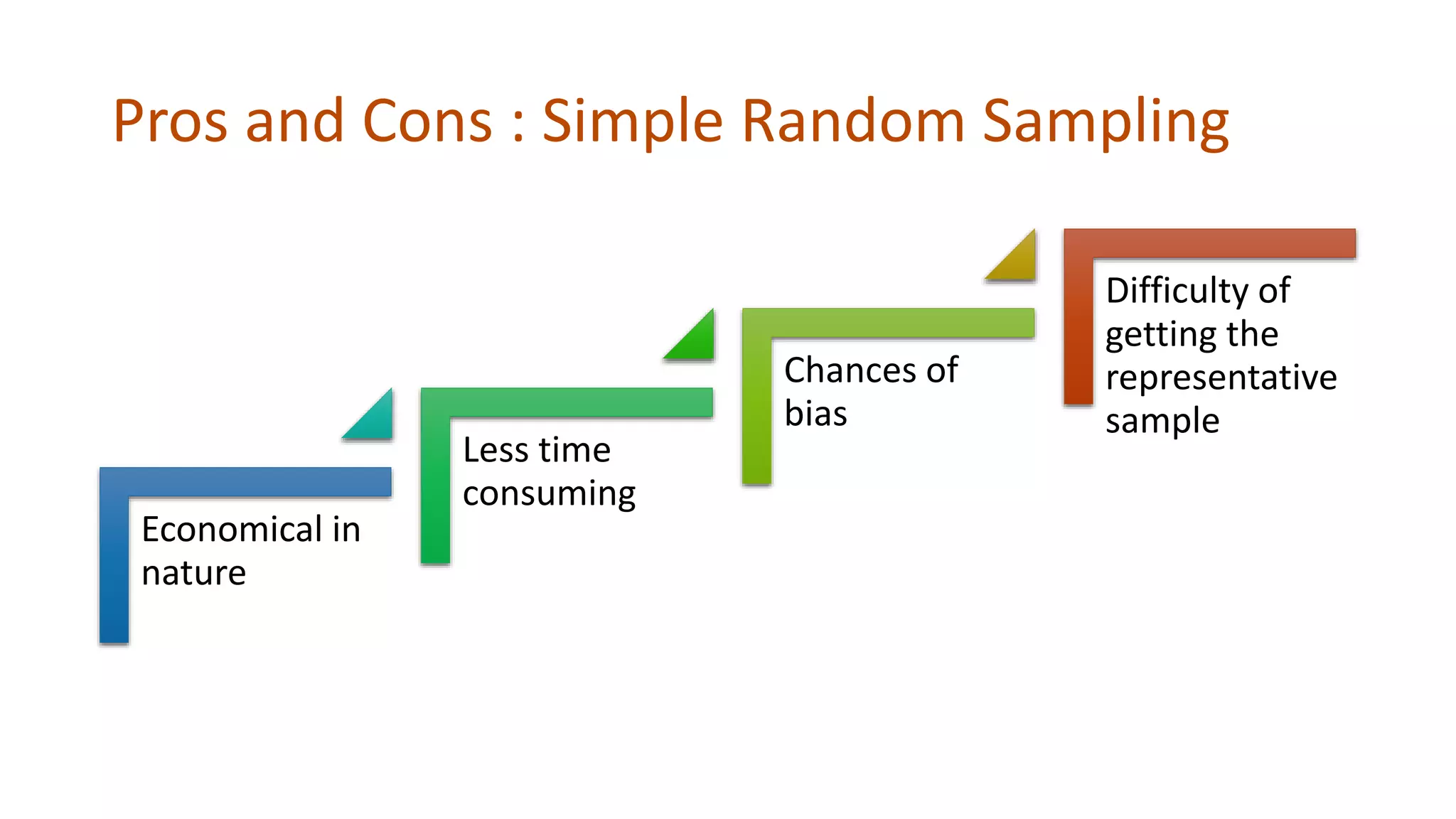
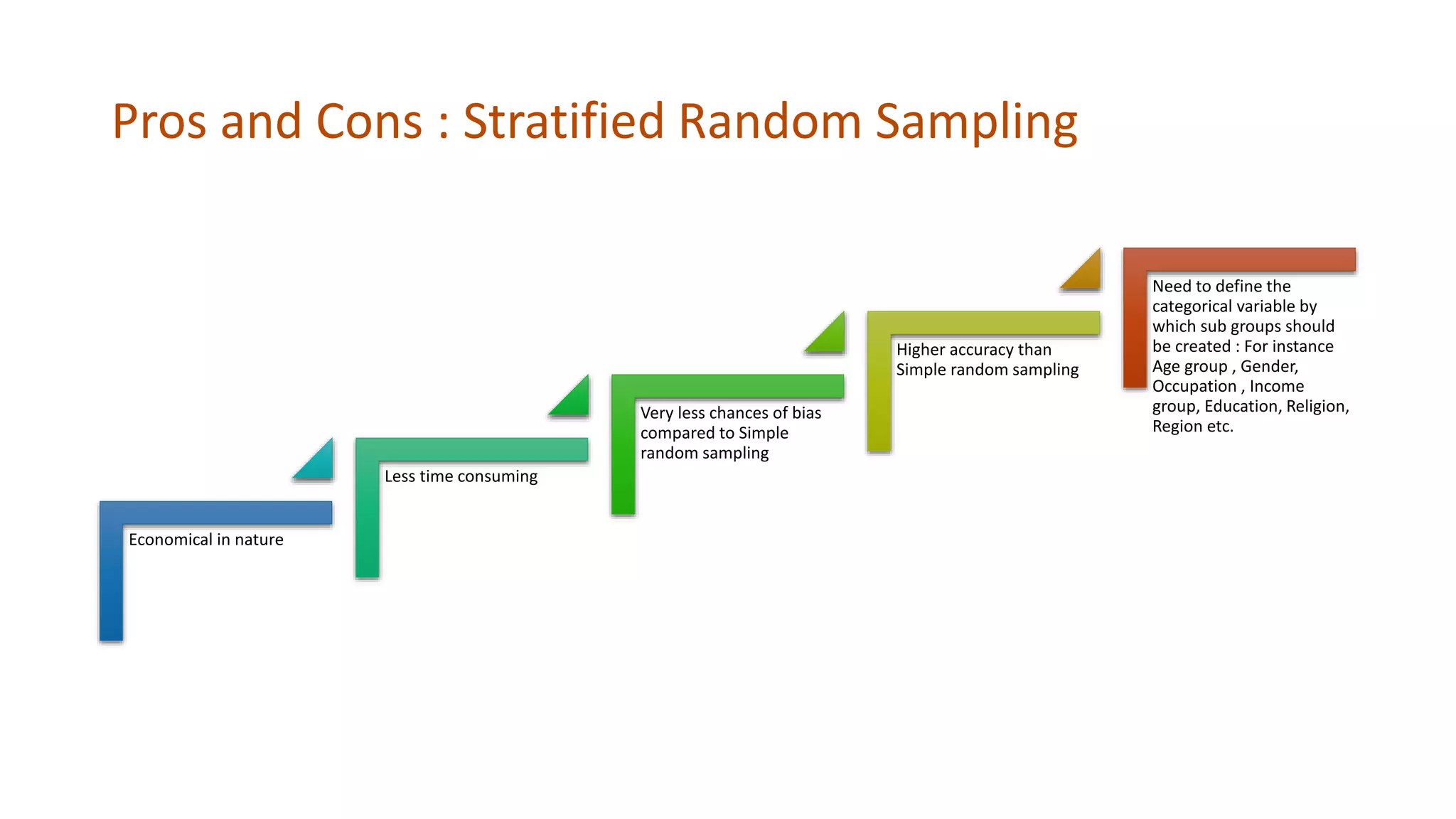
Simple random sampling involves randomly selecting items from the entire population so that each item has an equal chance of selection. Stratified random sampling first divides the population into subgroups, then randomly samples from each subgroup in proportion to its size. This ensures subgroups are represented in the sample.
Advantages and disadvantages of each method are provided. Simple random sampling is economical but risks not being representative. Stratified random sampling has less chance of bias and higher accuracy but requires defining subgroups first. Sampling allows analyzing large populations efficiently while capturing overall characteristics.