• Concept and nature of management
• Types of managers
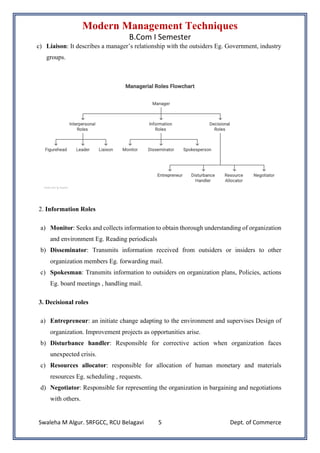
• Responsibilities and skills of professional managers, functions of management, Fayol’s
Principles of management
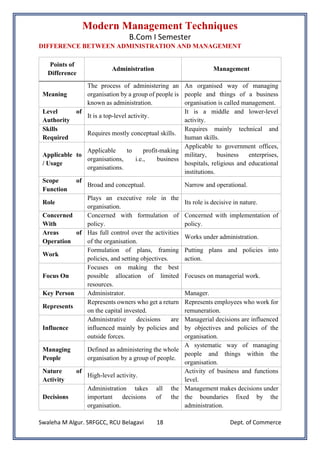
• Administration vs Management, management process
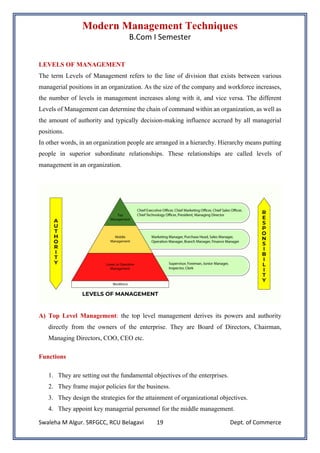
• Levels of management
• Challenges of Modern managers to manage the business organization.