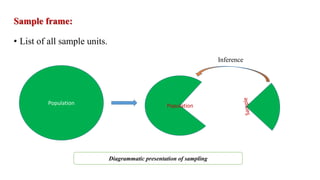
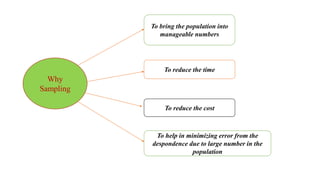
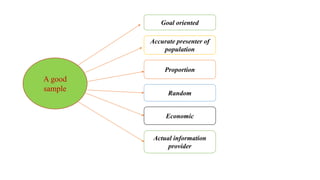
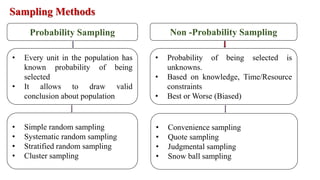
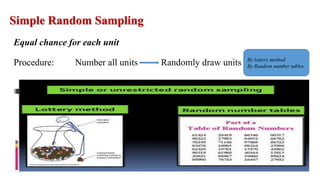
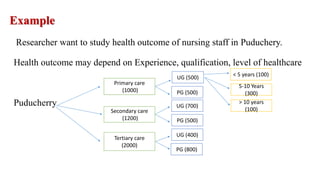
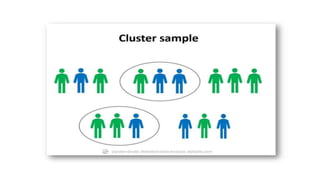
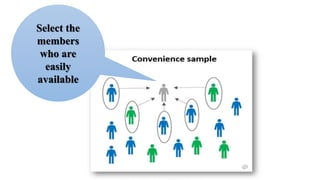
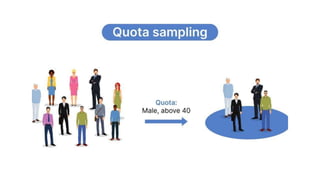
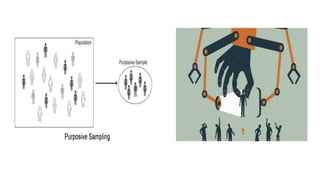
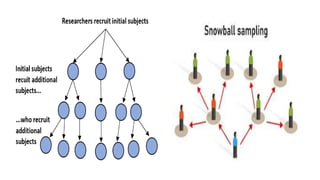
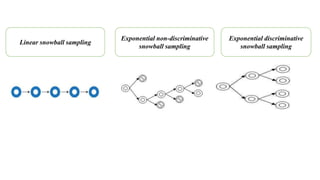
The document outlines various sampling methods used in research, including probability and non-probability sampling techniques. It explains procedures and examples for methods such as simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, convenience sampling, quota sampling, judgmental sampling, and snowball sampling. Each method is discussed regarding its pros and cons, focusing on aspects like validity, efficiency, and potential biases.