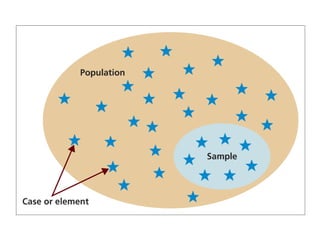
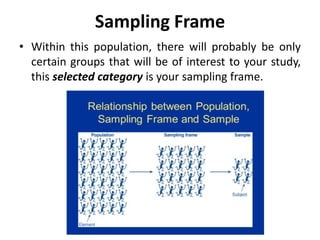
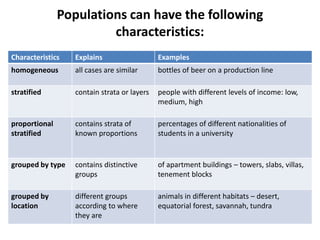
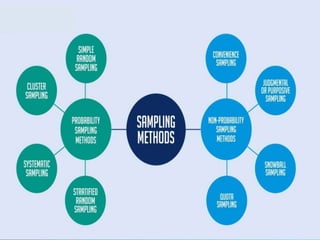
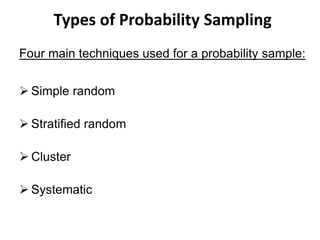
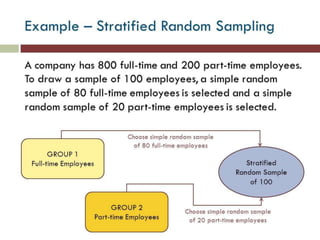
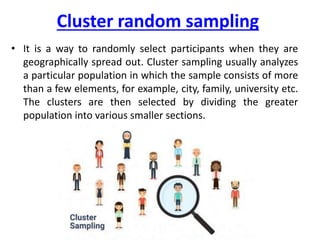
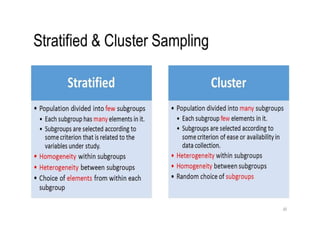
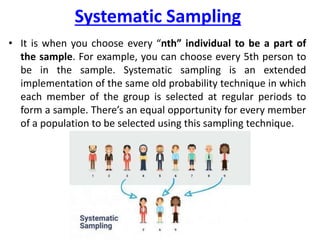
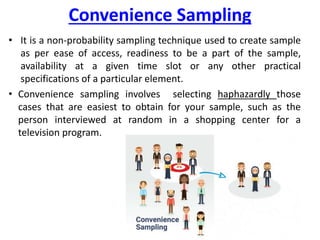
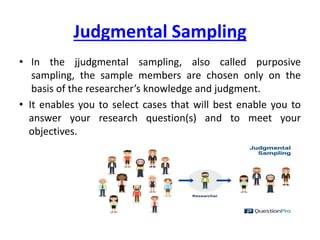
Probability and non-probability sampling techniques are used to select samples from populations. Probability sampling uses random selection so each member has an equal chance of selection, allowing results to be generalized. Common methods are simple random, stratified, cluster, and systematic sampling. Non-probability techniques like convenience, judgmental, snowball, and quota sampling rely on the researcher's judgment and cannot be generalized. The document provides definitions and examples of different sampling methods.