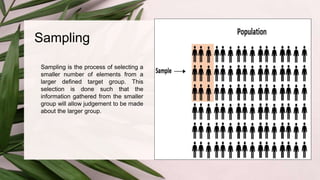
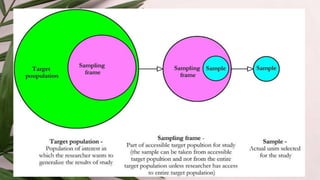
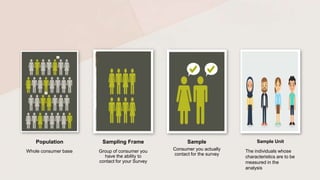
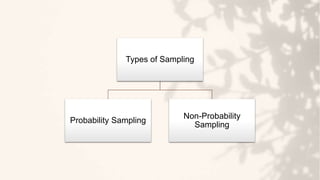
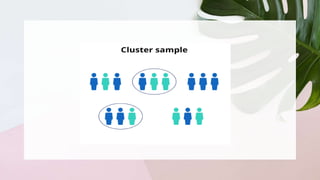
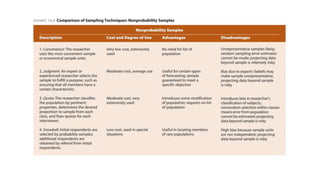
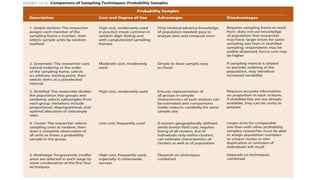
The document discusses different sampling methods used in business research. It defines sampling as selecting a smaller group from a larger population to make inferences about the whole population. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, which uses random selection so each unit has an equal chance of being chosen; and non-probability sampling, which relies on the researcher's judgement. Some key probability sampling methods described are simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, systematic sampling, and cluster random sampling. The main non-probability sampling techniques discussed are convenience sampling, judgmental sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling.