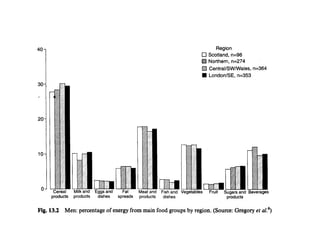
1. Cross-sectional studies measure exposures and outcomes in a population at a single point in time and are commonly used to estimate disease prevalence and describe population characteristics.
2. They can provide clues about associations but cannot determine causation due to their observational nature.
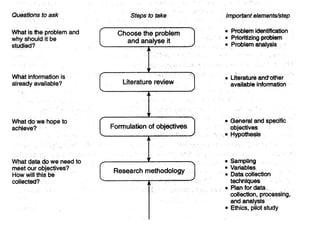
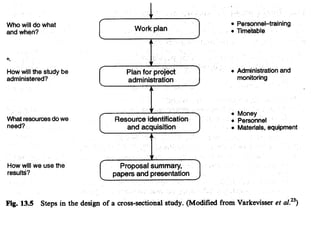
3. Planning is important for cross-sectional studies including clear objectives, sampling, data collection methods, and analysis of results with descriptive statistics.