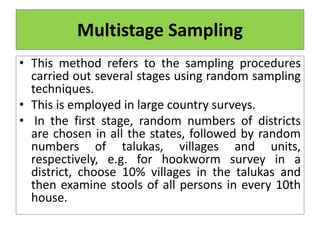
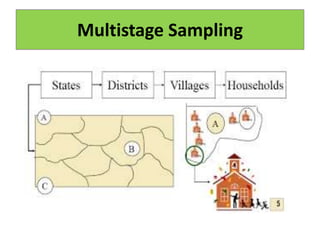
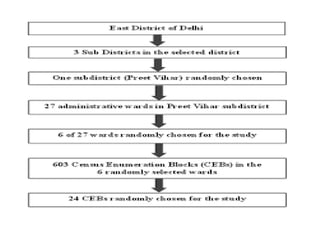
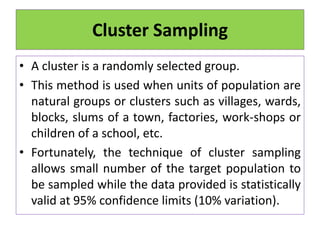
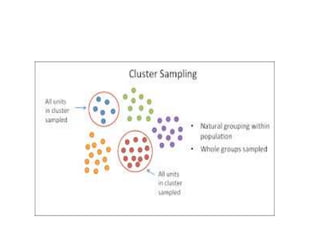
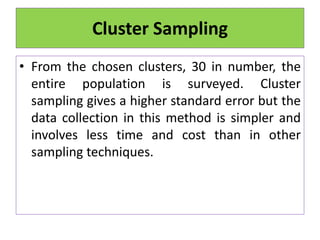
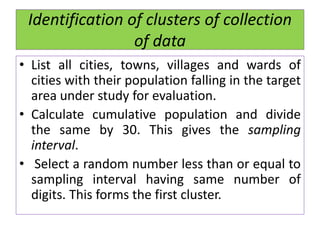
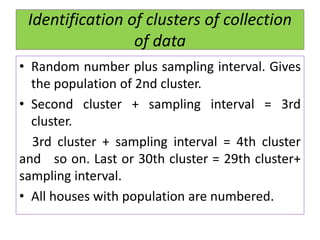
This document discusses different sampling techniques used in medical studies and research. It begins by explaining that sampling is necessary when not every member of a population can be included in a study. Some key points made about sampling include:
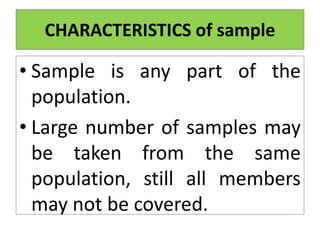
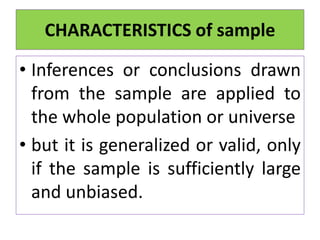
- Samples should be sufficiently large and representative of the overall population.
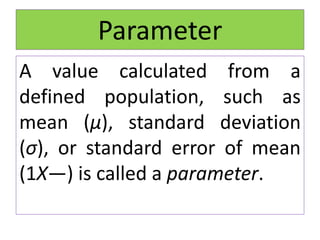
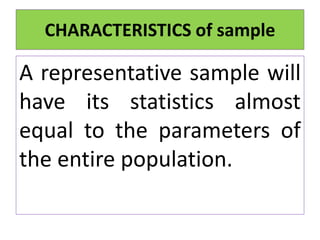
- Parameters describe values for the entire population, while statistics describe values calculated from a sample.
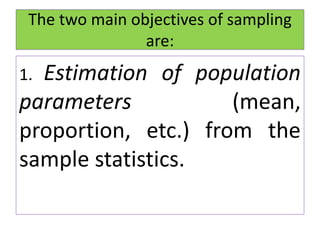
- The main objectives of sampling are to estimate population parameters from sample statistics and to test hypotheses about the population.
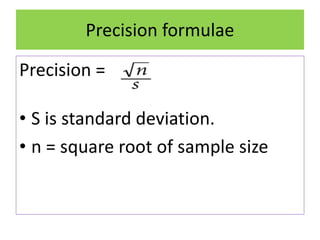
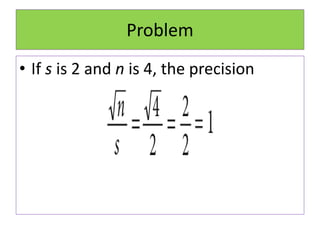
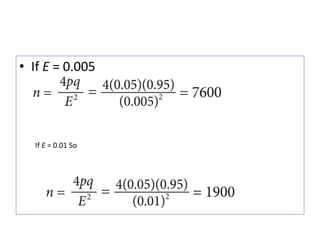
- Sample size, sampling technique, and sample representativeness impact the precision and validity of conclusions drawn about the population.







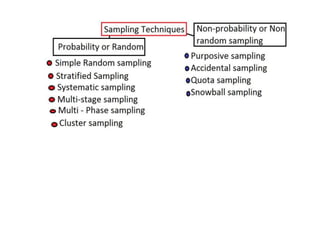
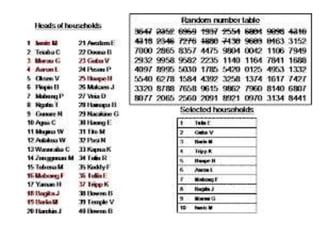
![Simple Random Sampling
The method is applicable when the population is
• Small.
• Homogeneous and
• Readily available
[such as patients coming to hospital or lying in
the wards.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sampling-210329094828/85/Sampling-20-320.jpg)