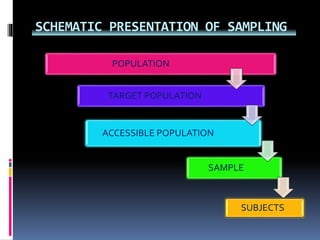
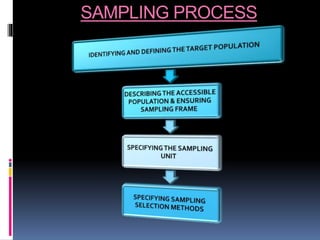
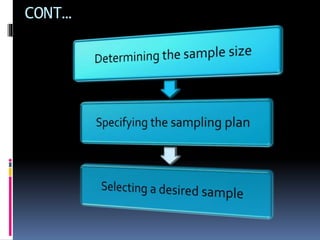
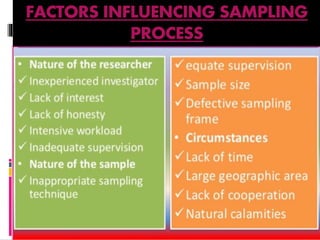
This document discusses sampling in research. It defines sampling as selecting a subset of a population to study and generalize findings to the larger group. Key terms are defined, like population, target population, sample, and sampling frame. The purposes of sampling are described as making research more economical, improving data quality, allowing for quicker study results, and increasing precision and accuracy. Characteristics of a good sample and factors influencing the sampling process are also outlined. In conclusion, sampling is an important part of research that aims to select a representative portion of a population to study.