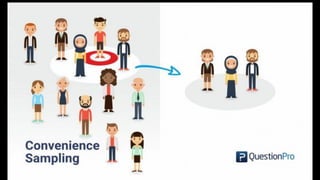
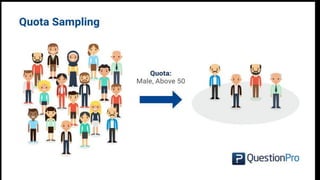
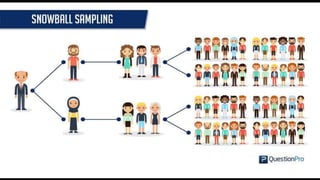
Non-probability sampling methods allow researchers to select sample subjects without assigning probabilities, which can lead to findings that are not generalizable to the population. These methods include convenience sampling, quota sampling, judgment sampling, and network sampling, each with their own advantages and disadvantages, often used for qualitative research or when time and budget are constraints. While effective for quick data collection, non-probability sampling may introduce bias and lack representation of the entire population.