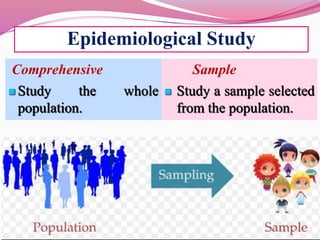
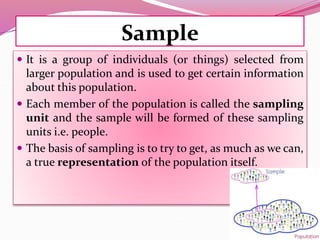
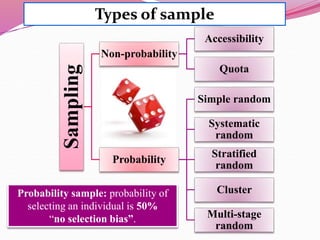
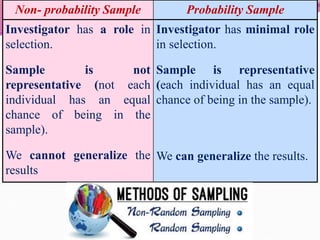
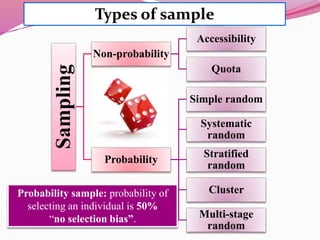
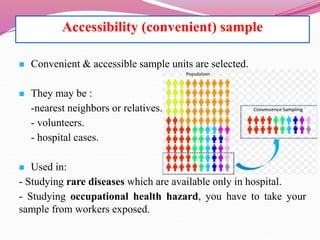
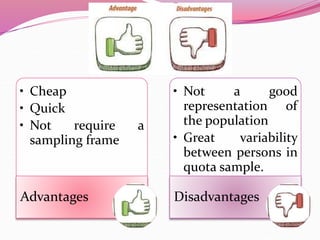
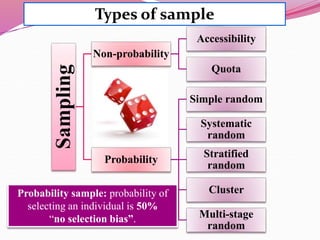
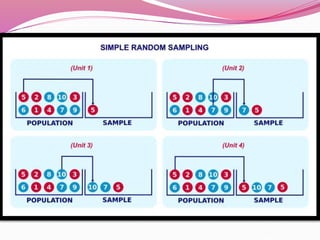
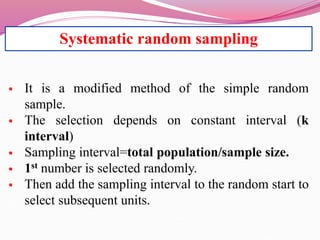
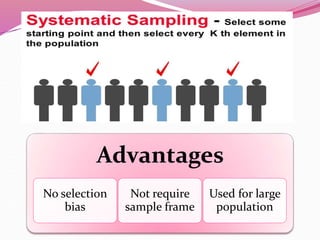
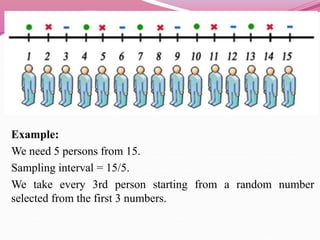
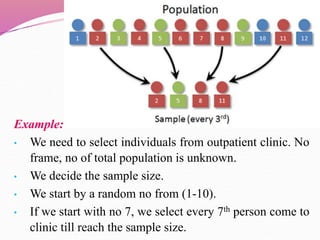
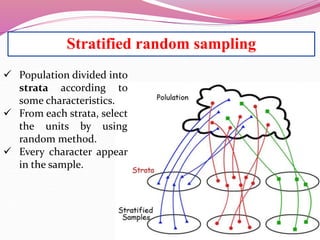
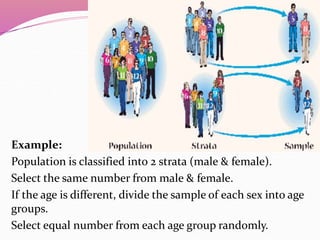
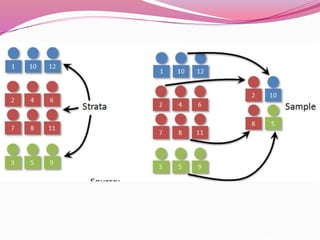
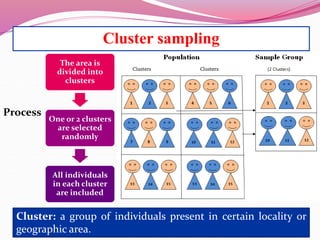
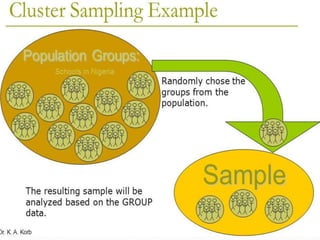
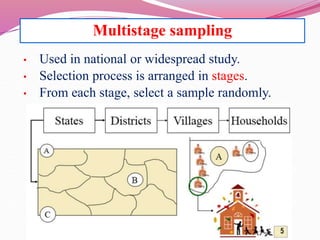
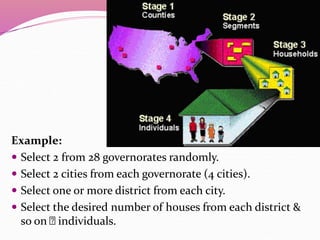
The document discusses various sampling methods used in epidemiological studies, emphasizing the importance of obtaining a representative sample from a population. It distinguishes between probability sampling, where each individual has an equal chance of selection, and non-probability sampling, which may introduce bias. Key sampling techniques include simple random, systematic random, stratified random, cluster, and multistage sampling, each with its advantages and disadvantages.