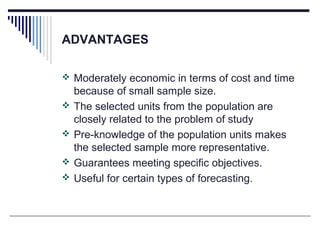
This document discusses sampling techniques used in educational research. It begins by defining key terms like population, sample, and sampling techniques. It then describes probability sampling methods like systematic sampling and non-probability sampling methods like purposive sampling. For systematic sampling, every kth unit is selected from an ordered population. Purposive sampling involves selecting units that are relevant to the research objectives. The document outlines the advantages and limitations of these sampling methods.
![Assignment in
EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH AND STATISTICS
[M.Ed 2011-12]
Assigned by:
Dr. Archna Dubey
Presented by:
• Neeraj Singh
• Rekha Boriwal
• Siddhi Sood
• Varsha Kapse](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samplingtechniques-systematicpurposive-141220081729-conversion-gate02/85/Sampling-techniques-Systematic-Purposive-Sampling-1-320.jpg)