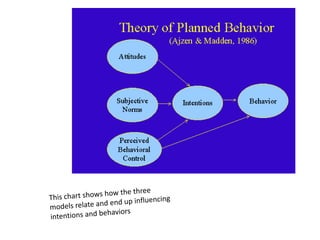
The Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) proposes that behavioral intention, which is the best predictor of actual behavior, is influenced by three factors: attitude toward the behavior, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control. More favorable attitudes, more positive social pressure, and greater perceived control over the behavior strengthens one's intention to perform that behavior. While intention predicts behavior, other factors can still interfere with actually performing the intended behavior. The TPB is useful for marketers and health researchers to predict behaviors and develop strategies. Some critics argue the subjective norm component needs improvement or that the three factors should interact rather than be separate models.