Embed presentation
Downloaded 37 times


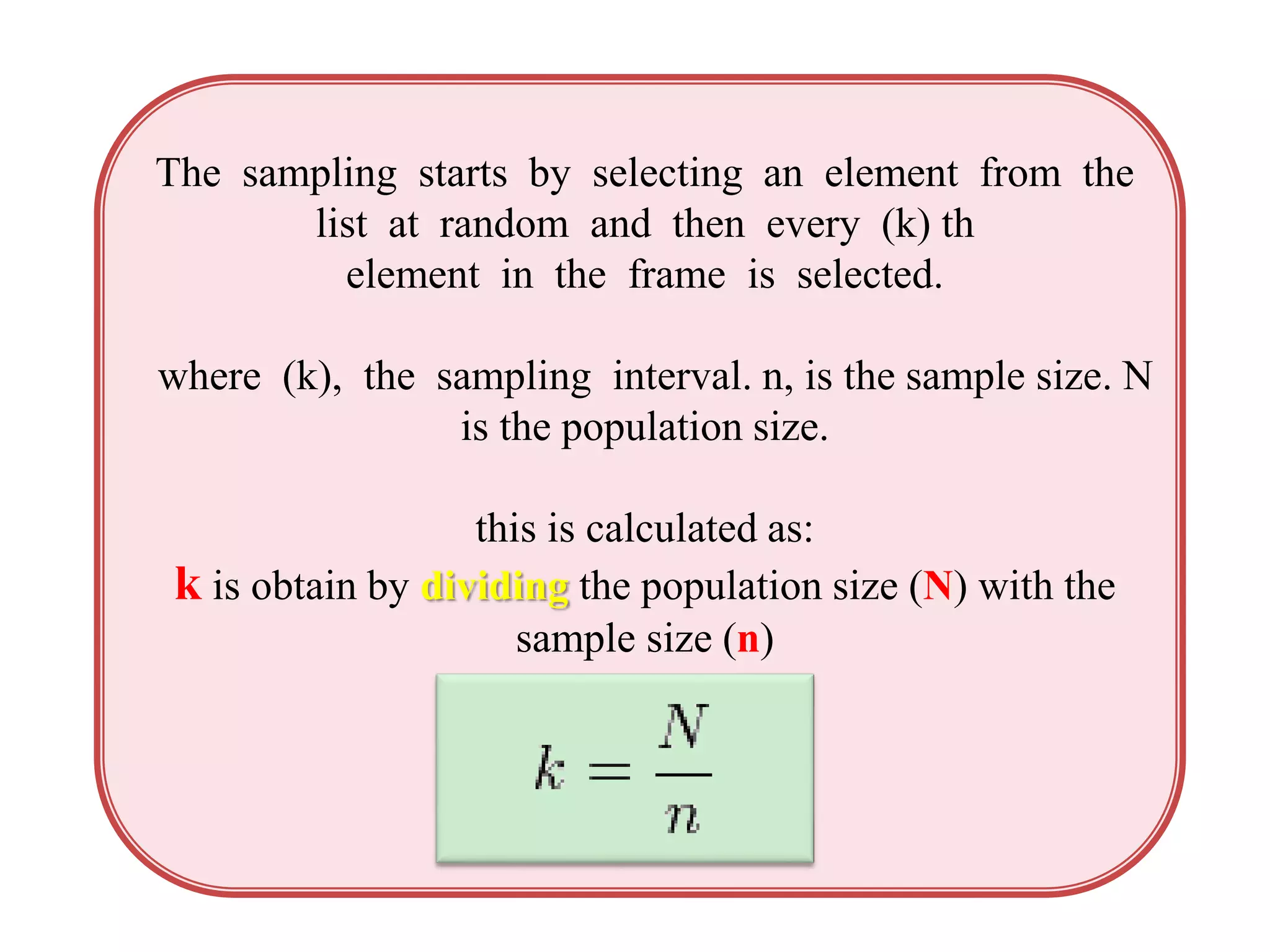

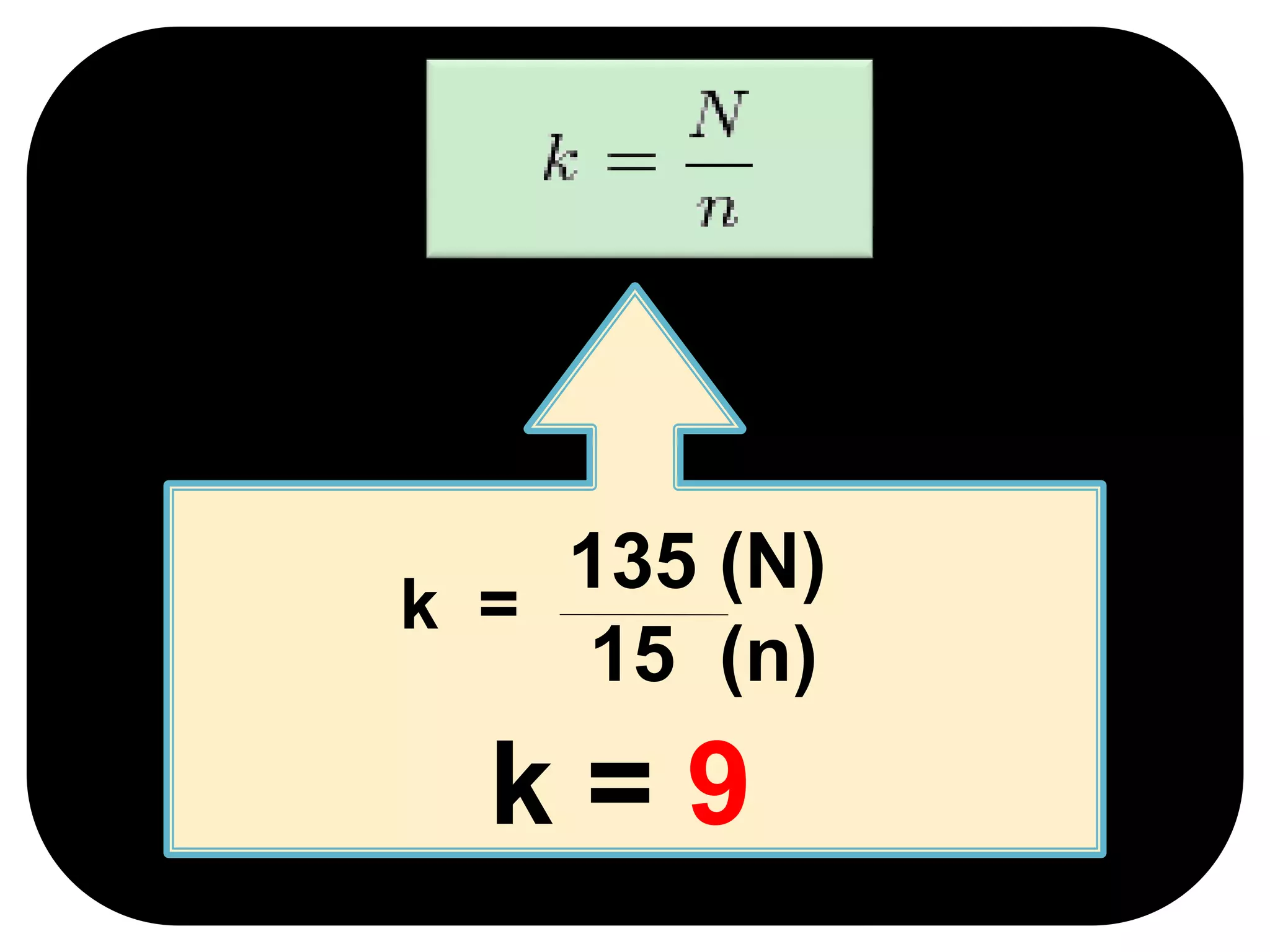




This document discusses systematic sampling, which is a statistical method for selecting elements from an ordered sampling frame. It involves randomly selecting the first element and then selecting every kth element thereafter, where k is the sampling interval calculated by dividing the population size by the sample size. For example, a study with a population of 135 students needing a sample of 15 would use a sampling interval of 9. The advantages are that it is simple to use, saves time and cost, and checks for bias. The disadvantages are the possibility of missing vital information and not being able to reach the required sample size if the population is too small.









