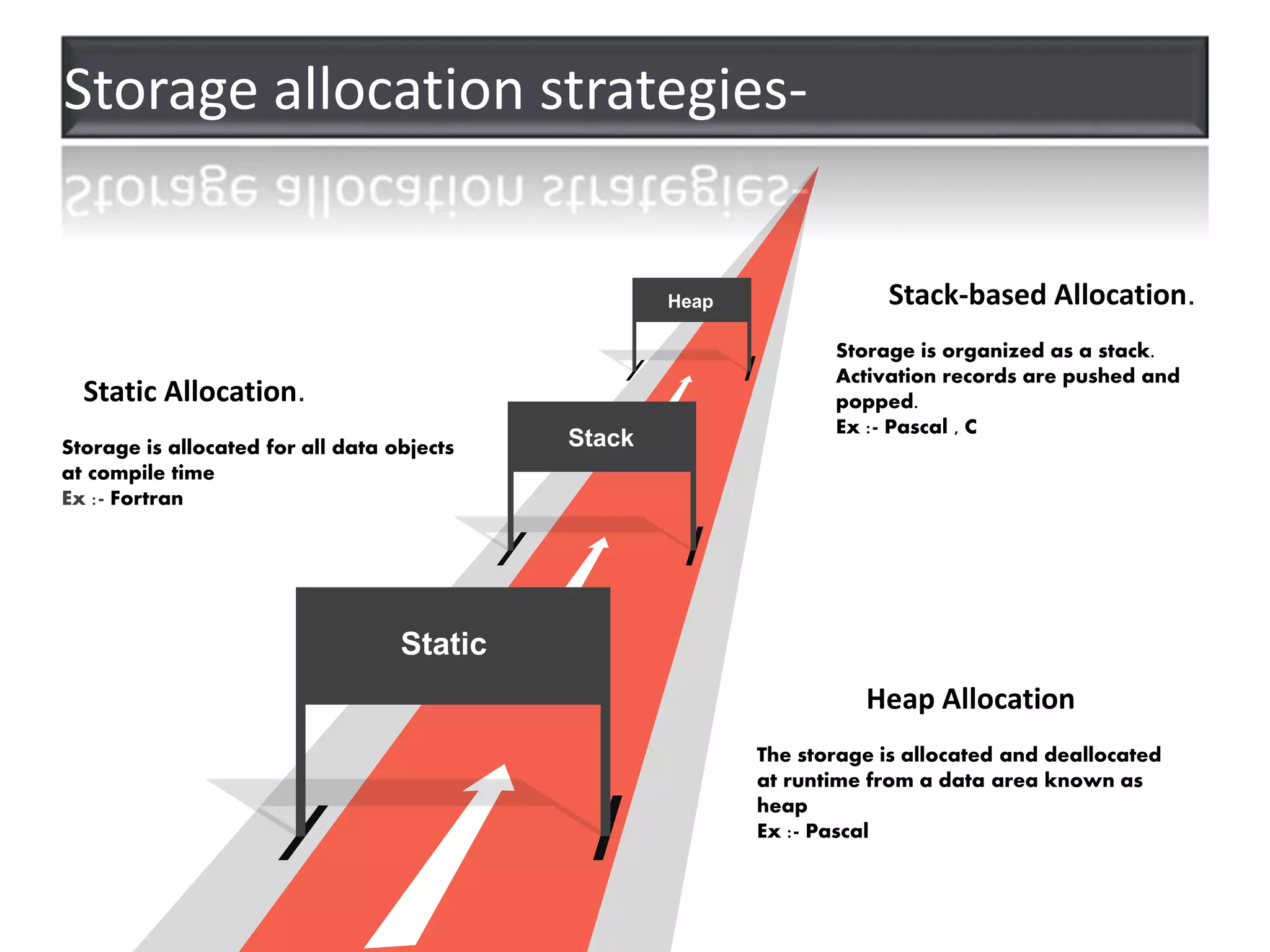
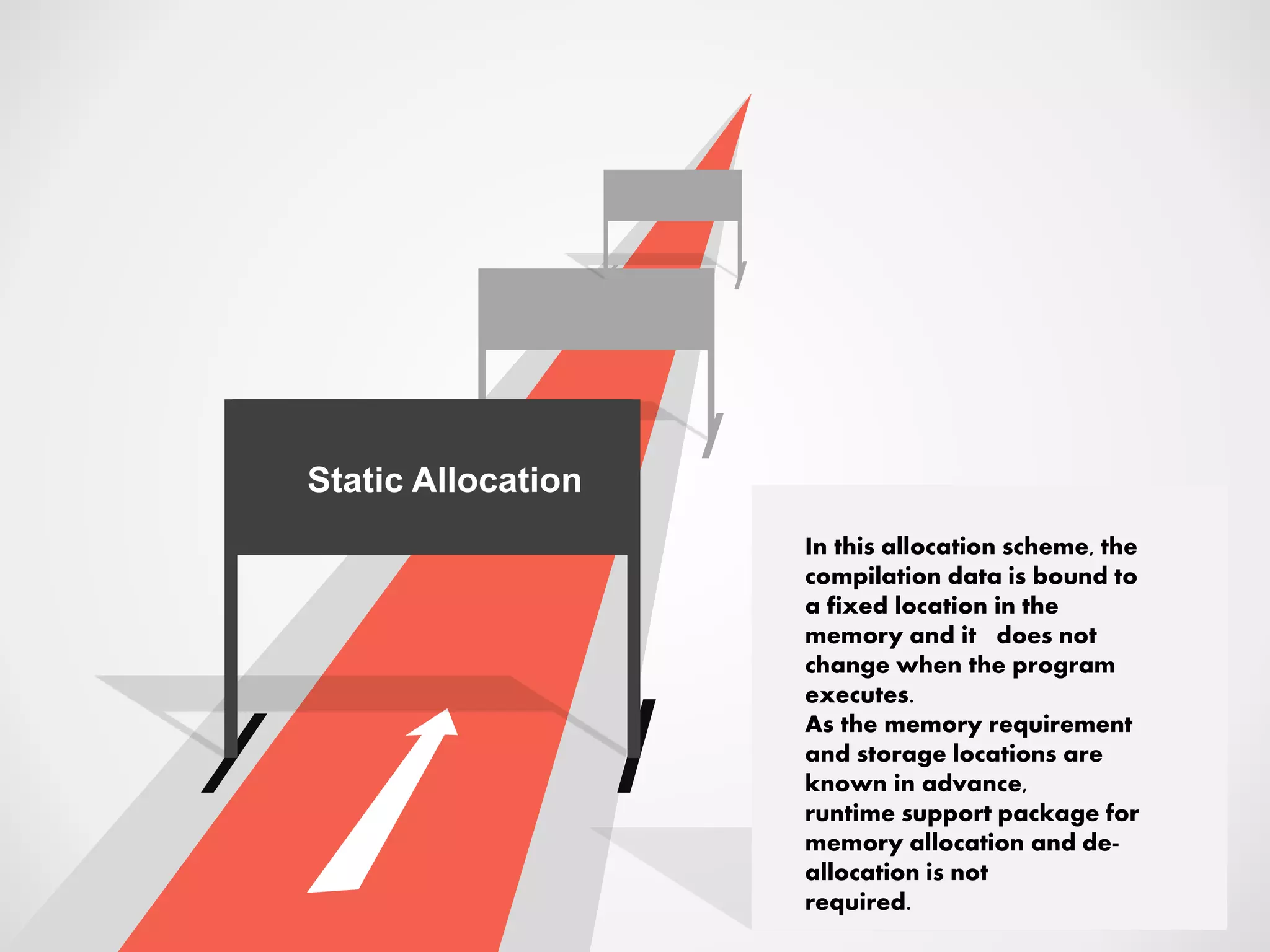
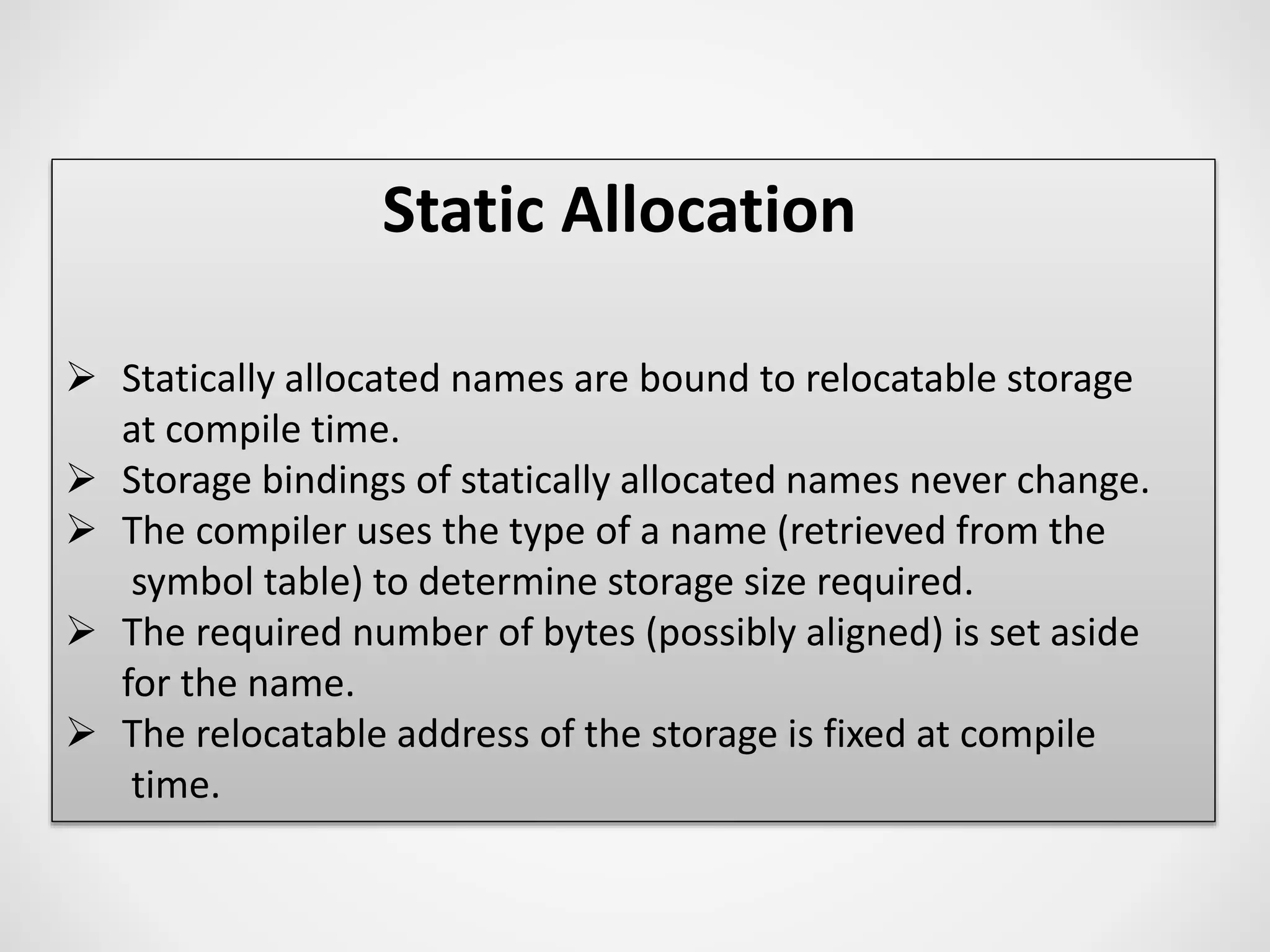
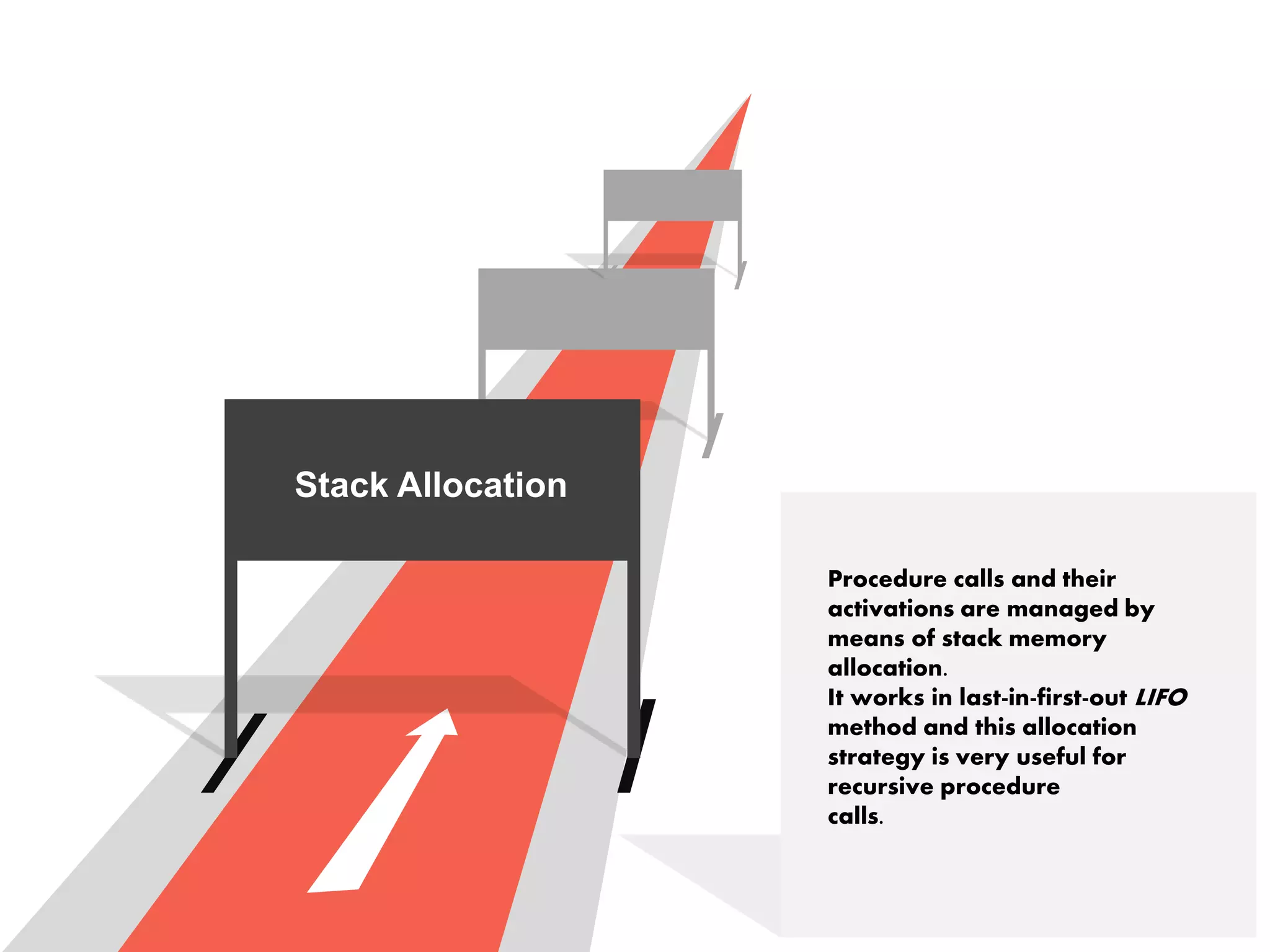
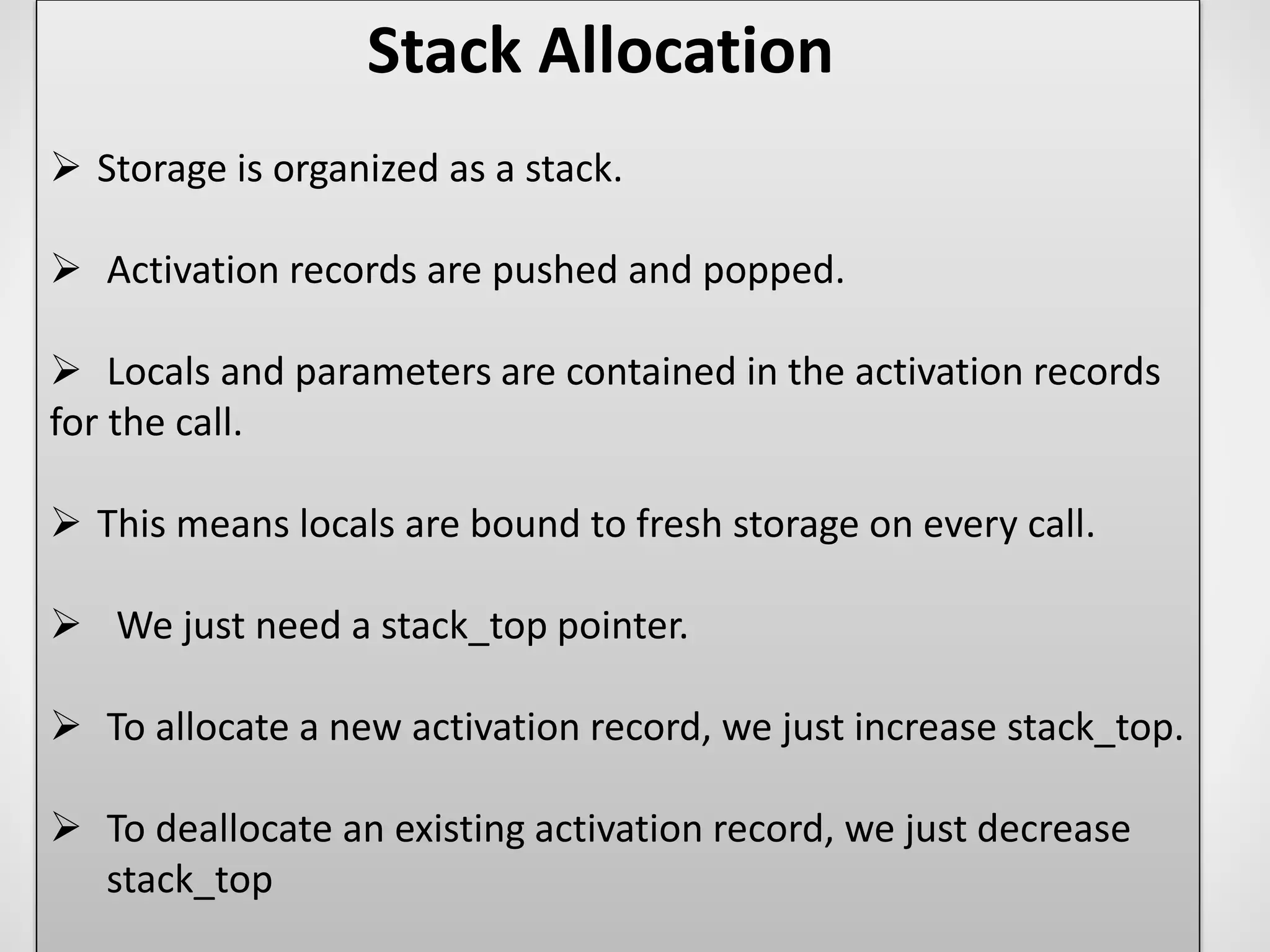
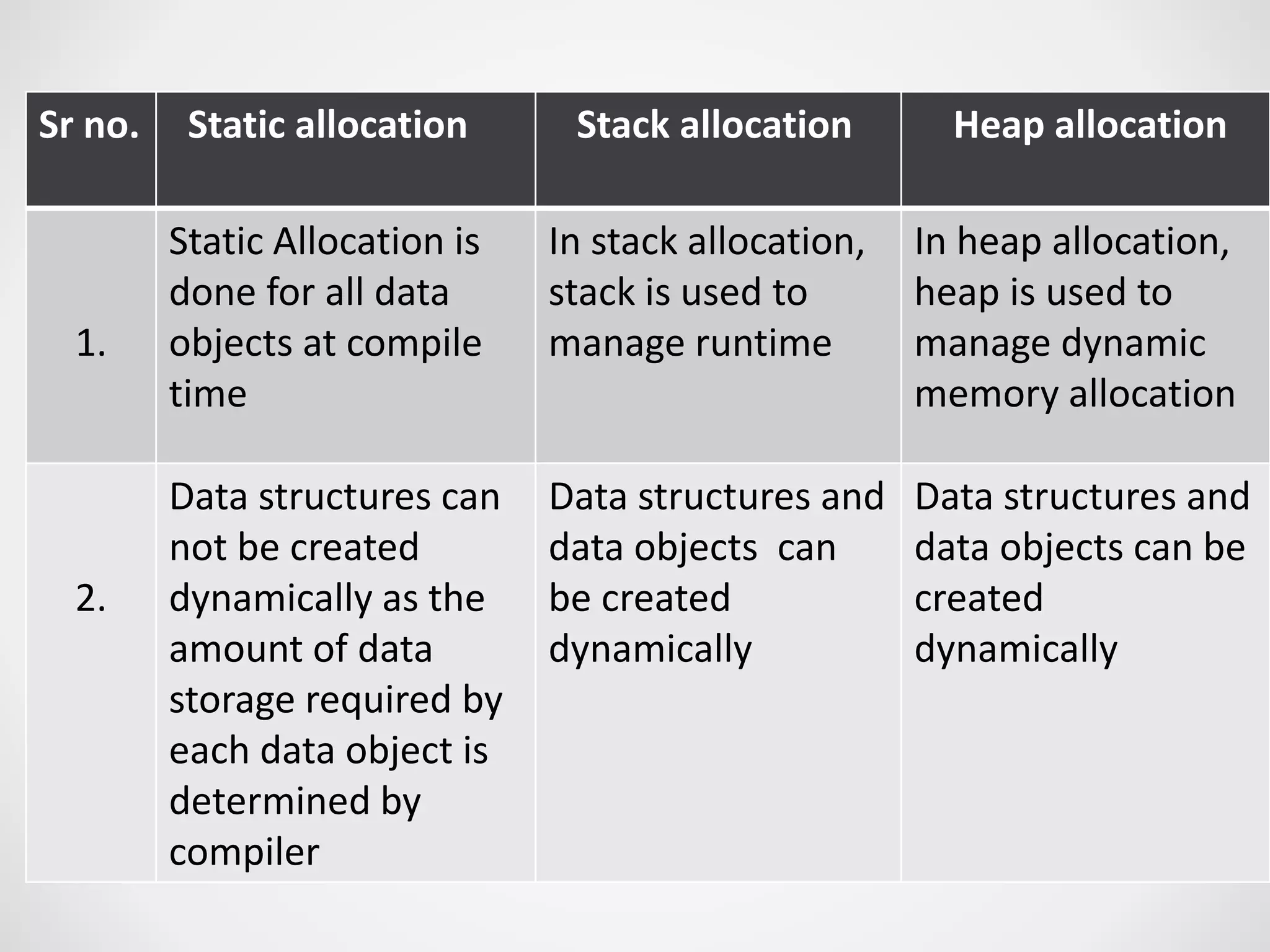
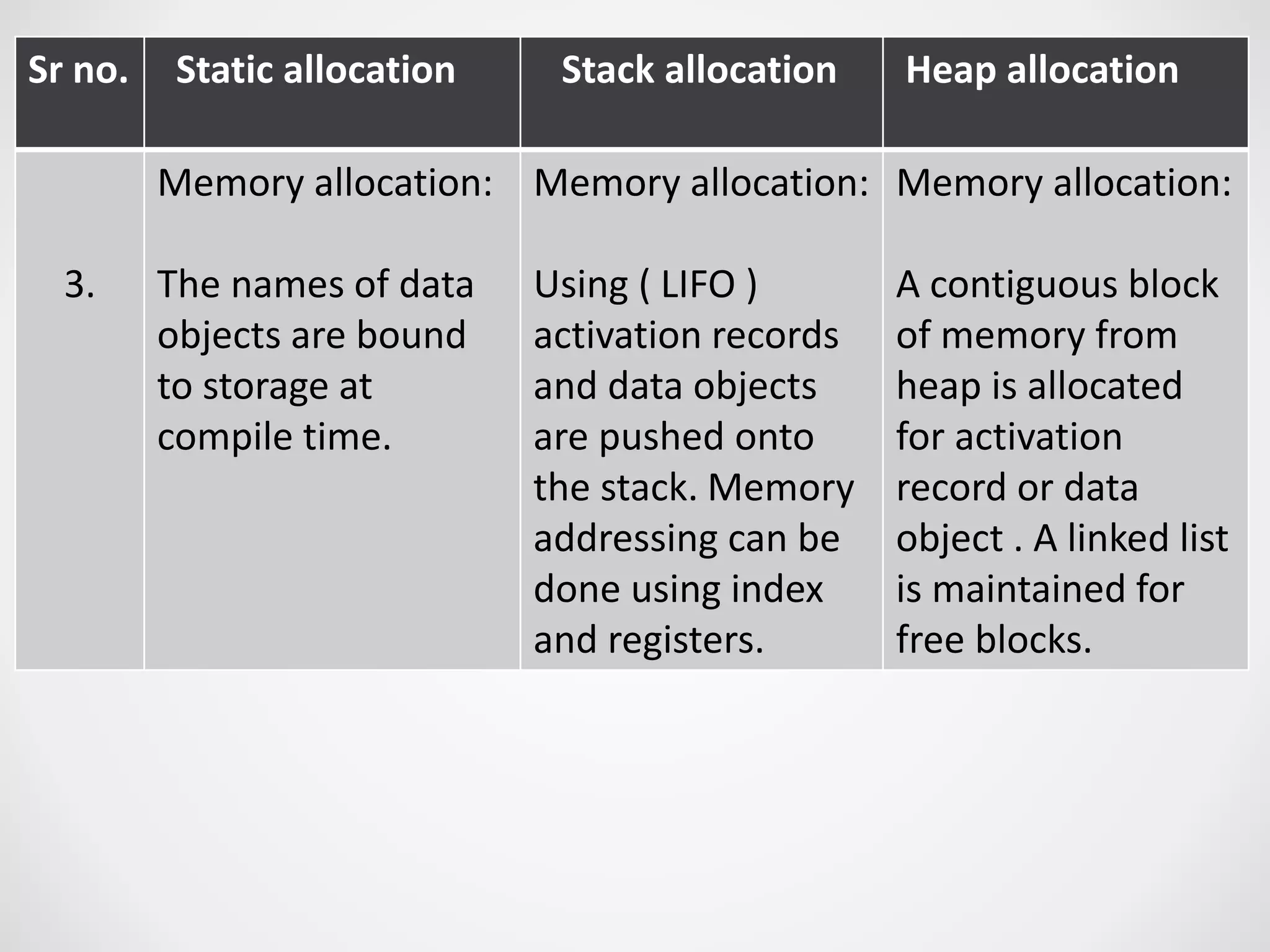
1. Static allocation assigns storage locations to data objects at compile time. Stack allocation uses a stack to dynamically allocate memory for procedure activations and local variables at runtime. Heap allocation allocates memory for dynamic data structures from a heap region at runtime.
2. Access to non-local names can use lexical scoping by following access links or displays, or dynamic scoping by searching the stack.
3. Blocks can be nested and treated as parameterless procedures, with memory allocated on the stack when entered and deallocated on exit.
4. The activation record stores information for a procedure execution, including local data, saved registers, parameters, return values, and links to enclosing activations.















![Access to non-local names
Static or Lexical scoping
Displays
Faster access to non-locals than with access links can be
obtained using an array d of pointers to activation records,
called a display.
We maintain the display so that storage for a non-
local a at nesting depth i is in the activation record pointed to
by display element d [i].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/runtimeadministration-170321135039/75/Run-time-administration-23-2048.jpg)









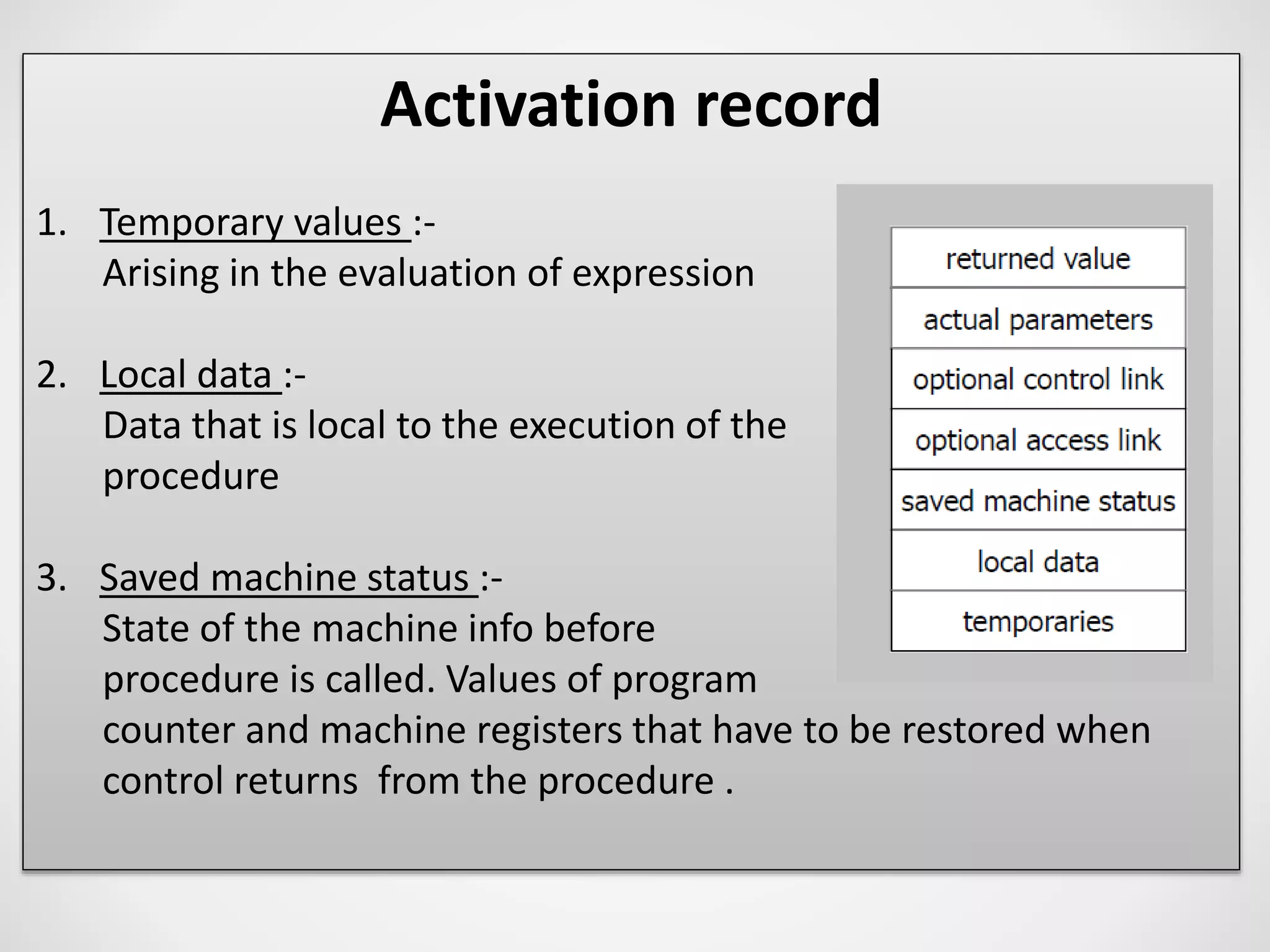
![Activation record
4. Access links :-
refers non local data held in other activation
records.
5. Control link :-
points to the activation record of the caller.
6. Actual parameters :-
used by the calling procedure to supply
parameters to the called procedure .
[ in practice these are passed in registers ]
7. Returned values :-
used by the called procedures to return a value to the calling
procedure.
[ in practice it is returned in a register ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/runtimeadministration-170321135039/75/Run-time-administration-34-2048.jpg)



