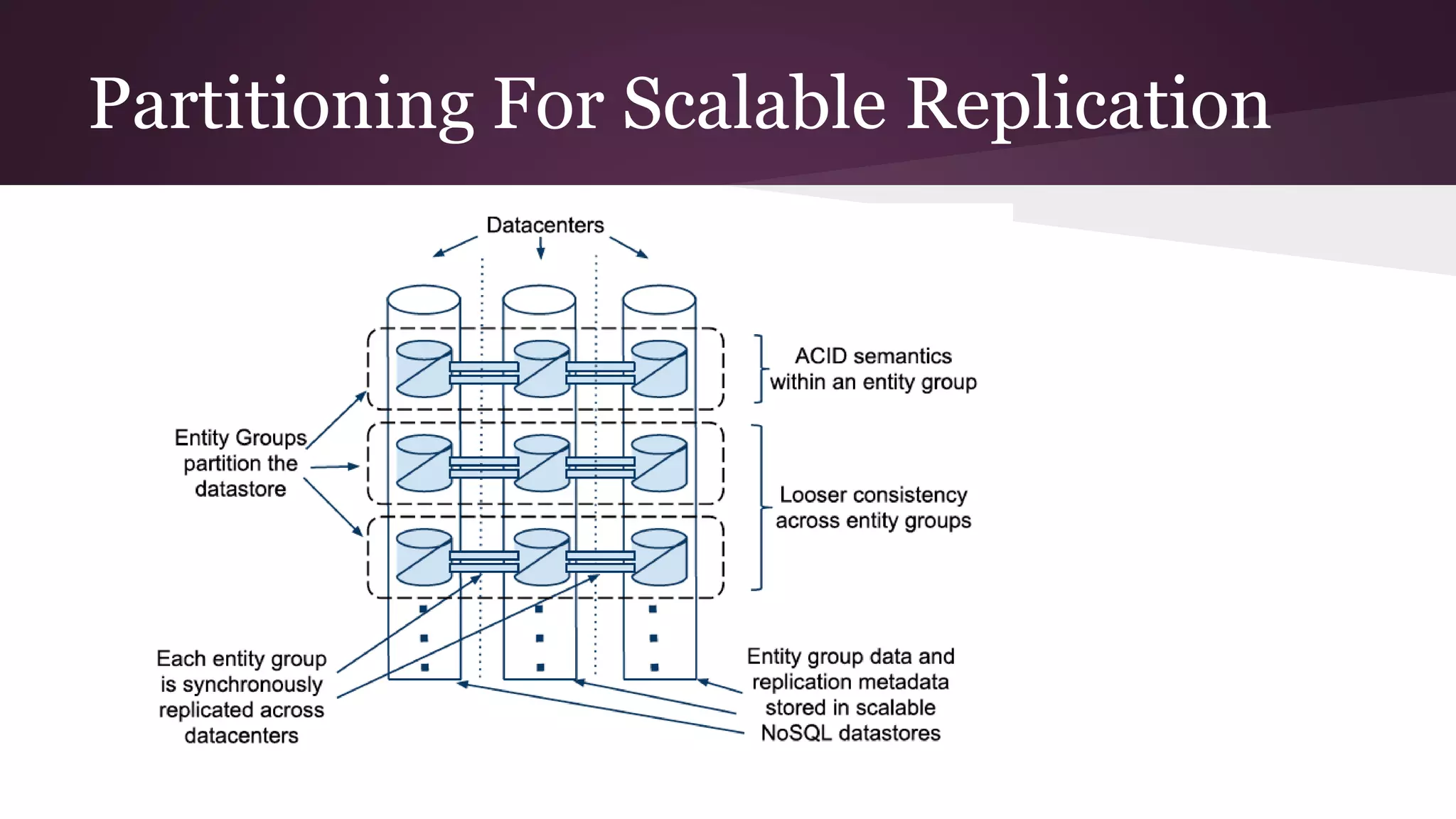
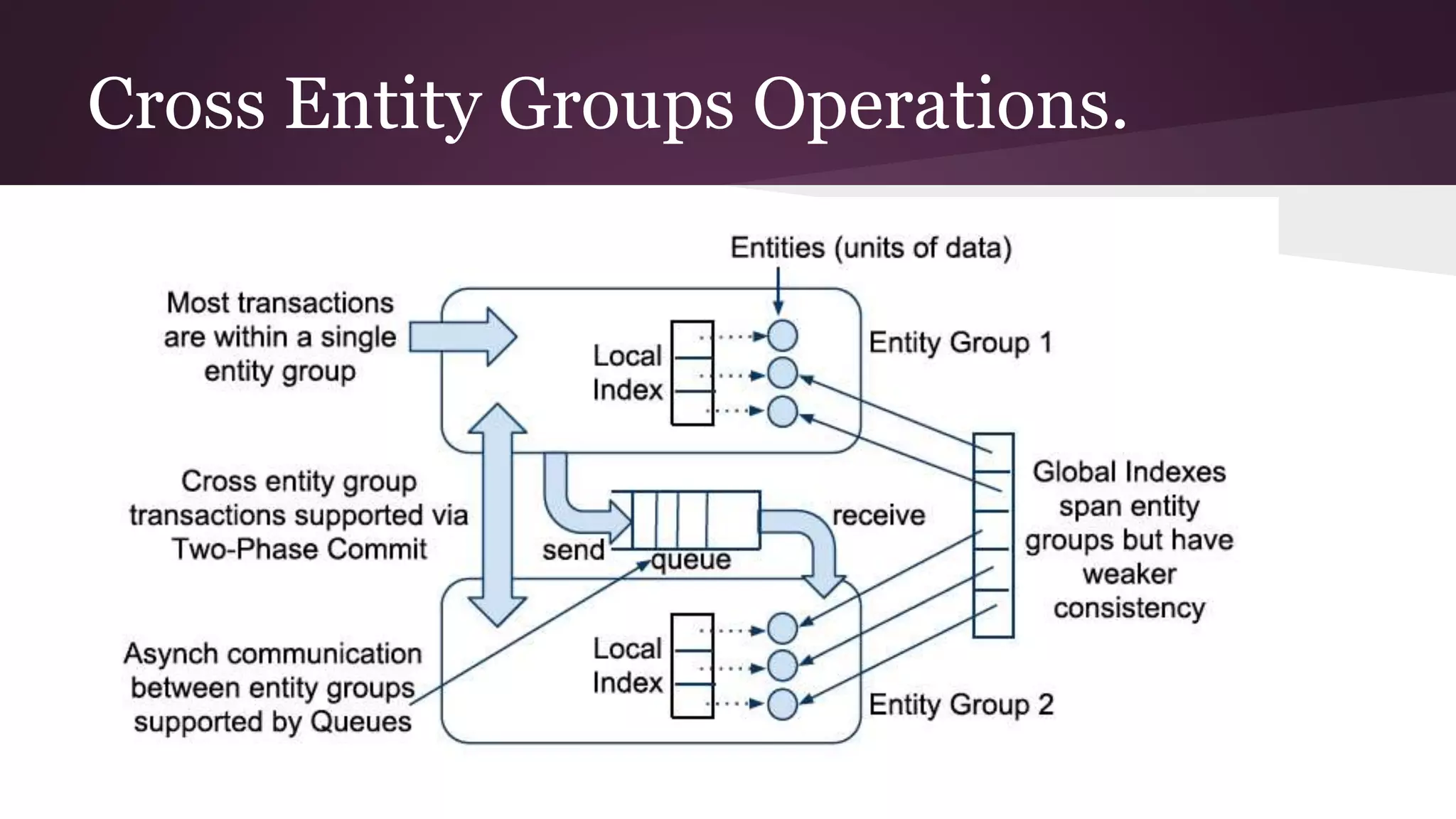
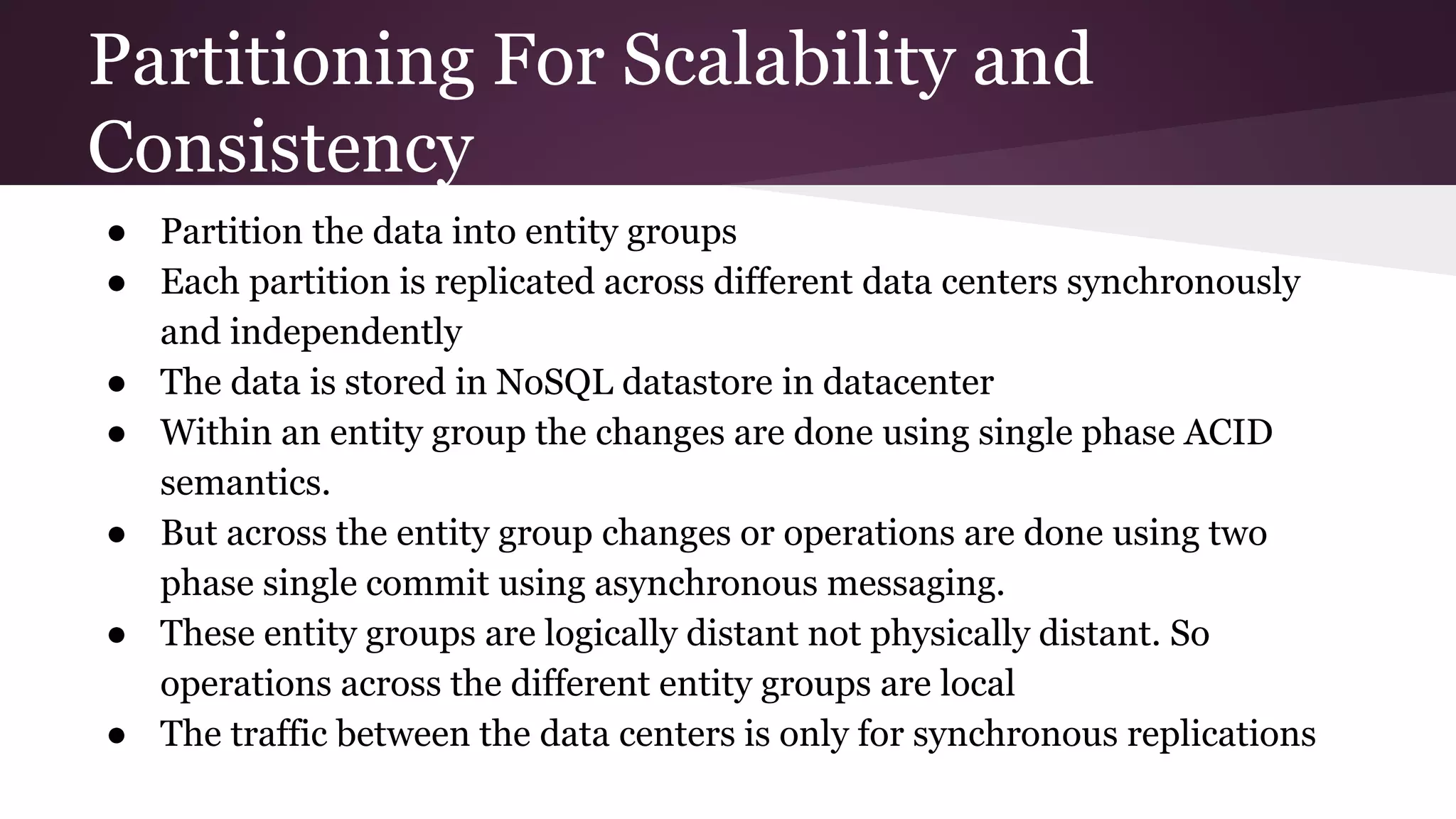
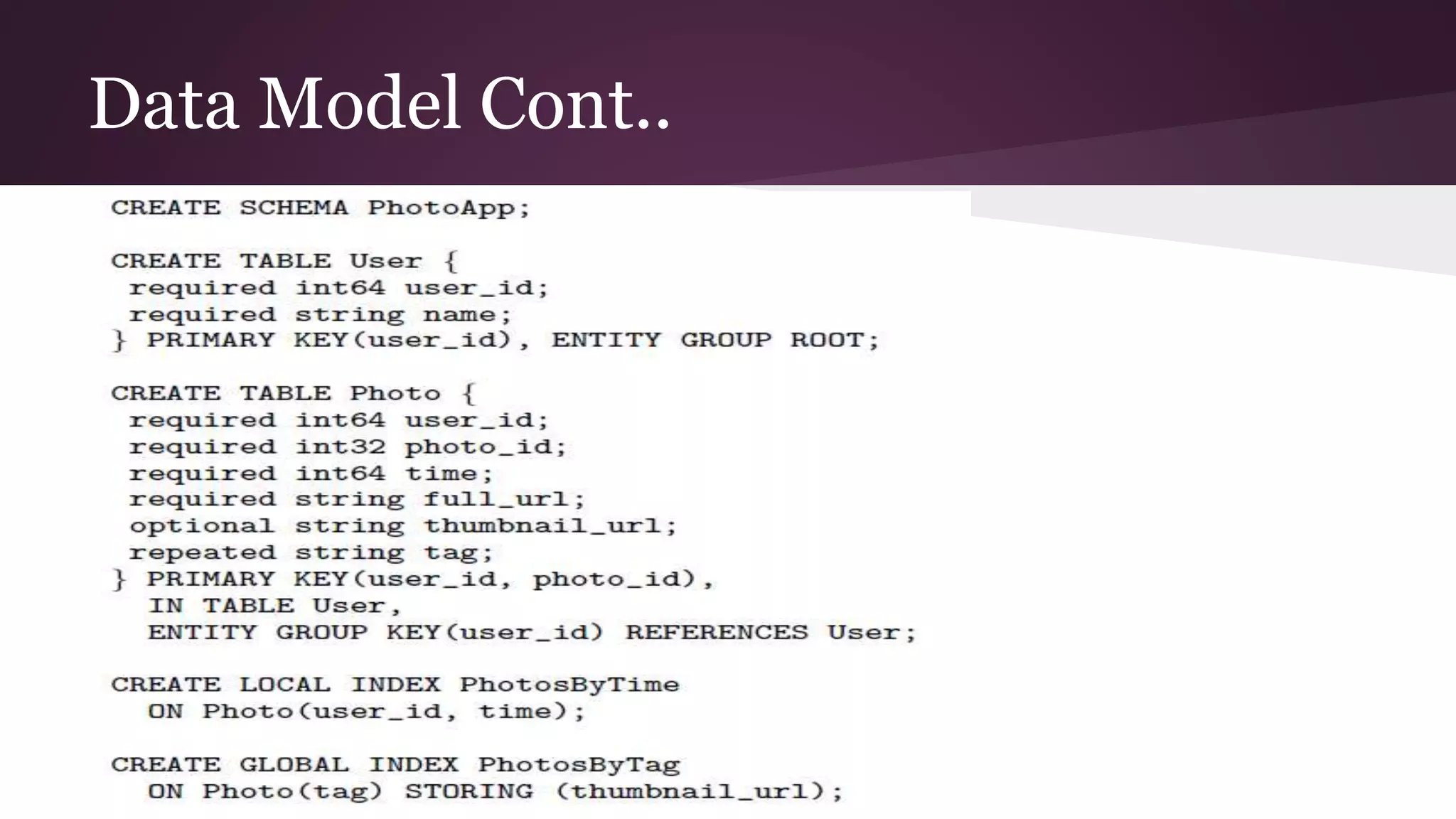
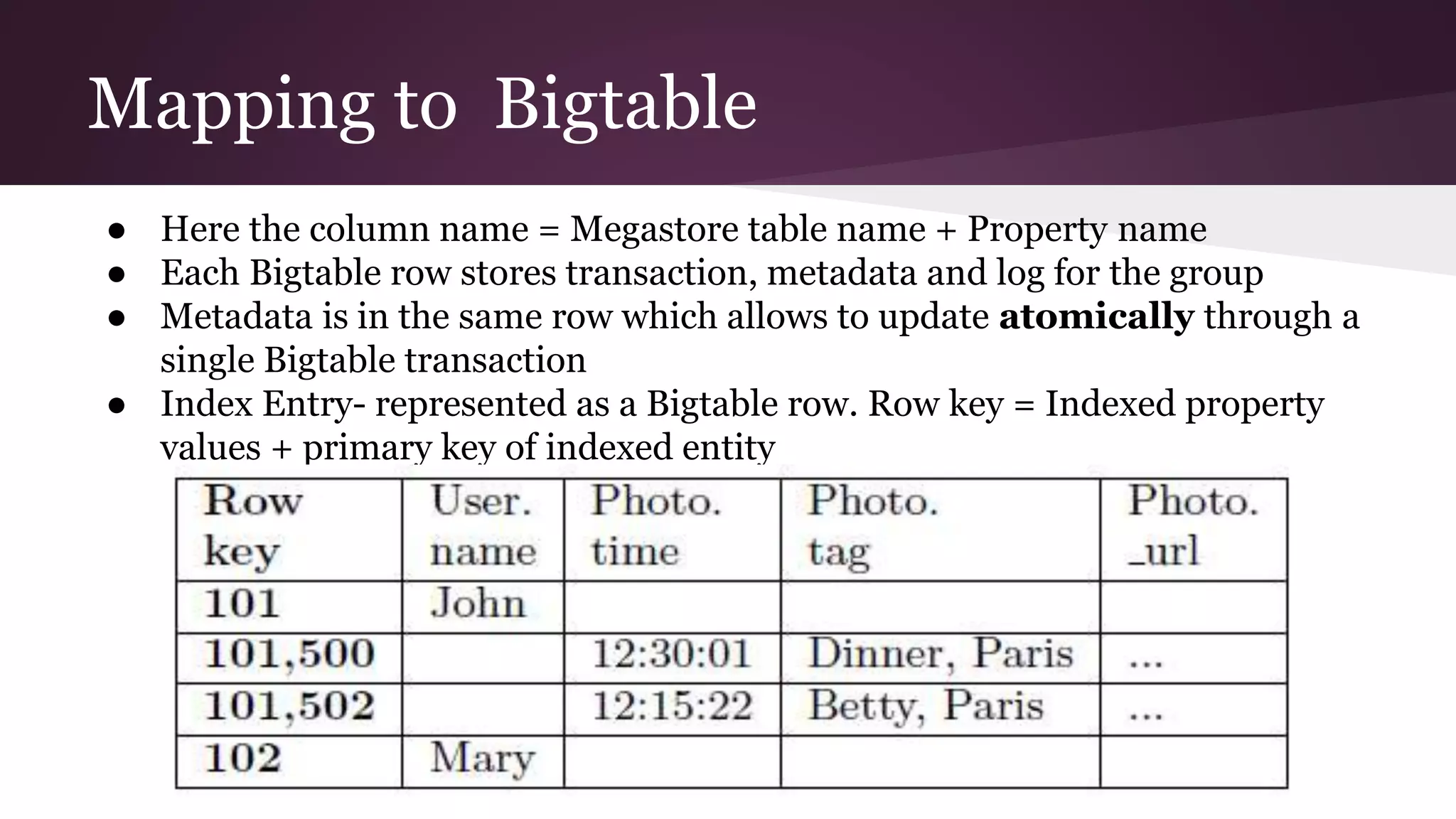
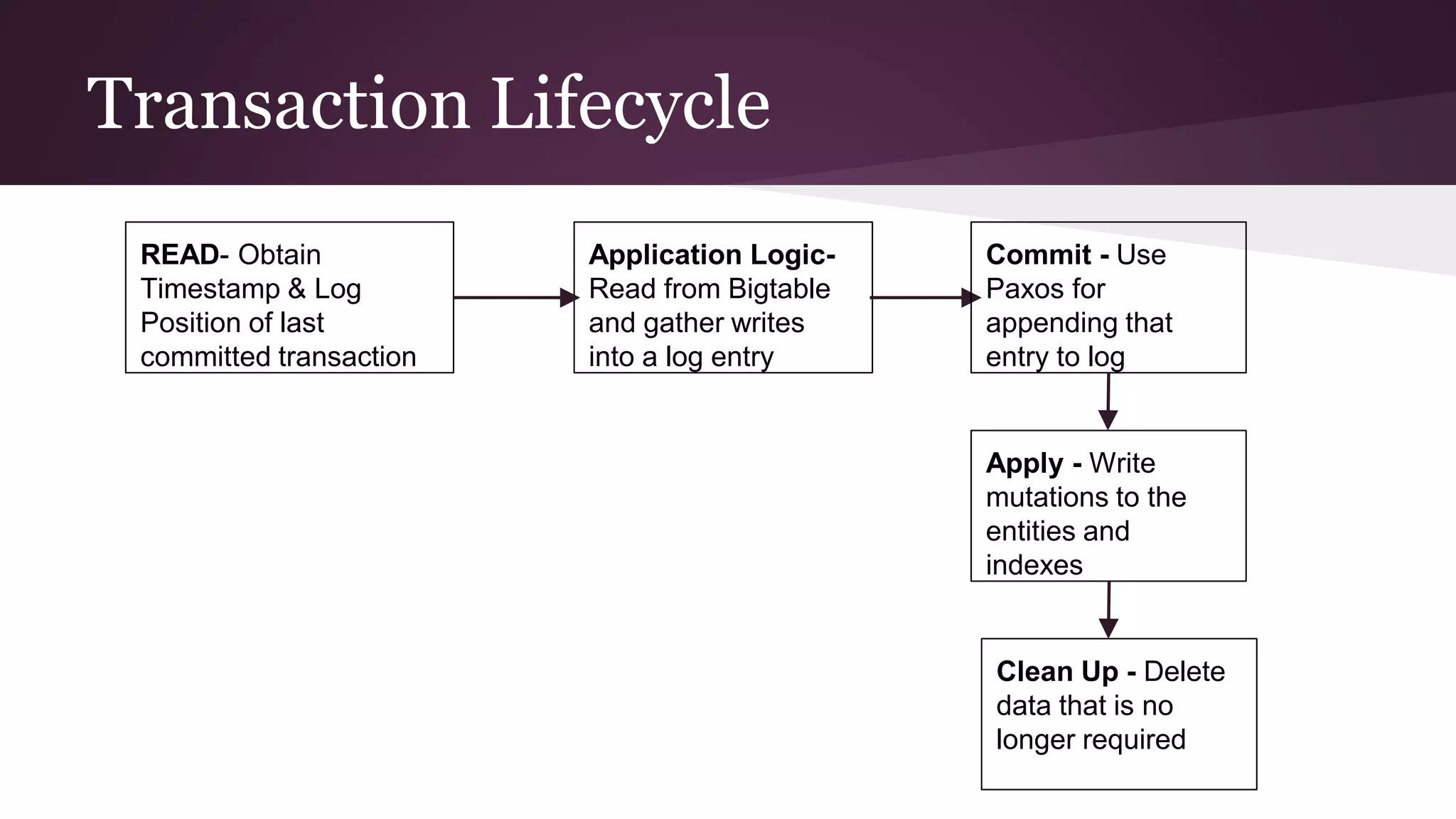
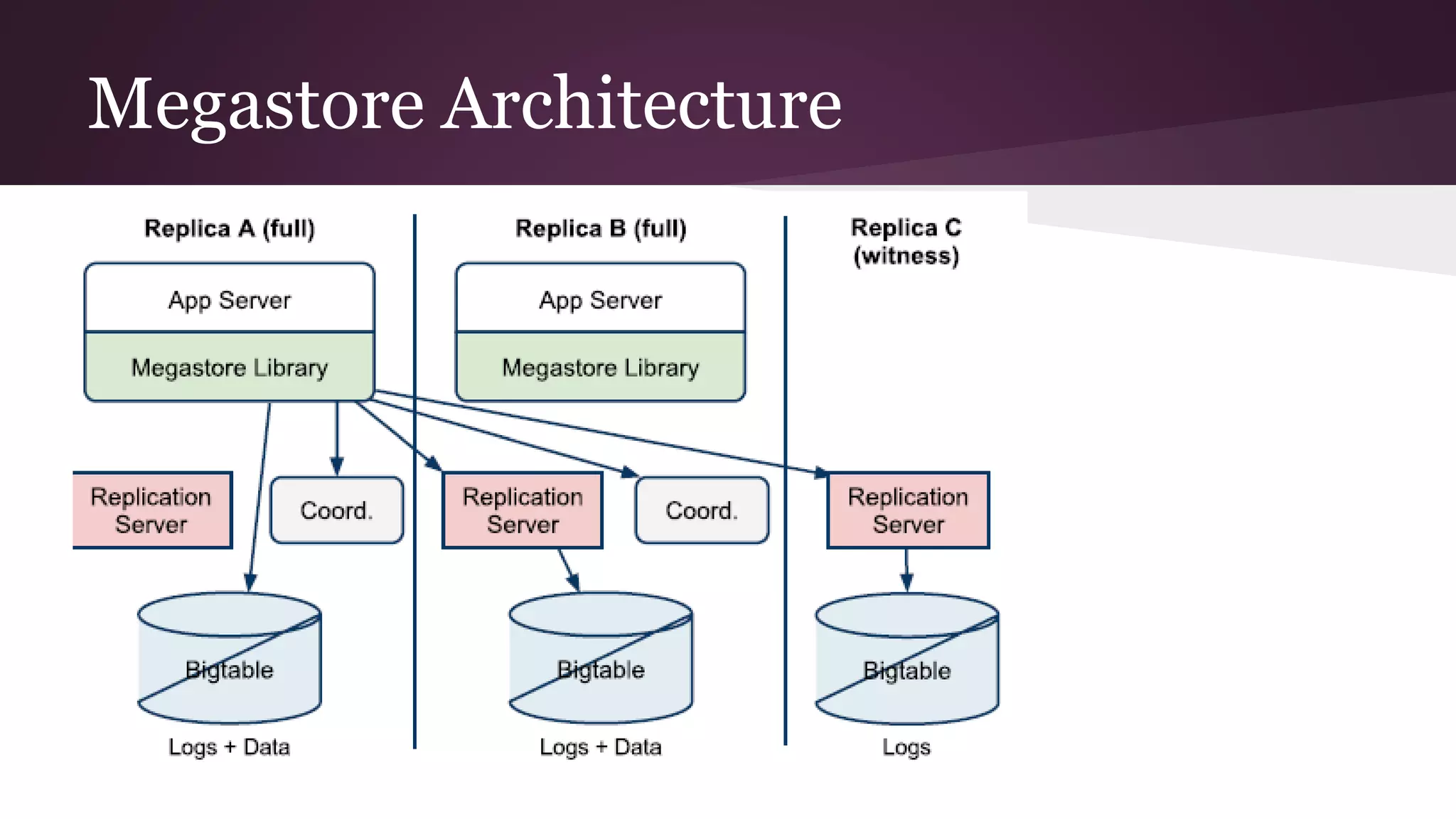
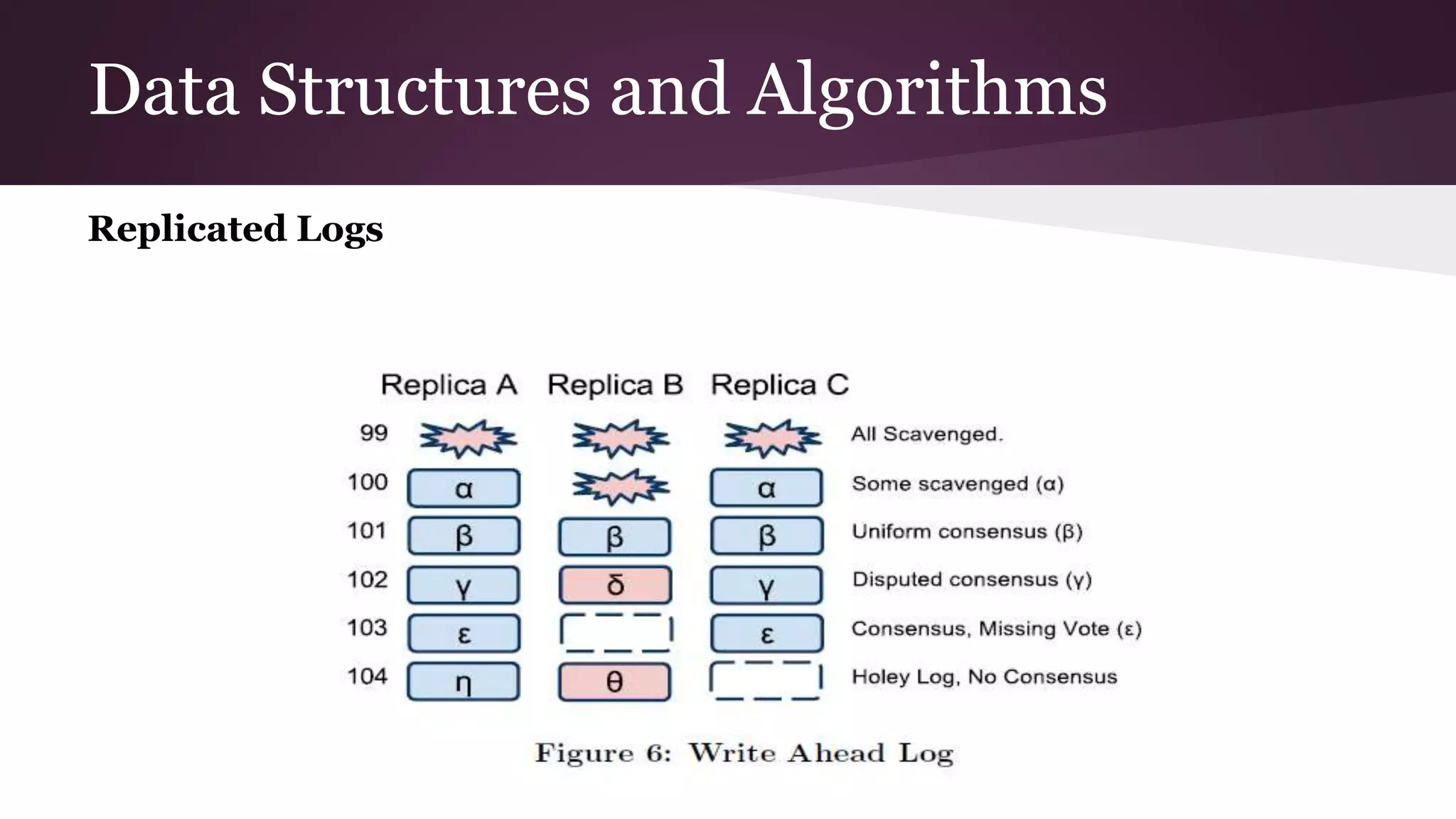
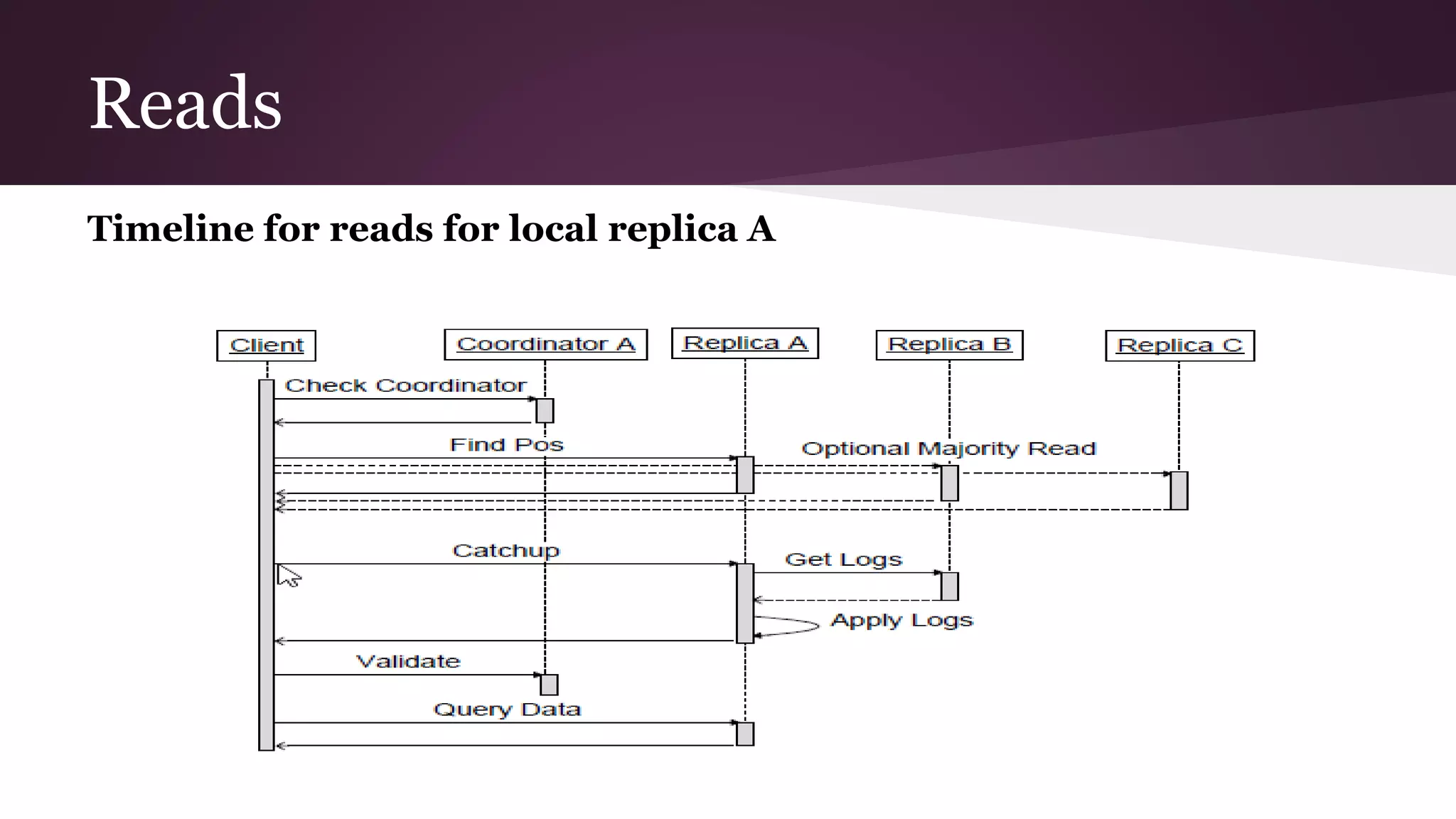
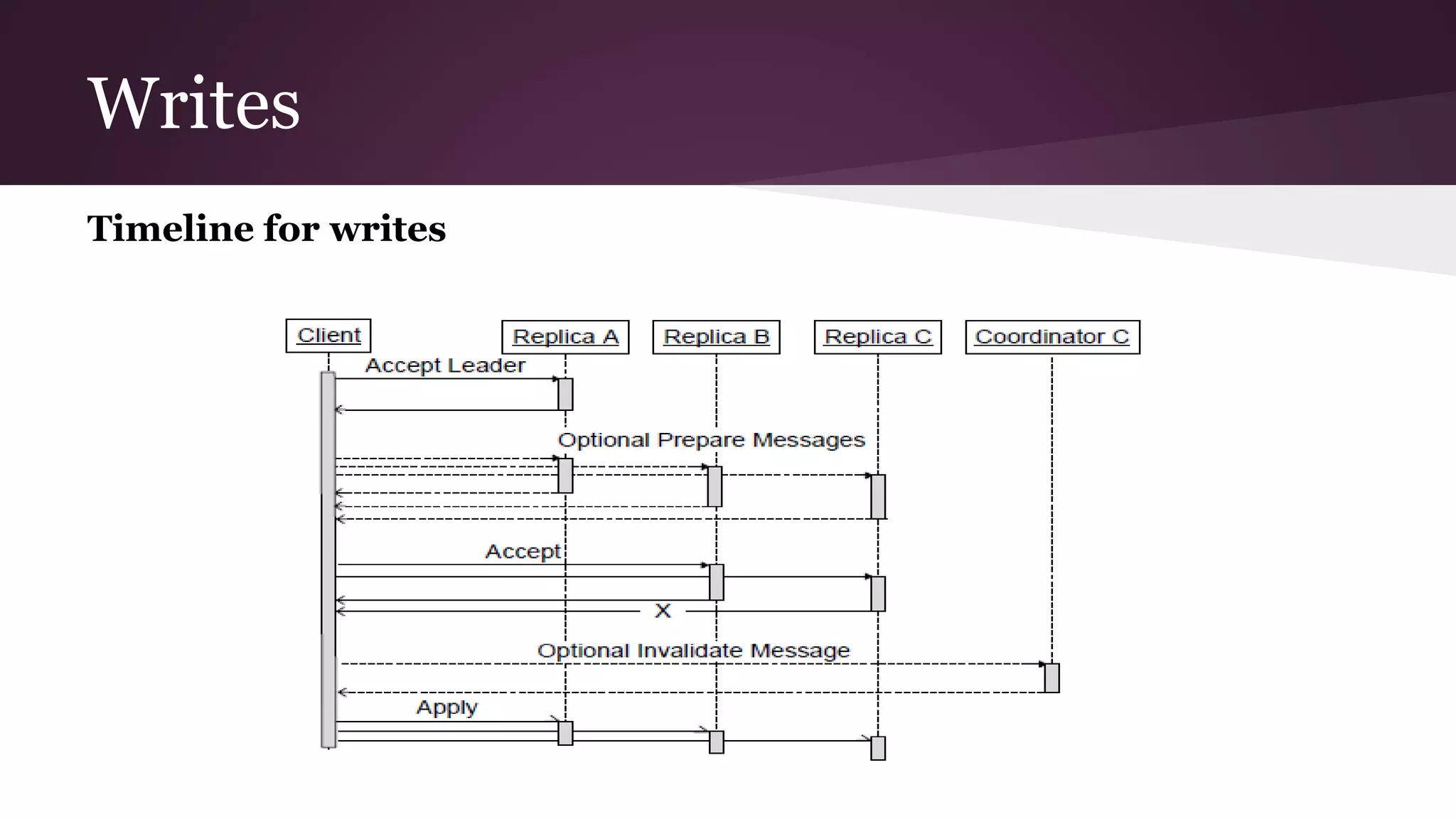
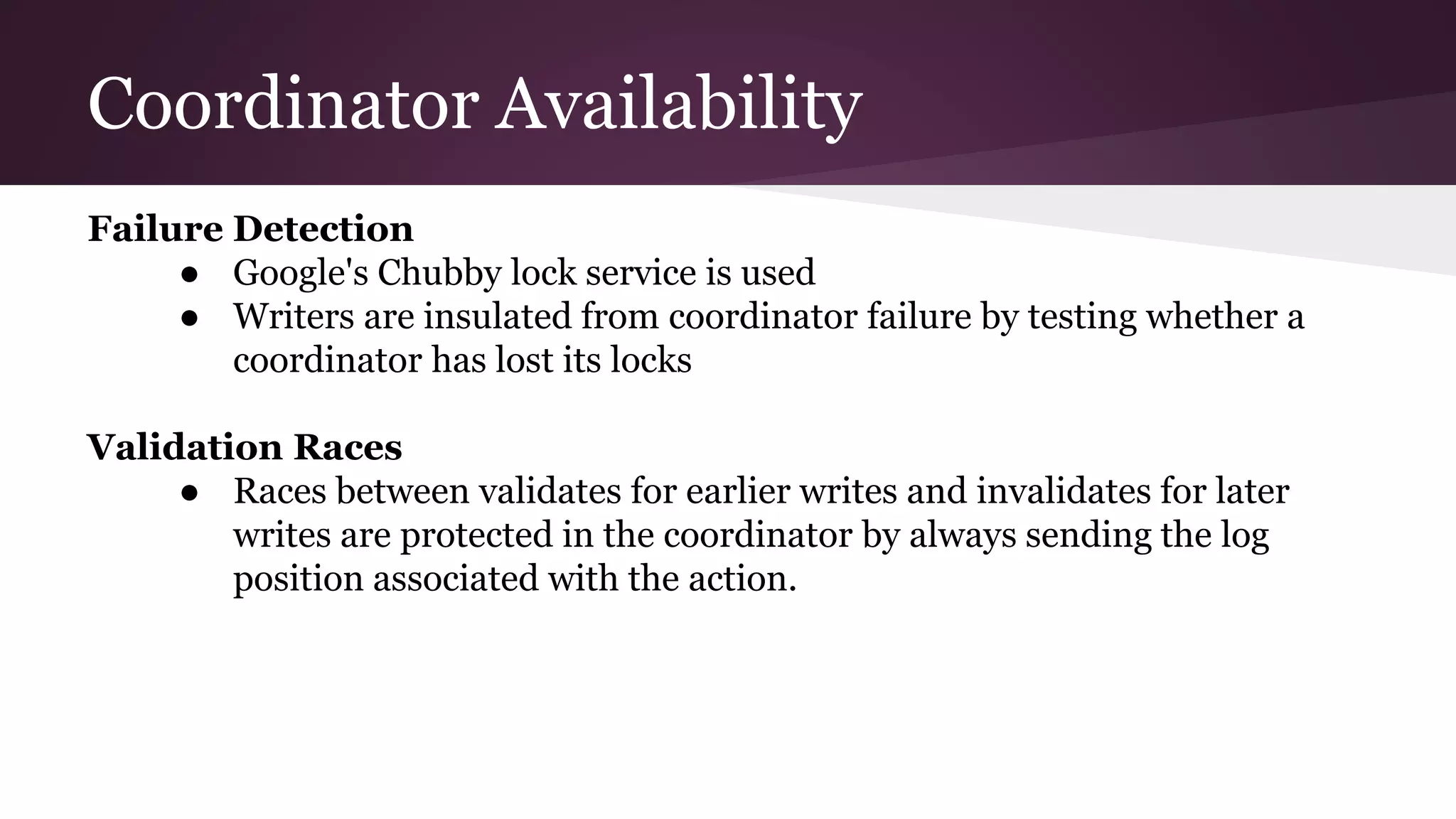
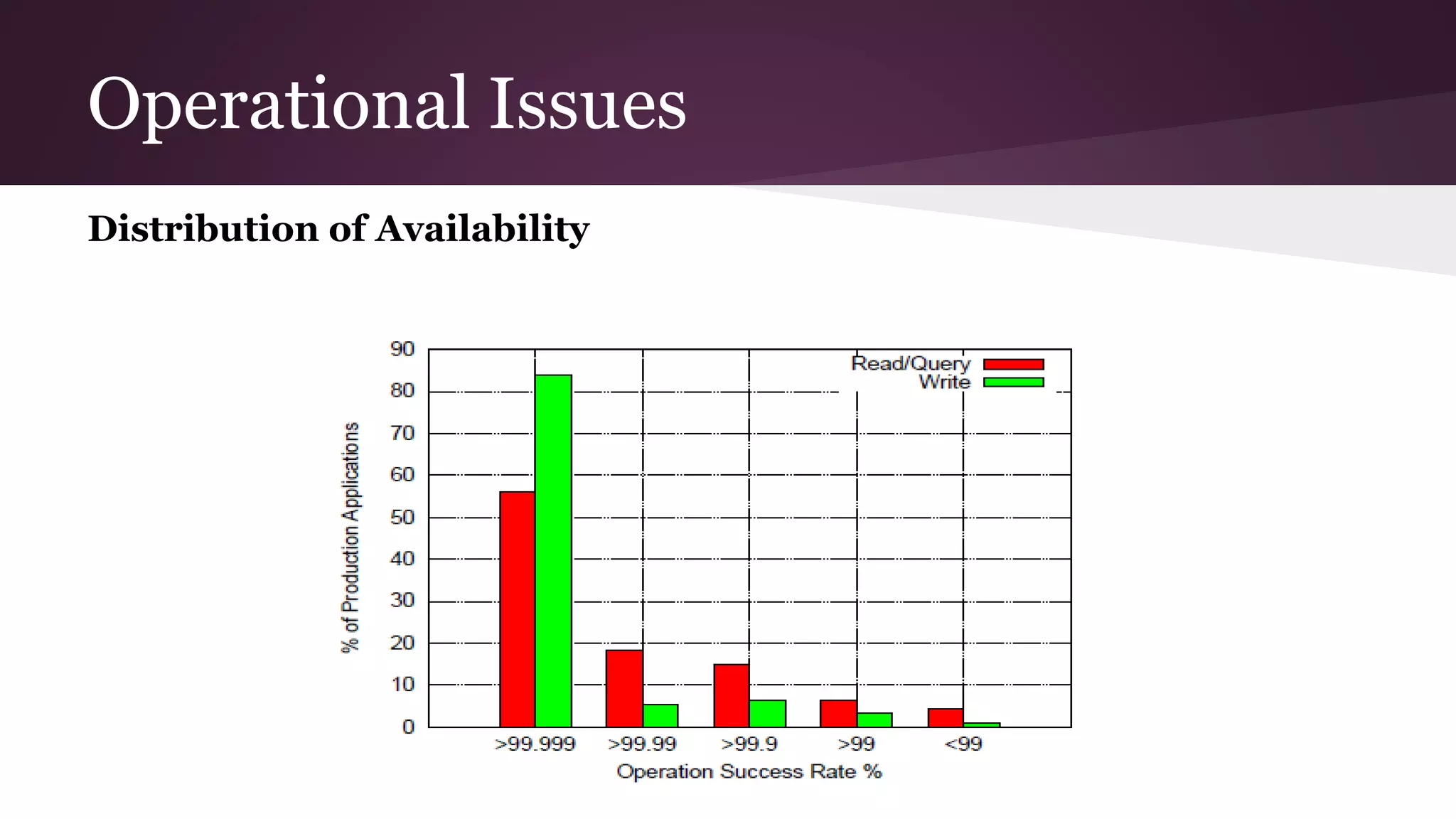
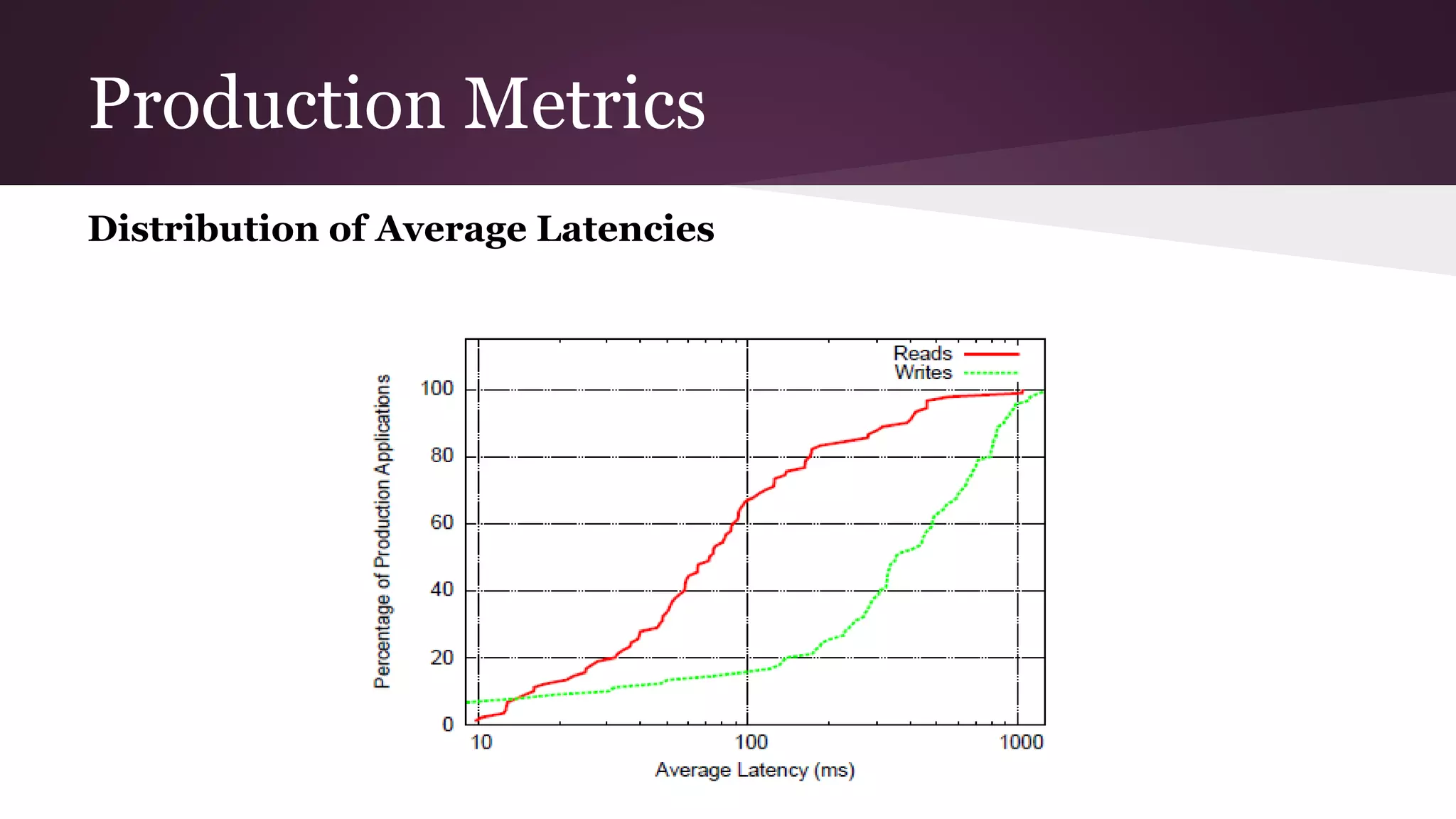
Megastore combines the scalability of NoSQL with the ACID properties of relational databases. It uses Paxos replication across data centers to provide high availability with low latency. The data is partitioned into entity groups which are replicated independently to allow for scale. Transactions within a group use multi-version concurrency control and across groups use two-phase commit. Coordinators track write ordering to prevent conflicts during reads and writes. Metrics from Google showed Megastore provided low latency access even with widespread data distribution.