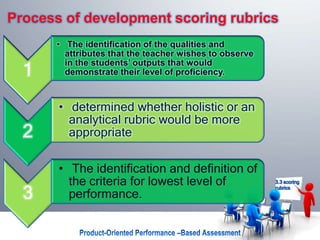
Scoring rubrics are descriptive schemes developed by teachers or evaluators to guide analysis of student work. They describe levels of quality expected for a task and can be used to evaluate a variety of projects and activities. When developing a rubric, teachers identify the key criteria for assessment, such as quality, creativity, accuracy, and aesthetics. Rubrics support evaluation by examining the extent criteria are met and provide feedback to help students improve. Rubrics are an appropriate technique for grading essays and can also be used to evaluate group activities, projects, and presentations.