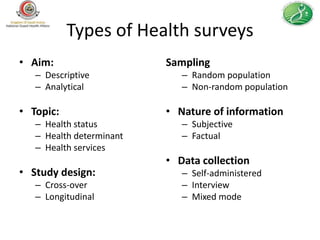
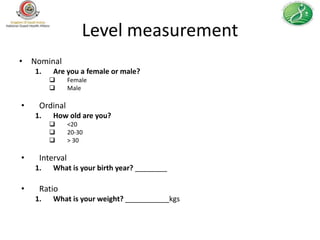
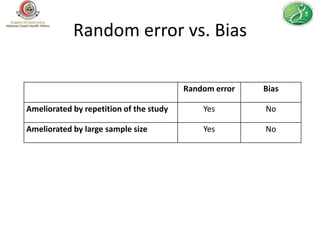
This document provides guidance on how to write an effective health survey. It outlines the key steps in designing a health survey, including formulating objectives, defining variables, choosing a data collection method, writing questions, formatting the questionnaire, sampling, and pilot testing. It discusses types of survey questions, such as factual, opinion, and knowledge questions, and how to format questions, response options, and scales. The document emphasizes writing clear, unbiased questions and avoiding errors like double questions or difficult recall questions. It also covers ethical considerations like informed consent and maintaining confidentiality.