Routes of Drug Administration
- 2. Oral Medications (p.o.) • Pills Must Dissolve/Breakdown • Syrups/Suspensions are more rapid onset • Most Absorbed in Small Intestine • compressed tablet – must be “scored” to divide
- 3. Sustained Release Oral • Do Not Break • Enteric Coated • Beads or Granules • Matrix i.e. Slow K • Repeat action i.e. Chlor-Trimetron • Osmotic Pump i.e. Acutrim
- 4. Sublingual / Buccal • Rapid absorption and response • Highly vascular areas • Avoids “First Liver Bypass”
- 6. Rectal • Advantages – nausea, NPO, difficulty swallowing – avoids first liver bypass • Disadvantages – Maybe erratic absorption – May cause irritation
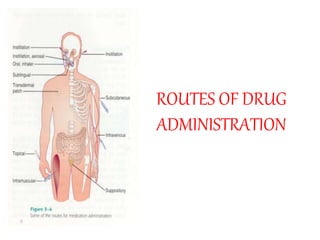
- 8. Definition: A route of administration is the path by which a drug, fluid, poison or other substance is brought into contact with the body.
- 9. Routes of Drug Administration The route of administration (ROA) that is chosen may have a profound effect upon the speed and efficiency with which the drug acts Important Info
- 10. • The possible routes of drug entry into the body may be divided into two classes: –Enteral –Parenteral
- 11. Classification Routes of administration can broadly be divided into: • Topical: Drugs are applied topically to the skin or mucous membranes, mainly for local action. • Oral: used for systemic (non-local) effect, substance is given via the digestive tract. • Parenteral: A drug administered parenterally is one injected via a hollow needle into the body at various sites and to varying depth. • Rectal: Drugs given through the rectum by suppositories or enema. • Inhalation: The lungs provide an excellent surface for absorption when the drug is delivered in gaseous, aerosol or ultrafine solid particle form.
- 13. Enteral Routes • Enteral - drug placed directly in the GI tract: –sublingual - placed under the tongue –oral - swallowing (p.o., per os) –rectum - Absorption through the rectum
- 14. 1- Topical route: I Skin A-Dermal – cream, ointment (local action) B- Transdermal- absorption of drug through skin (i.e systemic action) I. stable blood levels(controlled drug delivery system) II. No first pass metabolism III. Drug must be potent or patch becomes too large II Mucosal membranes •eye drops (onto the conjunctiva) • ear drops • intranasal route (into the nose)
- 15. 2- Oral route: - By swallowing. - It is intended for systemic effects resulting from drug absorption through the various epithelia and mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract.
- 16. Advantages: 1- Convenient - portable, no pain, easy to take. 2- Cheap - no need to sterilize, compact, multi-dose bottles, automated machines produce tablets in large quantities. 3- Variety - tablets, capsules, suspensions, mixtures . 2 -Oral route (Cont.)
- 17. Disadvantages: 1- Sometimes inefficient - low solubility drugs may suffer poor availability e.g. Griseofulvin 2- First-pass effect - drugs absorbed orally are transported to the general circulation via the liver. Thus drugs which are extensively metabolized will be metabolized in the liver during absorption. e.g. propranolol 2- Oral route (Cont.)
- 18. First-pass Effect • The first-pass effect is the term used for the hepatic metabolism of a pharmacological agent when it is absorbed from the gut and delivered to the liver via the portal circulation. The greater the first-pass effect, the less the agent will reach the systemic circulation when the agent is administered orally
- 19. First-pass Effect cont. Magnitude of first pass hepatic effect: Extraction ratio (ER) ER = CL liver / Q ; where Q is hepatic blood flow (usually about 90 L per hour. Systemic drug bioavailability (F) may be determined from the extent of absorption (f) and the extraction ratio (ER): F = f x (1 -ER)
- 20. First pass effect: First pass effect
- 21. - The first pass effect is the term used for the hepatic metabolism of a pharmacological agent when it is absorbed from the gut and delivered to the liver via the portal circulation. - The greater the first pass effect, the lower the bioavailability of the drug(the rate and extent of the drug reaching systemic circulation). First pass effect (Cont.):
- 22. 3- Food - Food and G-I motility can affect drug absorption. Often patient instructions include a direction to take with food or take on an empty stomach. - Absorption is slower with food(milk and milk products) for tetracyclines and penicillins, etc. However, for propranolol bioavailability is higher after food, and for griseofulvin absorption is higher after a fatty meal. 2-Oral route (Cont.):
- 23. 4- Sometimes may have adverse reactions – e.g. Antibiotics may kill normal gut flora and allow overgrowth of fungal varieties. Thus, antifungal agent may be included with an antibiotic. 5- Not suitable for unconscious patient - Patient must be able to swallow solid dosage forms. Liquids may be given by tube. 2- Oral route (Cont.)
- 24. 6- May cause irritation to gastric mucosa, nausea and vomiting. 7- Effect too slow for emergencies. 2-Oral route (Cont.)
- 25. Oral • Advantages – Convenient - can be self- administered, pain free, easy to take – Absorption - takes place along the whole length of the GI tract – Cheap - compared to most other parenteral routes
- 26. Oral • Disadvantages – Sometimes inefficient - only part of the drug may be absorbed – First-pass effect - drugs absorbed orally are initially transported to the liver via the portal vein – irritation to gastric mucosa - nausea and vomiting
- 27. Oral • Disadvantages cont. – destruction of drugs by gastric acid and digestive juices – effect too slow for emergencies – unpleasant taste of some drugs – unable to use in unconscious patient
- 28. 3- Buccal/Sublingual route: • Some drugs are taken as smaller tablets which are held in the mouth (buccal tablet) or under the tongue (sublingual tablet). • Buccal tablets are often harder tablets [4 hour disintegration time], designed to dissolve slowly. • E.g Nitroglycerin, as a softer sublingual tablet [2 min disintegration time], may be used for the rapid relief of angina.
- 29. Advantages 1- Avoid hepatic first pass - The liver is by-passed thus there is no loss of drug by first pass effect for buccal administration. Bioavailability is higher. 2- Rapid absorption - Because of the good blood supply to the area, absorption is usually quite rapid. 3- Drug stability - pH in mouth relatively neutral (gf. stomach - acidic). Thus a drug may be more stable. 3- Buccal/Sublingual route (Cont.)
- 30. Disadvantages 1- Holding the dose in the mouth is inconvenient. 2- Small doses only can be accommodated easily. 3- Buccal/Sublingual route (Cont.)
- 31. Sublingual/Buccal Some drugs are taken as smaller tablets which are held in the mouth or under the tongue. • Advantages – rapid absorption – drug stability – avoid first-pass effect
- 32. Sublingual/Buccal • Disadvantages – inconvenient – small doses – unpleasant taste of some drugs
- 34. A- Intravascular (IV, IA): - placing a drug directly into blood stream. -May be - Intravenous (into a vein) or - intraarterial (into an artery). Advantages 1- precise, accurate and immediate onset of action, 100% bioavailability. Disadvantages 1- risk of embolism. 2- high concentrations attained rapidly leading to greater risk of adverse effects. 4- Parenteral route (Cont.)
- 35. 4- Parenteral route (Cont) B-Intramuscular :(into the skeletal muscle). Advantages 1- suitable for injection of drug in aqueous solution (rapid action) and drug in suspension or emulsion (sustained release). Disadvantages 1- Pain at injection sites for certain drugs.
- 36. C- Subcutaneous (under the skin), e.g. insulin. D- Intradermal, (into the skin itself) is used for skin testing some allergens. E- Intrathecal (into the spinal canal) is most commonly used for spinal anesthesia . F- Intraperitoneal, (infusion or injection into the peritoneum) e.g. peritoneal dialysis in case of renal insuffeciency. 4- Parenteral route (Cont)
- 37. 5-Rectal route: Most commonly by suppository or enema. Advantages 1- By-pass liver - Some of the veins draining the rectum lead directly to the general circulation, thus by-passing the liver. Reduced first-pass effect. 2- Useful - This route may be most useful for patients unable to take drugs orally (unconscious patients) or with younger children. - if patient is nauseous or vomiting
- 38. Disadvantages 1- Erratic absorption - Absorption is often incomplete and erratic. 2- Not well accepted. 5- Rectal route (Cont.)
- 39. 6- Inhalation route: - Used for gaseous and volatile agents and aerosols. - solids and liquids are excluded if larger than 20 micron. the particles impact in the mouth and throat. Smaller than 0.5 micron , they aren't retained. Advantages A- Large surface area B- thin membranes separate alveoli from circulation C- high blood flow - As result of that a rapid onset of action due to rapid access to circulation.
- 40. Disadvantages 1- Most addictive route of administration because it hits the brain so quickly. 2- Difficulties in regulating the exact amount of dosage. 3- Sometimes patient having difficulties in giving themselves a drug by inhaler. 6- Inhalation route (Cont.)
- 41. 1. unconscious patients and children 2. if patient is nauseous or vomiting 3. easy to terminate exposure 4. absorption may be variable 5. good for drugs affecting the bowel such as laxatives 6. irritating drugs contraindicated Rectal
- 42. Parenteral Routes – Intravascular (IV, IA)- placing a drug directly into the blood stream – Intramuscular (IM) - drug injected into skeletal muscle – Subcutaneous - Absorption of drugs from the subcutaneous tissues – Inhalation - Absorption through the lungs
- 45. Intravascular Absorption phase is bypassed (100% bioavailability) 1.precise, accurate and almost immediate onset of action, 2. large quantities can be given, fairly pain free 3. greater risk of adverse effects a. high concentration attained rapidly b. risk of embolism c. OOPS factor or !@#$%
- 46. Intramuscular 1. very rapid absorption of drugs in aqueous solution 2.repository and slow release preparations 3.pain at injection sites for certain drugs
- 47. Subcutaneous 1. slow and constant absorption 2. absorption is limited by blood flow, affected if circulatory problems exist 3. concurrent administration of vasoconstrictor will slow absorption
- 48. 1.gaseous and volatile agents and aerosols 2.rapid onset of action due to rapid access to circulation a.large surface area b.thin membranes separates alveoli from circulation c.high blood flow Particles larger than 20 micron and the particles impact in the mouth and throat. Smaller than 0.5 micron and they aren't retained. Inhalation
- 49. Inhalation cont. • Respiratory system. Except for IN, risk hypoxia. • Intranasal (snorting) Snuff, cocaine may be partly oral via post- nasal dripping. Fairly fast to brain, local damage to septum. Some of the volatile gases also appear to cross nasal membranes. • Smoke (Solids in air suspension, vapors) absorbed across lung alveoli: Nicotine, opium, THC, freebase and crack cocaine, crystal meth.Particles or vapors dissolve in lung fluids, then diffuse. Longer action than volatile gases. Tissue damage from particles, tars, CO. • Volatile gases: Some anaesthetics (nitrous oxide, ether) [precise control], petroleum distillates. Diffusion and exhalation (alcohol). • Lung-based transfer may get drug to brain in as little as five seconds.
- 50. Topical •Mucosal membranes (eye drops, antiseptic, sunscreen, callous removal, nasal, etc.) •Skin a. Dermal - rubbing in of oil or ointment (local action) b. Transdermal - absorption of drug through skin (systemic action) i. stable blood levels ii. no first pass metabolism iii. drug must be potent or patch becomes to large
- 51. • intravenous 30-60 seconds • intraosseous 30-60 seconds • endotracheal 2-3 minutes • inhalation 2-3 minutes • sublingual 3-5 minutes • intramuscular 10-20 minutes • subcutaneous 15-30 minutes • rectal 5-30 minutes • ingestion 30-90 minutes • transdermal (topical) variable (minutes to hours) Route for administration -Time until effect-
- 52. Time-release preparations • Oral - controlled-release, timed-release, sustained-release – designed to produce slow,uniform absorption for 8 hours or longer – better compliance, maintain effect over night, eliminate extreme peaks and troughs
- 53. Time-release preparations • Depot or reservoir preparations - parental administration (except IV), may be prolonged by using insoluble salts or suspensions in non-aqueous vehicles.
- 54. The ROA is determined by the physical characteristics of the drug, the speed which the drug is absorbed and/ or released, as well as the need to bypass hepatic metabolism and achieve high conc. at particular sites Important Info
- 55. No single method of drug administration is ideal for all drugs in all circumstances
- 56. Oral Drugs • Oral medications should be poured and measured at eye level to ensure accuracy.
- 57. Parenteral Drugs • Although the physician will determine the dose and route of a parenteral drug, the nurse is responsible for choosing the correct gauge and length of the needle to be used.
- 58. Equipment to Administer Parenteral Drugs • Syringes (three basic parts: the hub, the barrel, the plunger). • Needles (three basic parts: the hub, the cannula, or shaft, and the bevel). • Ampules (glass containers of single-dose drugs). • Vials (glass, single- or multiple-dose rubber- capped drug containers).
- 59. Intradermal Injection • Injections typically used to diagnose tuberculosis, identify allergens, and administer local anesthetics.
- 60. Subcutaneous Injection • Injections into the subcutaneous tissue, between the dermis and the muscle. • Commonly used in the administration of medications such as insulin and heparin.
- 61. Intramuscular Injection • Used to promote rapid drug absorption and to provide an alternate route when the drug is irritating the subcutaneous tissue.
- 62. Intravenous Therapy • Requires parenteral fluids (hypotonic fluid, isotonic fluid, hypertonic fluid) • Special equipment needed: – Administration set. – IV pole. – Filter. – Regulators to control IV flow rate. – Established venous route.
- 63. Blood Transfusion • To replace blood loss (deficit) with whole blood or blood components. • Special equipment needed: –Administration set. –IV pole. –Filter. –Regulators to control IV flow rate. –Established venous route.
- 64. The Importance of Monitoring • The nurse must always carefully monitor client reactions to medications and ensure that clients are appropriately educated as to the actions, side effects, and contraindications of all medications they are receiving. • Clients receiving IV therapy or blood transfusions require constant monitoring for complications.
- 65. Topical Medications • Eye medications. • Ear medications. • Nasal instillations. • Respiratory inhalants. • Rectal instillations. • Vaginal instillations.
- 66. Transdermal • Absorbed through the skin at a slow, steady rate • Method: – BSI – Clean administration site – Apply medication – Leave medication in place for required time. Monitor the patient for desirable or adverse effects.
- 67. Mucous Membranes • Absorbed through the mucous membranes at a moderate to rapid rate
- 68. Place the pill or direct spray between the underside of the tongue and the floor of the oral cavity. Sublingual Medication Administration
- 69. Place the medication between the patient’s cheek and gum. Buccal Medication Administration
- 70. Use a medication dropper to place the prescribed dosage on the conjunctival sac. Eye Drop Administration
- 72. Manually open the ear canal and administer the appropriate dose. Aural Medication Administration
- 73. Pulmonary Drug Administration • Medications are administered into the pulmonary system via inhalation or injection.
- 75. Nebulizer with attached face mask, bag-valve mask, and endotracheal tube
- 77. Endotracheal Tube • Several medications can be administered through an endotracheal tube: – Lidocaine – Epinephrine – Atropine – Naloxone
- 78. Enteral Drug Administration • The delivery of any medication that is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract
