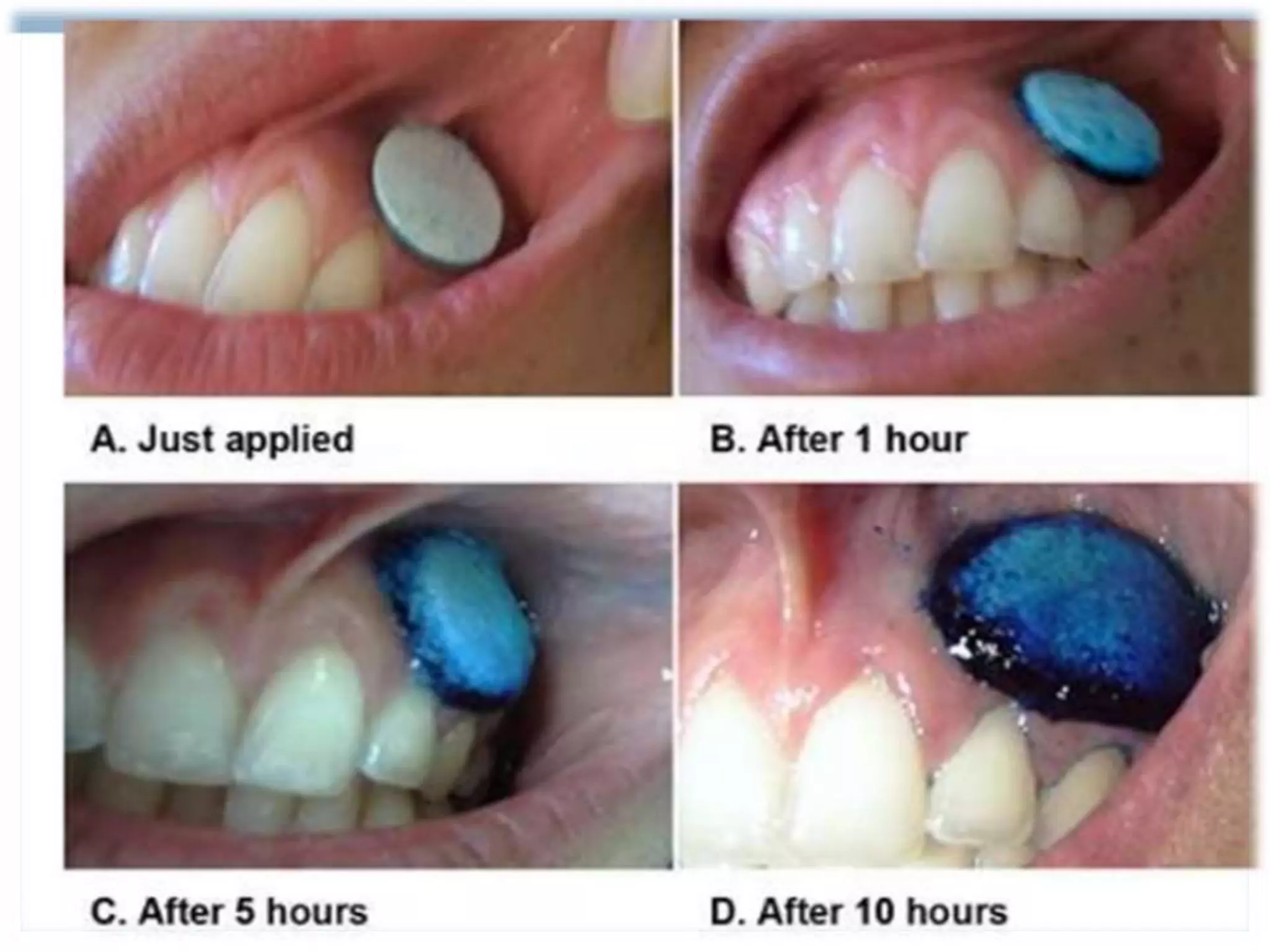
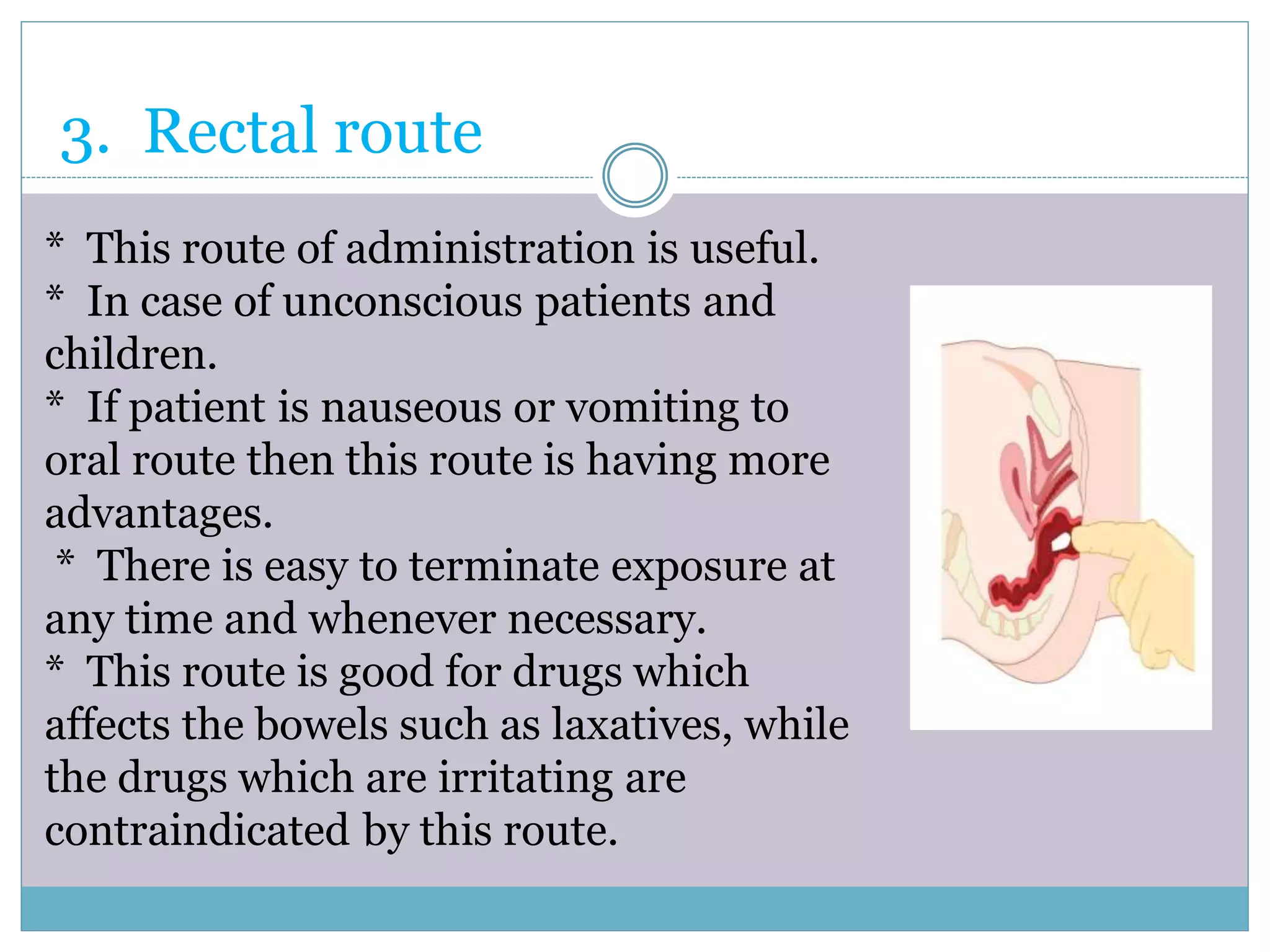
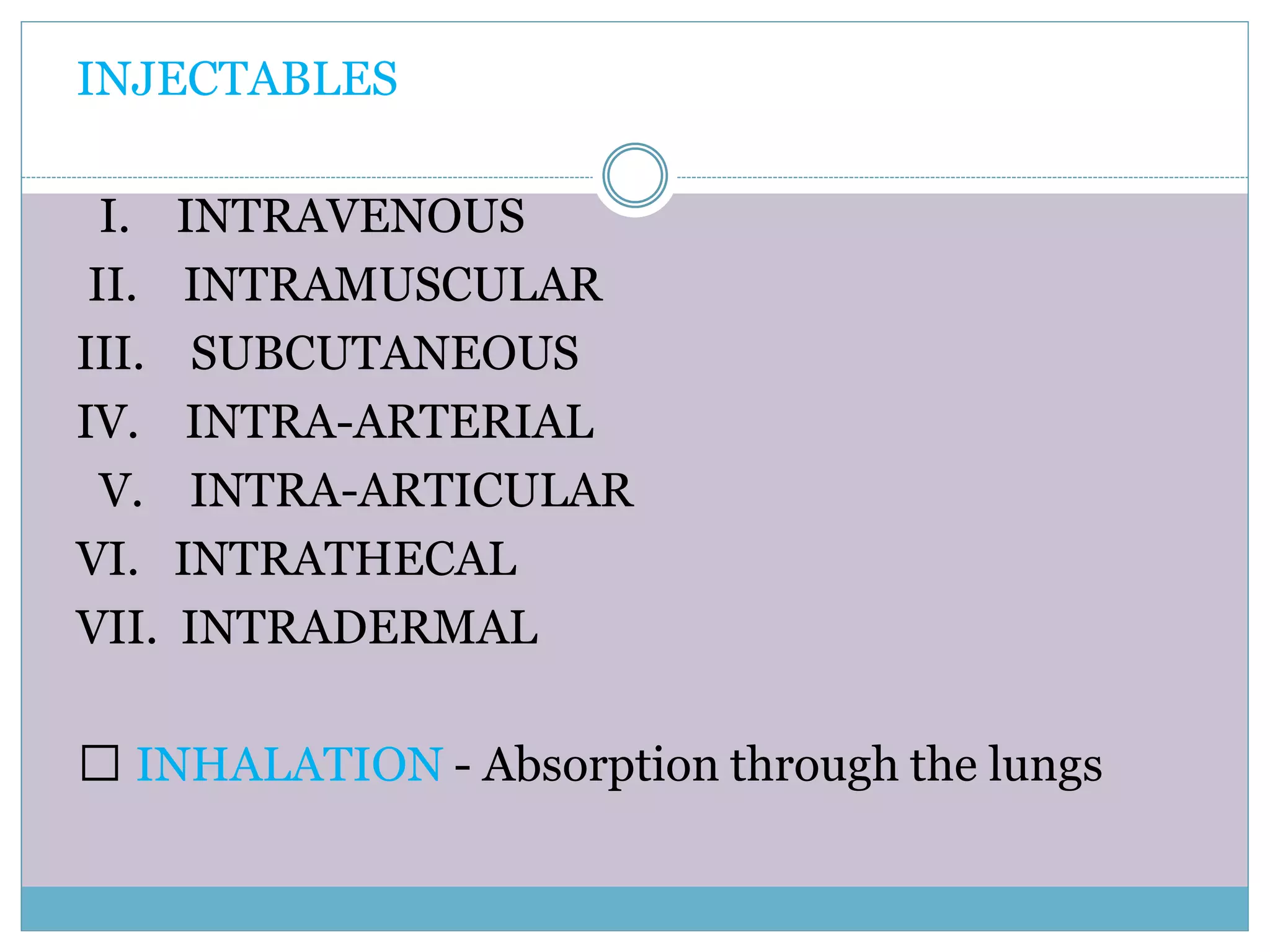
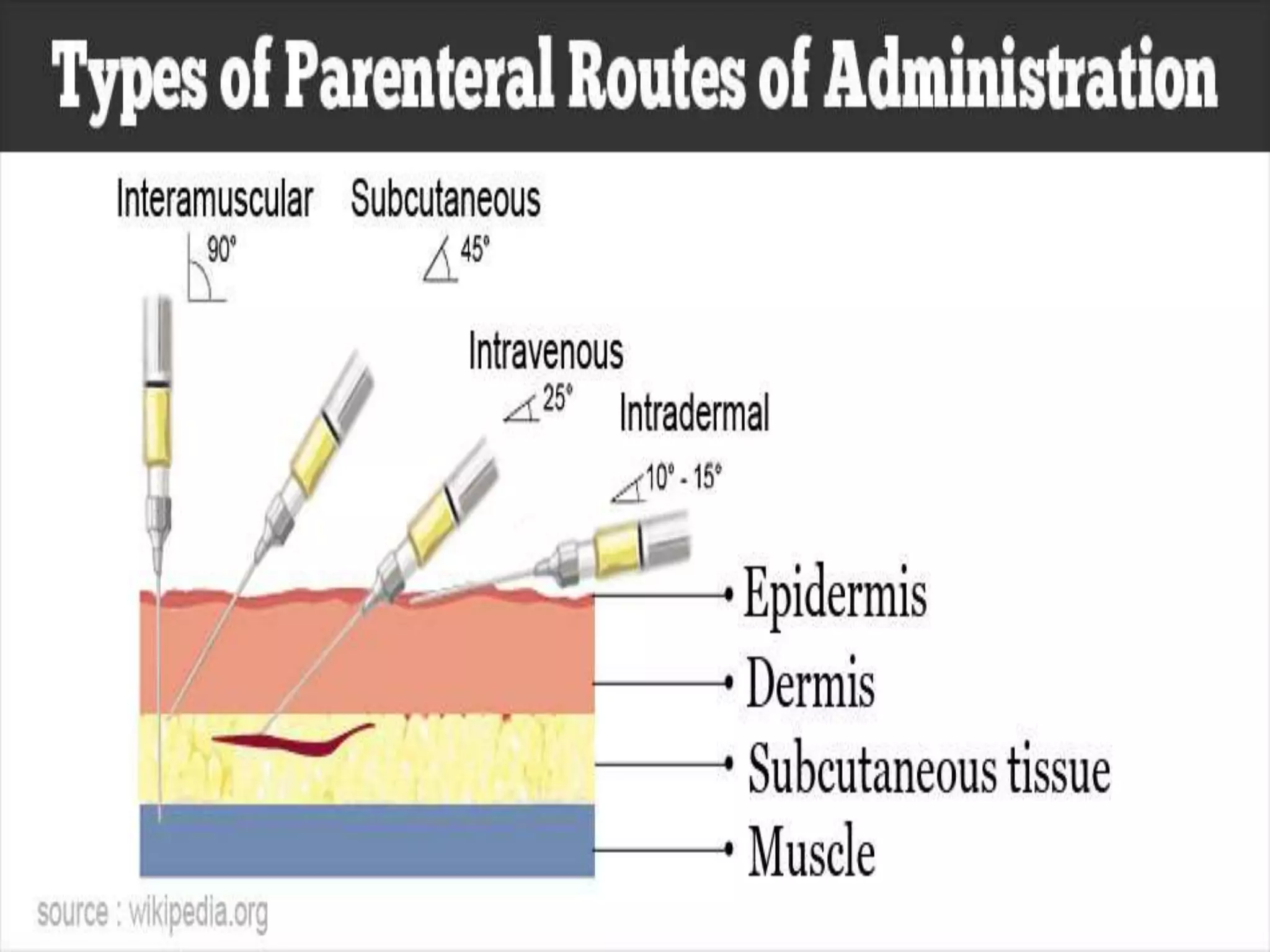
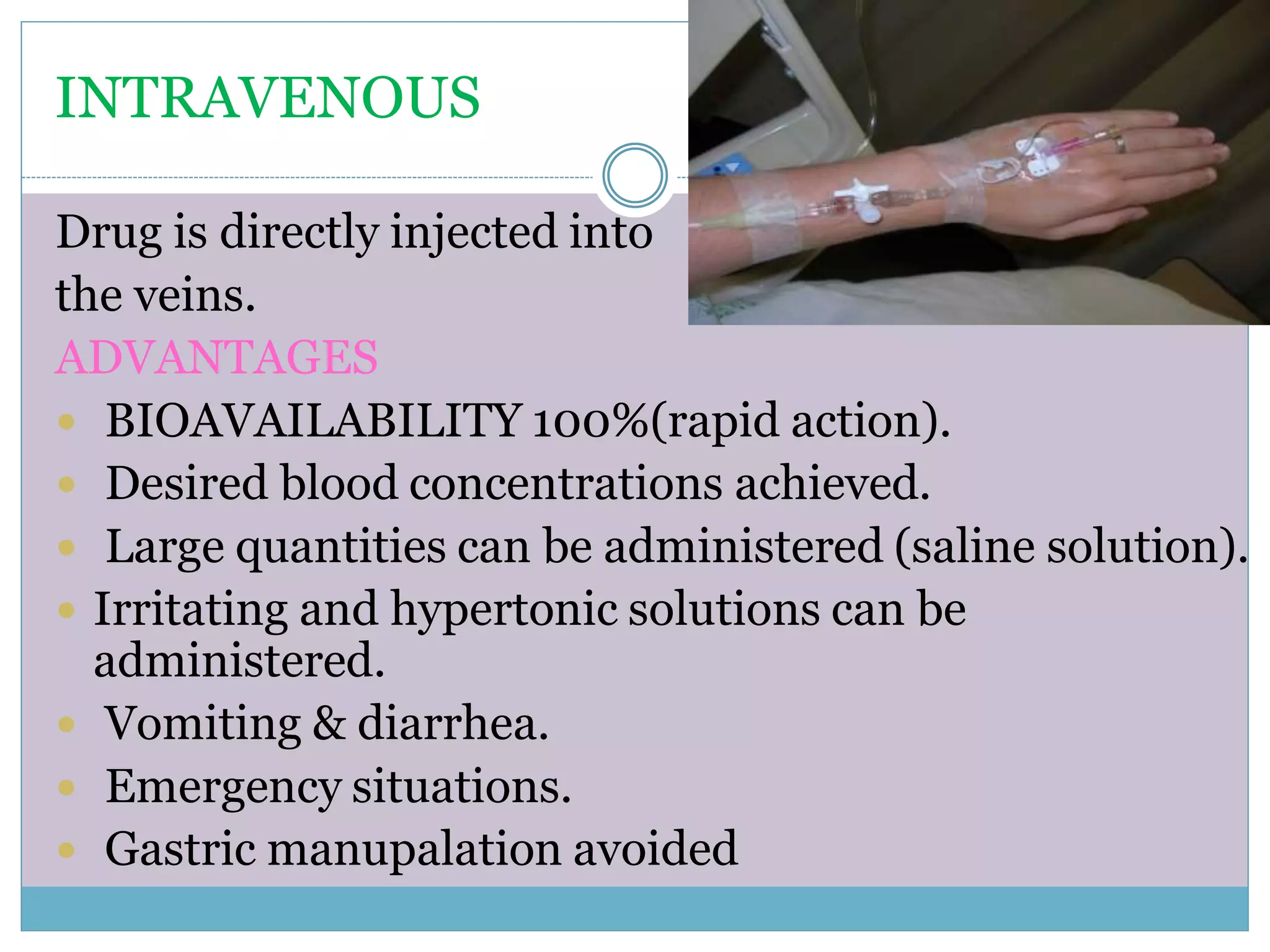
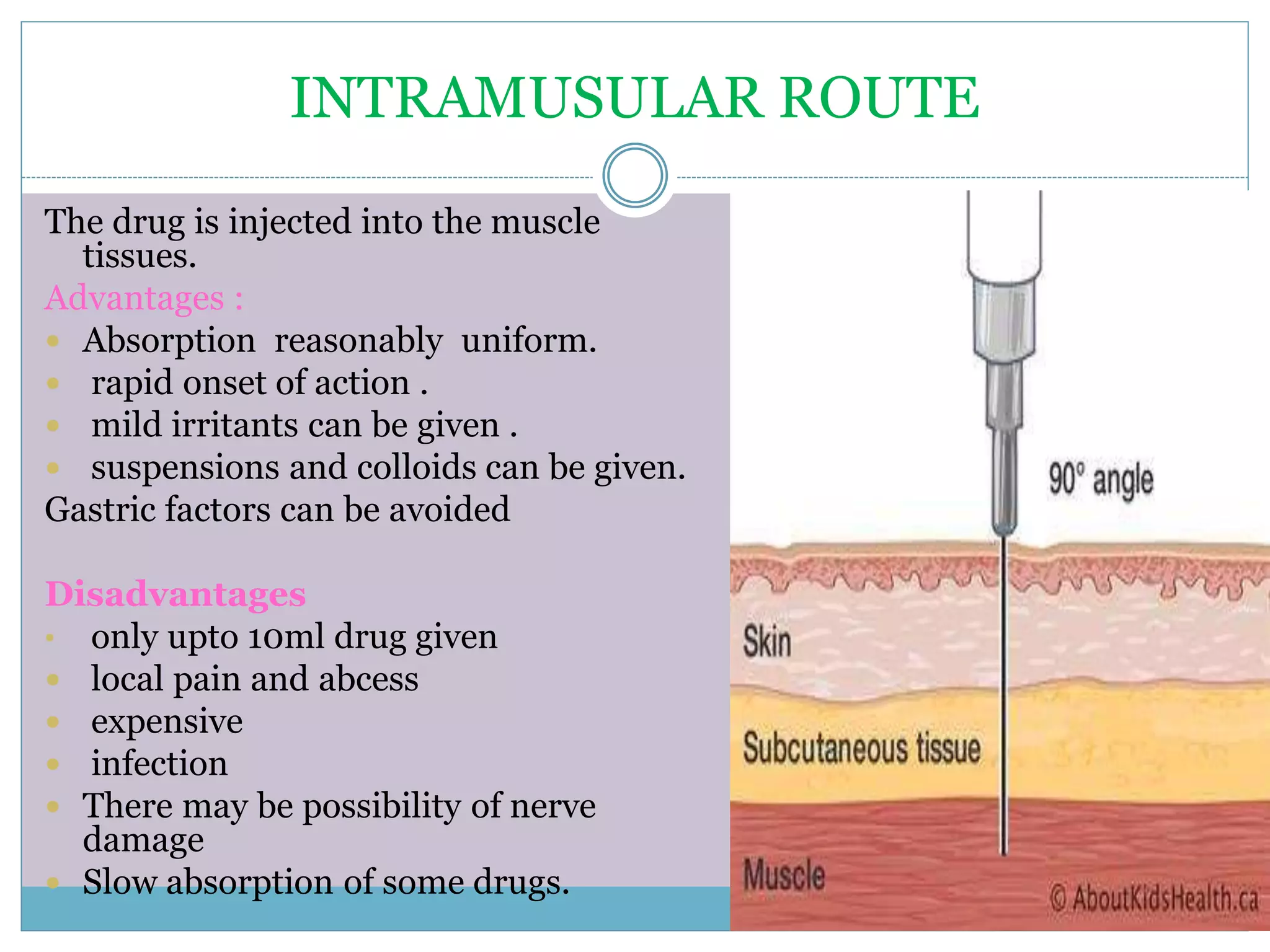
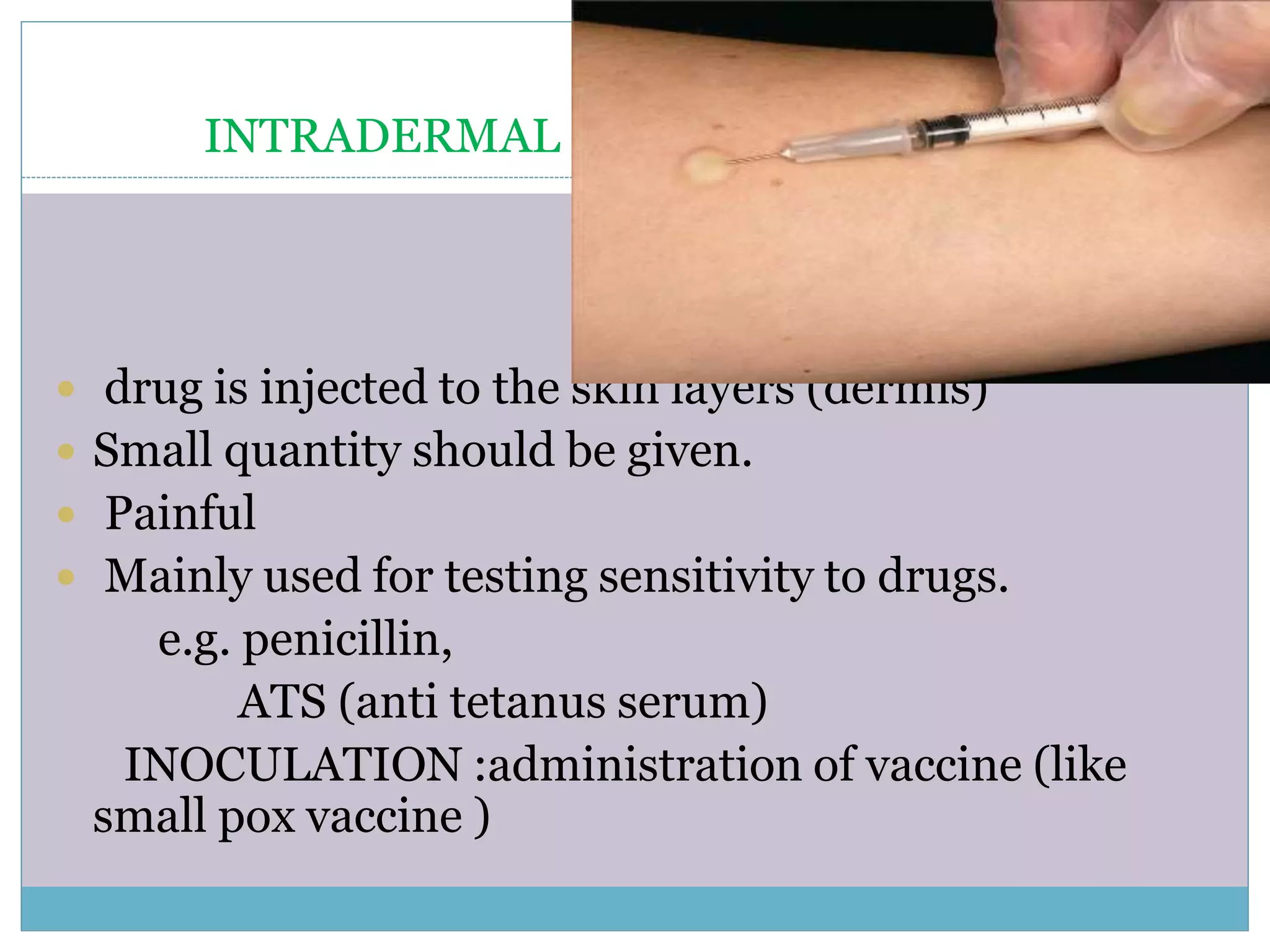
The document discusses various routes of drug administration including oral, parenteral, and topical routes. The oral route is the most commonly used as it is convenient, allows self-administration, and is inexpensive. However, it has disadvantages like first-pass metabolism and variable absorption. Parenteral routes like intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous allow direct entry of drugs into systemic circulation but require more technical skill. Topical routes provide local drug effects without systemic absorption. The choice of route depends on the drug properties and patient condition.