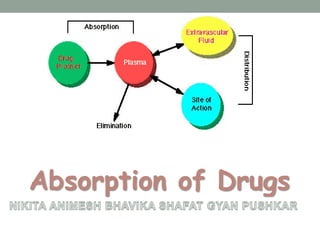
The document discusses drug absorption and the factors that influence it. It begins by defining absorption as the movement of an unchanged drug from the site of administration into systemic circulation. It then describes the various mechanisms of drug absorption, including passive diffusion, active transport, facilitated diffusion, pore transport, ion pair formation, and endocytosis. It discusses important physiological factors like drug solubility, permeability, and stability, as well as formulation factors such as dosage form, particle size, and polymorphism that can impact a drug's rate and extent of absorption. In summary, drug absorption is a complex process dependent on the drug's properties and formulation characteristics as well as physiological conditions in the gastrointestinal tract.